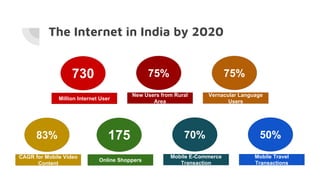
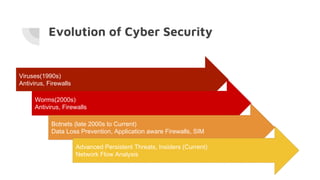
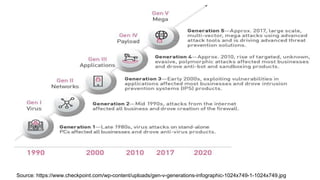
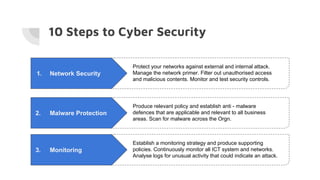
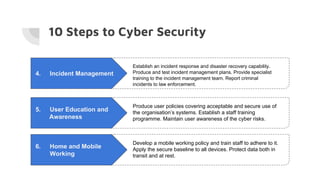
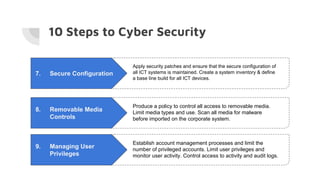
This document provides an overview of cyber security and discusses recent issues in India. It begins with definitions of cyberspace and discusses the rapid growth of internet connectivity globally and in India. It then covers cyber security challenges, the evolution of threats, and recent cyber attacks impacting India. The document concludes with 10 steps for organizations to improve cyber security, such as network security, malware protection, user education, and information risk management.