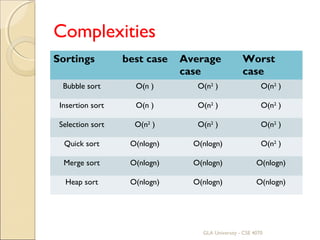
The document discusses various sorting algorithms like bubble sort, insertion sort, selection sort, quick sort, merge sort, and heap sort. It provides descriptions of each algorithm, outlines their processes through pseudocode, and compares their time complexities. The key sorting algorithms covered are bubble sort, insertion sort, selection sort, quick sort, merge sort, and heap sort.


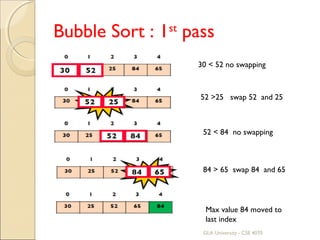
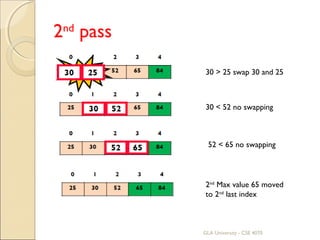
![Bubble Sort
It sort the array elements by repeatedly moving
the largest element to the highest index position
of the array[for ascending order].
Consecutive adjacent pair of elements in the
array are compared with each other.
Two elements are interchanged if lower index
value is greater than upper index value.
Process is continued till list of unsorted elements
exhausted.
It is called bubble sort because larger elements
‘bubble’ to the end of the list.
GLA University - CSE 4070](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sorting-180510120527/85/Sorting-ppt-read-only-3-320.jpg)
![Algorithm
Bubble_sort(a[ ], n)
{
Repeat for i = 0 to n-1
Repeat for j = 0 to n-i-2
if(a[j]>a[j+1])
swap a[j] and a[j+1]
end if
end for
end for
}
GLA University - CSE 4070](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sorting-180510120527/85/Sorting-ppt-read-only-4-320.jpg)
![Algorithm
Insertion_sort(a[ ], n)
{
Repeat for i = 0 to n-1
set temp = a[i]
set j=i-1
Repeat while temp< a[j] and j>=0
set a[j+1]= a[j]
set j=j-1
end while
set a[j+1] = temp
end for
}
GLA University - CSE 4070](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sorting-180510120527/85/Sorting-ppt-read-only-8-320.jpg)
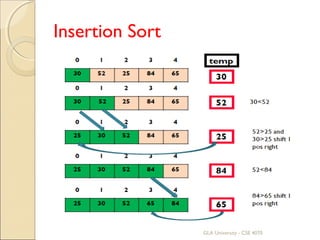

![Algorithm
Selection_sort(a[ ], n)
{
Repeat for i = 0 to n-1
Repeat for j = i+1 to n-1
if(a[i]>a[j])
swap a[i] and a[j]
end if
end for
end for
}
GLA University - CSE 4070](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sorting-180510120527/85/Sorting-ppt-read-only-11-320.jpg)
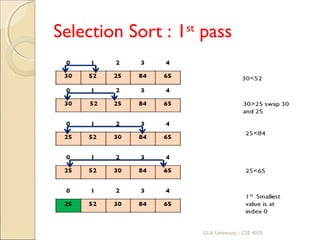
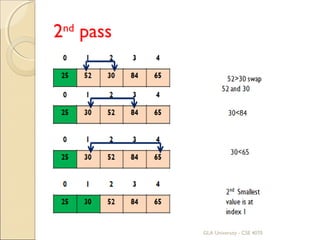


![Partition algorith
partition (arr[], first, last)
{
set pivot = first, i = first , j=last
Repeat while i < j
Repeat while arr[i] < arr[pivot]
set i= i+1
end while
Repeat while arr[j] > arr[pivot]
set j= j-1
end while
if i<j
swap arr[i] and arr[j]
end if
End while
Swap arr[pivot] and arr[j]
Return pivot }
GLA University - CSE 4070](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sorting-180510120527/85/Sorting-ppt-read-only-16-320.jpg)
![quickSort(arr,0,5)
Partition Initialization...
first moves to the right until
Array element > pivot element
last moves to the left until
Array element < pivot element
swap arr[first] and arr[last]
GLA University - CSE 4070](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sorting-180510120527/85/Sorting-ppt-read-only-17-320.jpg)
![quickSort(arr,0,5)
first moves to the right
until
Array element > pivot
element
last moves to the left
until
Array element < pivot
element
swap arr[first] and arr[last]
pivot=6
partition(arr,0,5)
GLA University - CSE 4070](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sorting-180510120527/85/Sorting-ppt-read-only-18-320.jpg)
![quickSort(arr,0,5)
repeat right/left scan
UNTIL left & right cross
first & last CROSS!!!
Swap pivot and arr[last]
Return new
location of pivot
to quicksort
function
= return 3
GLA University - CSE 4070](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sorting-180510120527/85/Sorting-ppt-read-only-19-320.jpg)

![Recursive calls to quickSort()
first & llast CROSS!!!
1 - Swap pivot element and arr[last]
2 - Return new location of pivot element
to quicksort function
Return 0 GLA University - CSE 4070](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sorting-180510120527/85/Sorting-ppt-read-only-21-320.jpg)
![Recursive calls to quickSort()
first & llast CROSS!!!
1 - Swap pivot element and arr[last]
2 - Return new location of pivot element
to quicksort function
Return 0 GLA University - CSE 4070](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sorting-180510120527/85/Sorting-ppt-read-only-22-320.jpg)
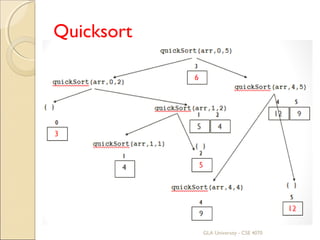

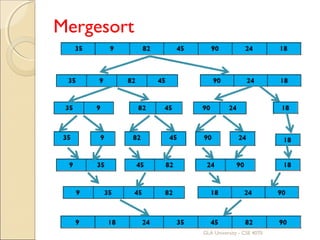
![Algorithm
MergeSort(arr[], l, r)
{ if r>l
set mid = (l+r)/2
Call mergeSort(arr, l, mid)
Call mergeSort(arr, mid+1, r)
Call merge(arr, l, m, r)
end if
}
GLA University - CSE 4070](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sorting-180510120527/85/Sorting-ppt-read-only-25-320.jpg)
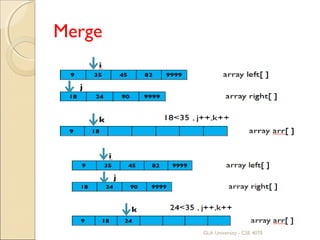
![Algorithm
Merge(arr[], l, mid, r)
{ compute n1 and n2
copy n1 elements in left[]
copy n2 elements in right[]
set left[n1]= 9999, rightt[n1]= 9999
set i=0,j=0,k=0
for k = l to r
if left[i]<right[j]
set arr[k]= left[i]
i=i+1
else arr[k]=right[j]
j=j+1
end if
end for
}
GLA University - CSE 4070](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sorting-180510120527/85/Sorting-ppt-read-only-27-320.jpg)
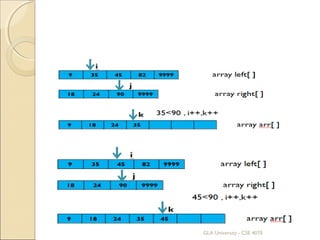
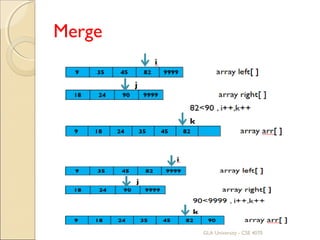
![Merge
array arr[ ]
GLA University - CSE 4070](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sorting-180510120527/85/Sorting-ppt-read-only-28-320.jpg)

![Heap
Max-heap :
A[Parent(i)] ≥ A[i]
Min-heap : A[Parent(i)] ≤ A[i]
PARENT (i) where i is index of any key
return floor(i/2)
LEFT (i)
return 2i
RIGHT (i)
return 2i + 1
GLA University - CSE 4070](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sorting-180510120527/85/Sorting-ppt-read-only-33-320.jpg)

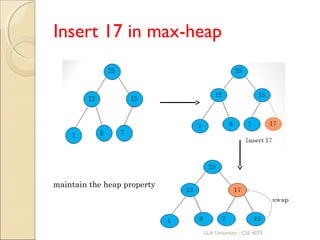

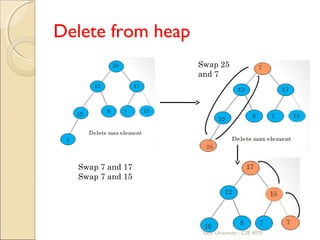

![Algorithm
Heapsort(A,n)
{
Buildheap(A)
for i = 0 to n-1
call Insert_heap(A,n,A[i])
End for
Repeat while n>0
call Delete_heap(A,n,value)
set n = n – 1
end while loop
}
// heapify
// Get max value after
deletion (for
descending order)
GLA University - CSE 4070](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sorting-180510120527/85/Sorting-ppt-read-only-39-320.jpg)