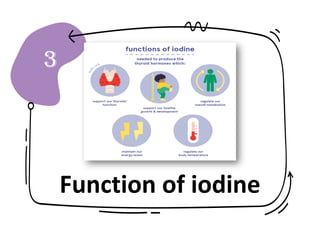
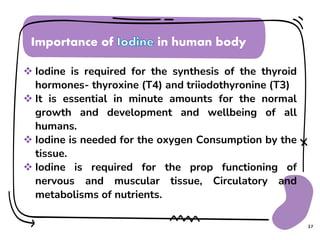
Iodine is an essential micronutrient needed to synthesize thyroid hormones. Iodine deficiency can cause iodine deficiency disorder (IDD) which impacts public health worldwide. IDD results in goiter (enlarged thyroid gland), hypothyroidism, impaired brain development in children, and increased infant mortality. Prevention focuses on iodizing salt, dietary sources like seafood, and public education. Addressing IDD requires sustained efforts to ensure populations receive adequate iodine intake, especially during pregnancy and childhood.