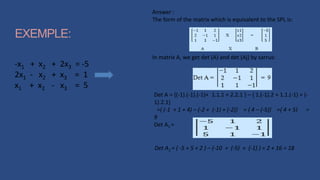
This document discusses two methods for solving systems of linear equations using matrix algebra: Cramer's Rule and the inverse matrix method.
Cramer's Rule is described as a simple method that uses determinants and the inverse of the coefficient matrix to solve systems of linear equations. An example is shown working through applying Cramer's Rule to solve a 3x3 system.
The inverse matrix method is also explained. It involves converting the system of equations to matrix form Ax=b, then solving the equivalent inverse form x=A^-1b to find the solution values. An example 2x2 system is worked through using the inverse matrix method.
In summary, the document outlines Cramer's Rule and the inverse






![• MATRIX INVERS METHOD
The purpose of solving a two-variable linear system
of equations is to determine the value of x and value
of y that satisfies the equation. Therefore, we must
convert the matrix form AX = B to inverse form as
follows.
AX = B
X = A-1B
A-1 is the inverse matrix A. Using the matrix inverse
formula above, the matrix form of X = A-1B is as
follows.
[
x
] =
1
[
d −b
] [
p
]
y ad – bc −c a q](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pptpresentasimatrixalgebra-211202061354/85/Ppt-presentasi-matrix-algebra-8-320.jpg)
![EXEMPLE :
2x – 3y = 3
x + 2y = 5
First, we convert the above SPLDV into matrix
form AX = B
Second, we change the matrix AX = B to the
inverse form X = A-1B
Third, solve the matrix equation above
[
2 −3
] [
x
] =
[
3
]
1 2 y 5
So, we get the value of x = 3 and the value of y
= 1. Thus, the solution set for the above
system of linear equations is HP = {(3, 1)}.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pptpresentasimatrixalgebra-211202061354/85/Ppt-presentasi-matrix-algebra-9-320.jpg)
