This presentation provides an overview of web fundamentals, including:
1) The evolution of the web from Tim Berners-Lee's original invention (Web 1.0) to user-generated content (Web 2.0) to artificial intelligence and personalization (Web 3.0).
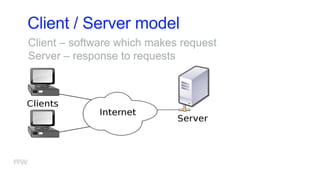
2) The basic components of the web including websites, webpages, web applications, clients like browsers, and servers.
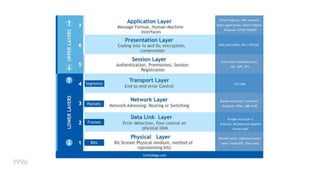
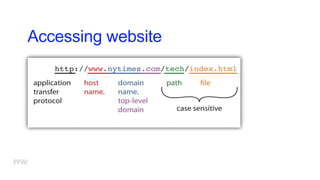
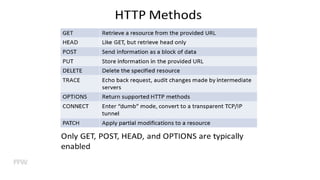
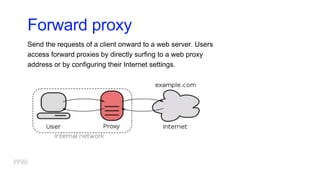
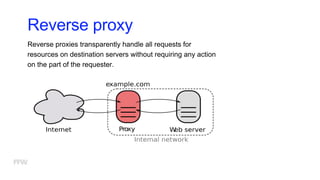
3) How web communication works using protocols like HTTP and techniques like cookies to transfer information between clients and servers.