The document provides an overview of the key concepts related to internet and web technology including:
- A brief history of the internet from 1980 to present day outlining major milestones and innovations.
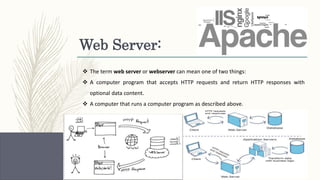
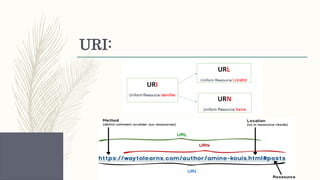
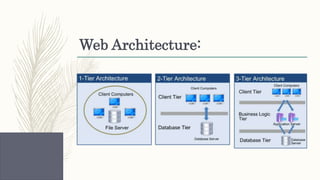
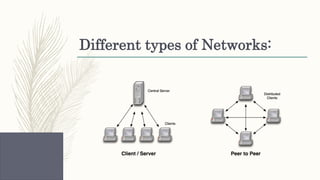
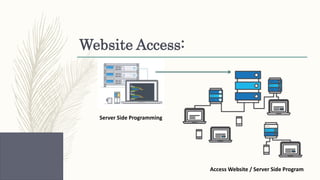
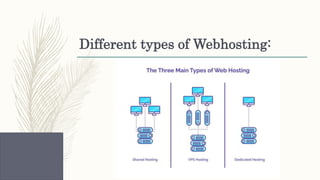
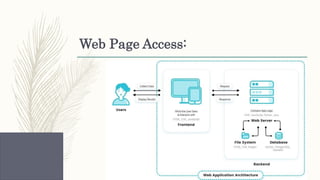
- Descriptions of foundational web technologies like HTTP, HTML, URIs, web browsers, web servers and how they enable the functioning of the world wide web.
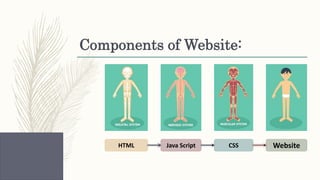
- An overview of common web development topics covered in the syllabus like CSS, JavaScript, XML, AJAX, jQuery, React and programming languages like Java, Node.js, JSP and Servlets.
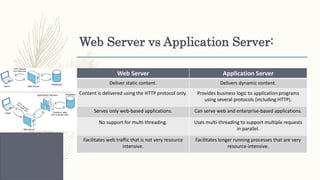
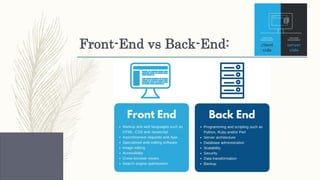
- Distinctions between related concepts like the differences between a web server and application server or front-end and back-end development.