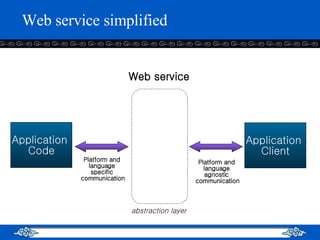
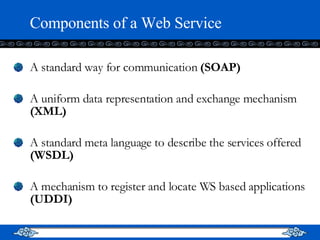
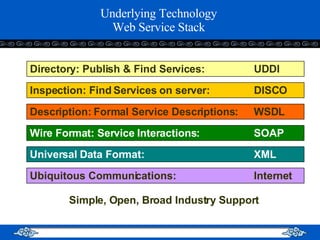
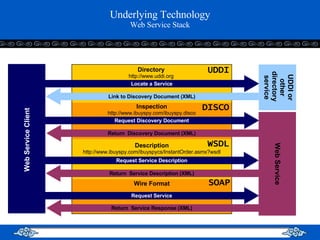
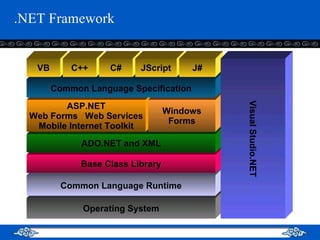
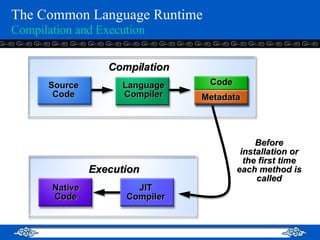
The document introduces web services and the .NET framework. It defines a web service as a network-accessible interface that allows applications to communicate over the internet using standard protocols. It describes the key components of a web service including SOAP, WSDL, UDDI, and how they allow services to be described, discovered and accessed over a network in a standardized way. It also provides an overview of the .NET framework and how it supports web services and applications using common languages like C#.

















![Gerard Sylvester Questions? [email_address] http://germic.blogspot.com http://www.gerardsylvester.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/webservices-1221471753856207-9/85/Webservices-24-320.jpg)