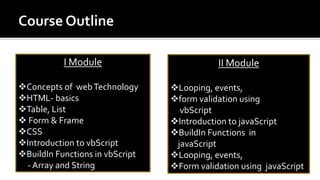
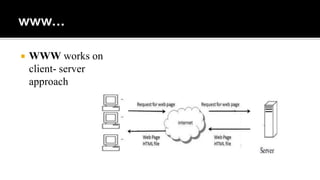
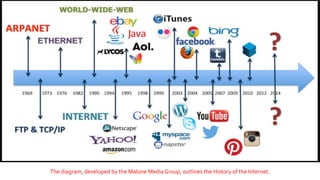
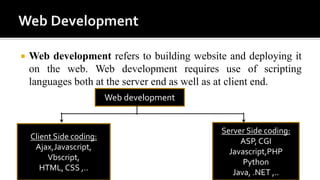
The document discusses key concepts in web technology including markup languages like HTML and CSS, scripting languages like JavaScript and VBScript, and how they are used to create dynamic and interactive web pages. It also provides an outline of two course modules that will introduce students to these concepts and languages and how to use them to add functionality and validate forms. Additionally, it summarizes the history and development of the internet and world wide web, defines common web terms like URLs, HTTP, websites, web browsers, and email.