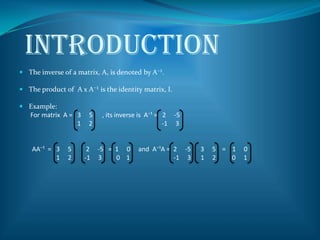
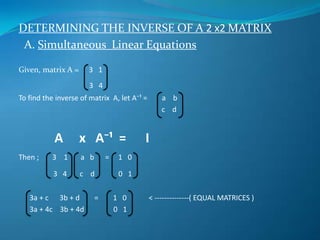
The document discusses determining the inverse of matrices. It provides examples of finding the inverse of 2x2 matrices using simultaneous linear equations and formulas. The simultaneous equation method involves setting up equations where the product of the matrix and its inverse equals the identity matrix. The formula method uses the determinant of the matrix and the positions of the elements to determine the inverse. Exercises provide additional practice finding inverses of matrices using these methods.