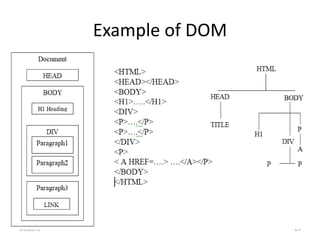
- CSS (Cascading Style Sheets) is a style sheet language used to describe the presentation of HTML documents, including how elements should be rendered on screen, paper, or in other media.
- CSS allows separation of document content from document presentation, including elements sizing, color, font, layout, etc.
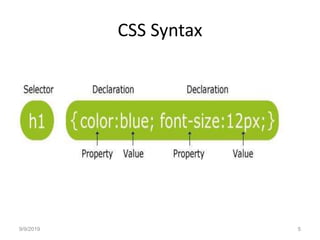
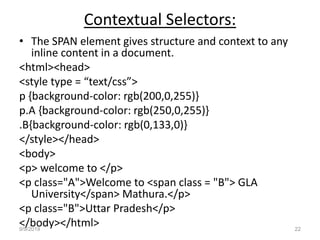
- There are three main ways to insert CSS - internal style sheets within <style> tags, external style sheets linked via <link> tags, and inline styles within HTML elements. CSS rules contain selectors that point to elements to style and declarations to set property values.