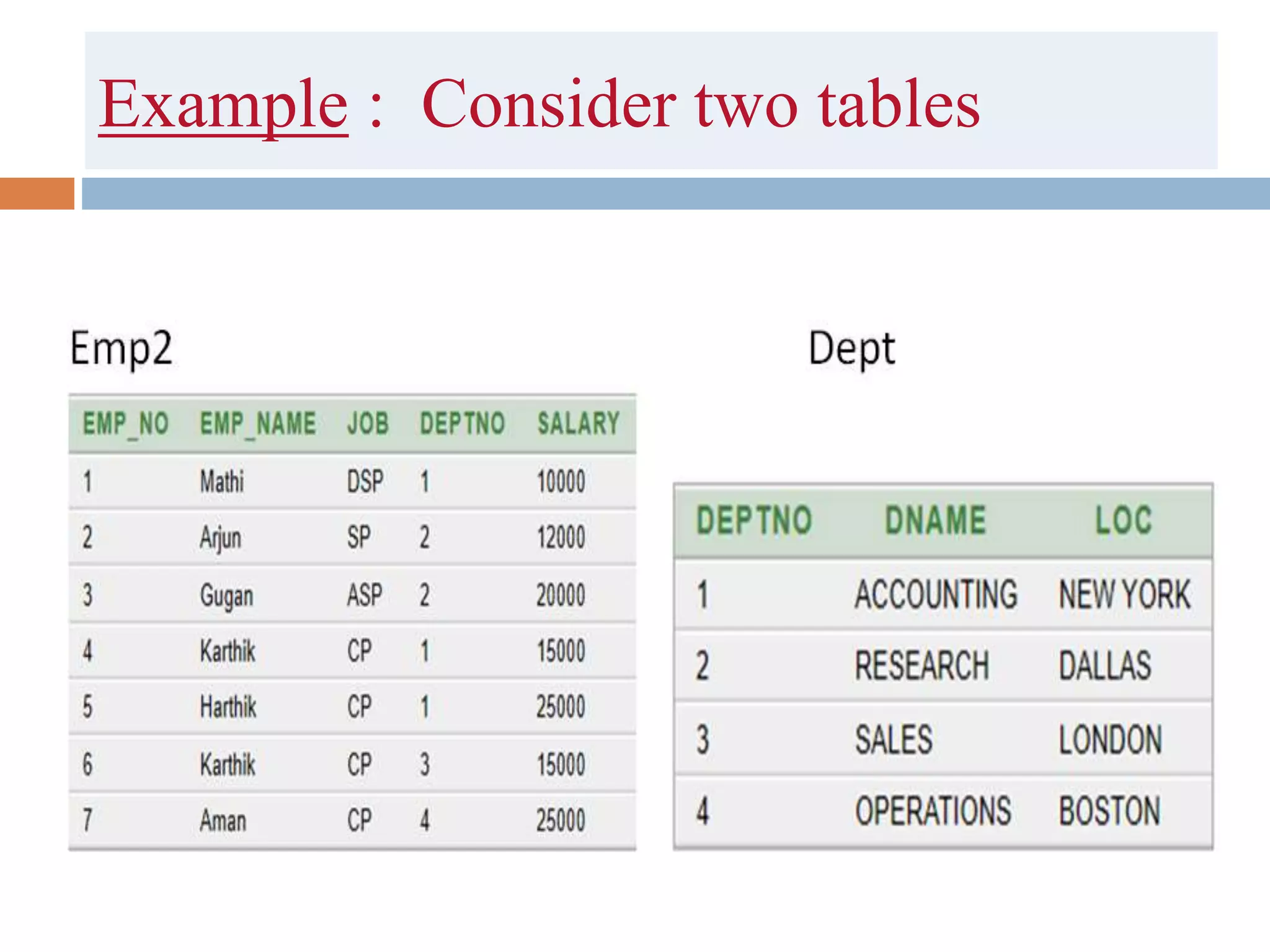
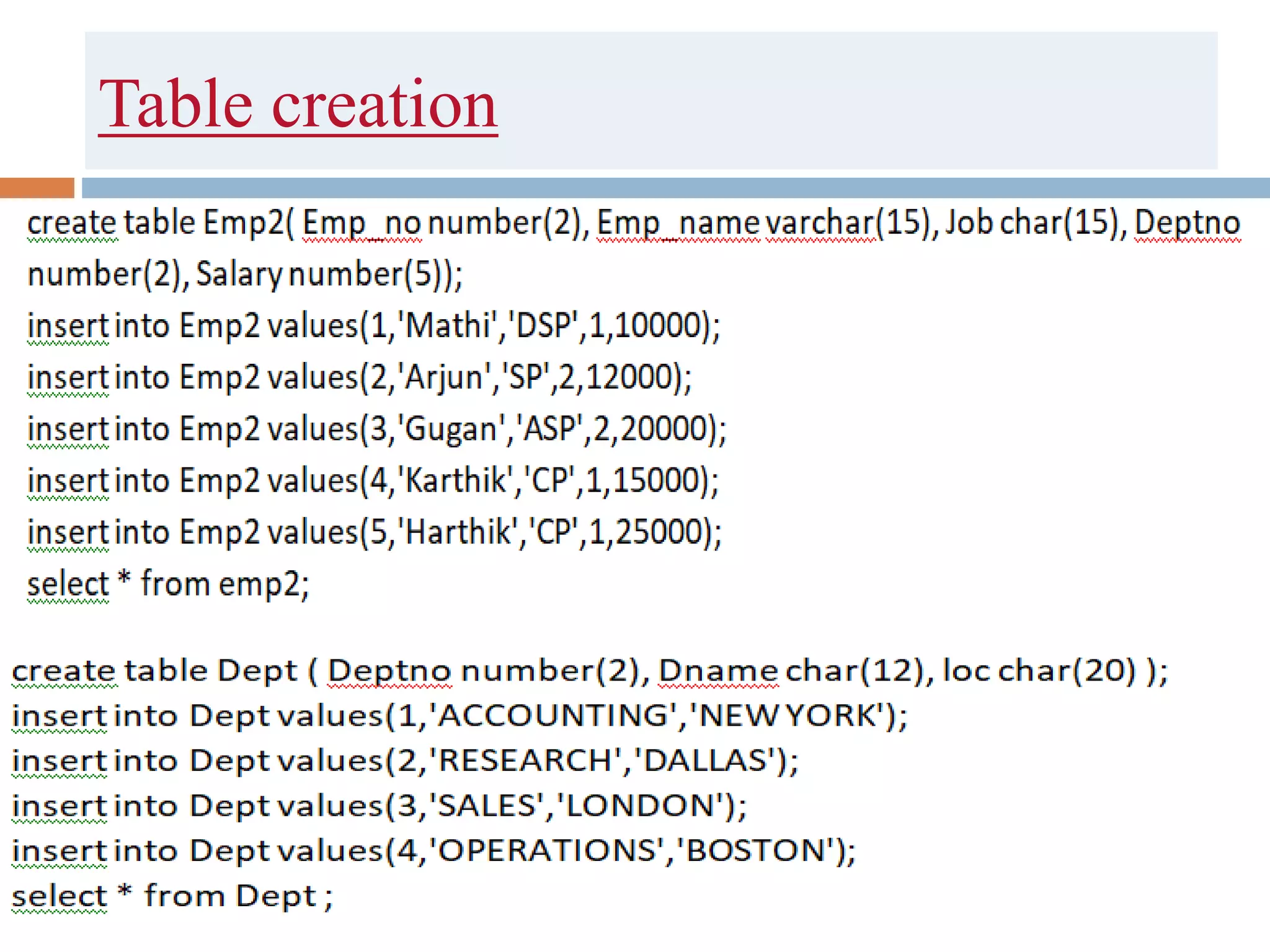
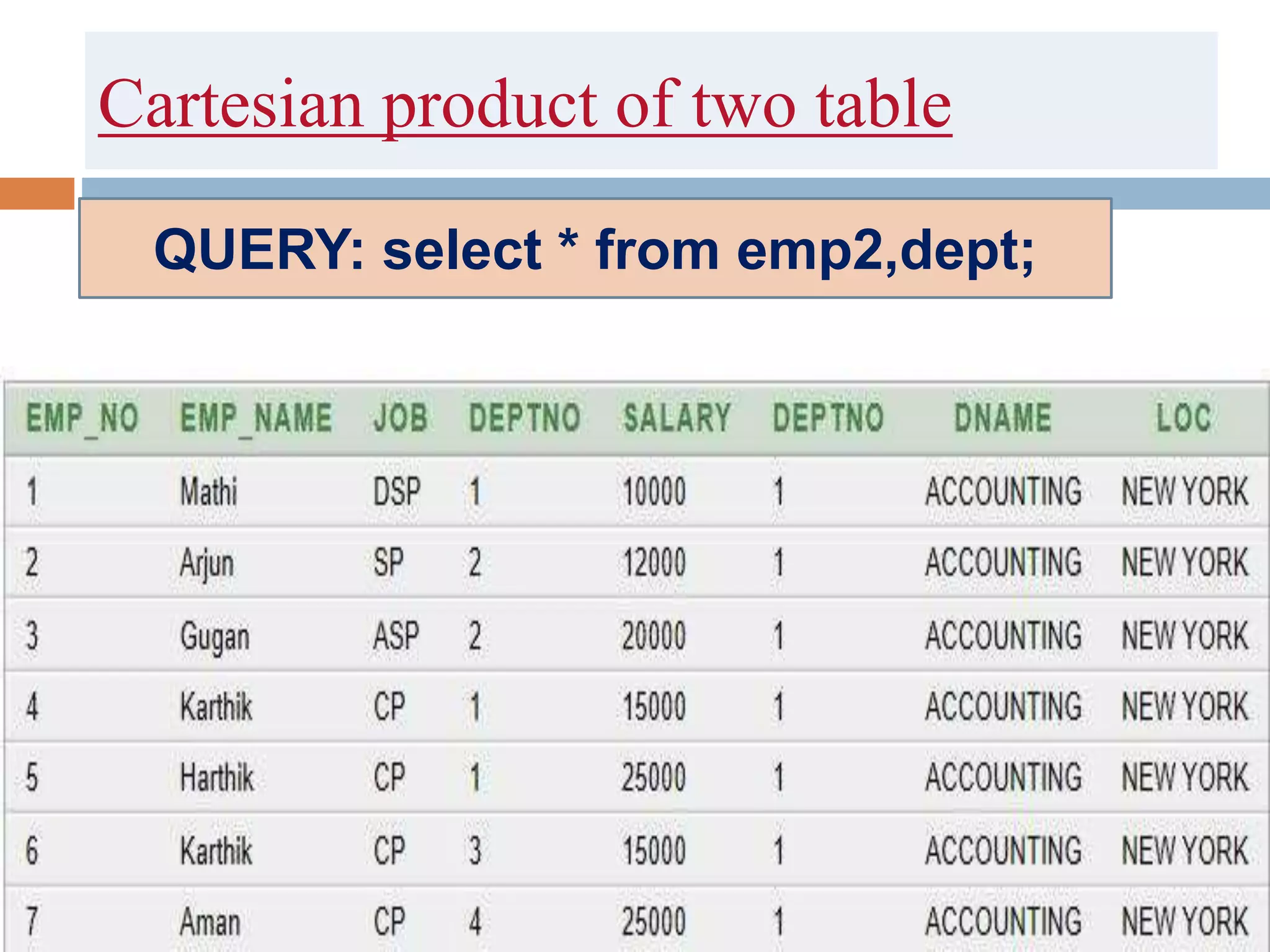
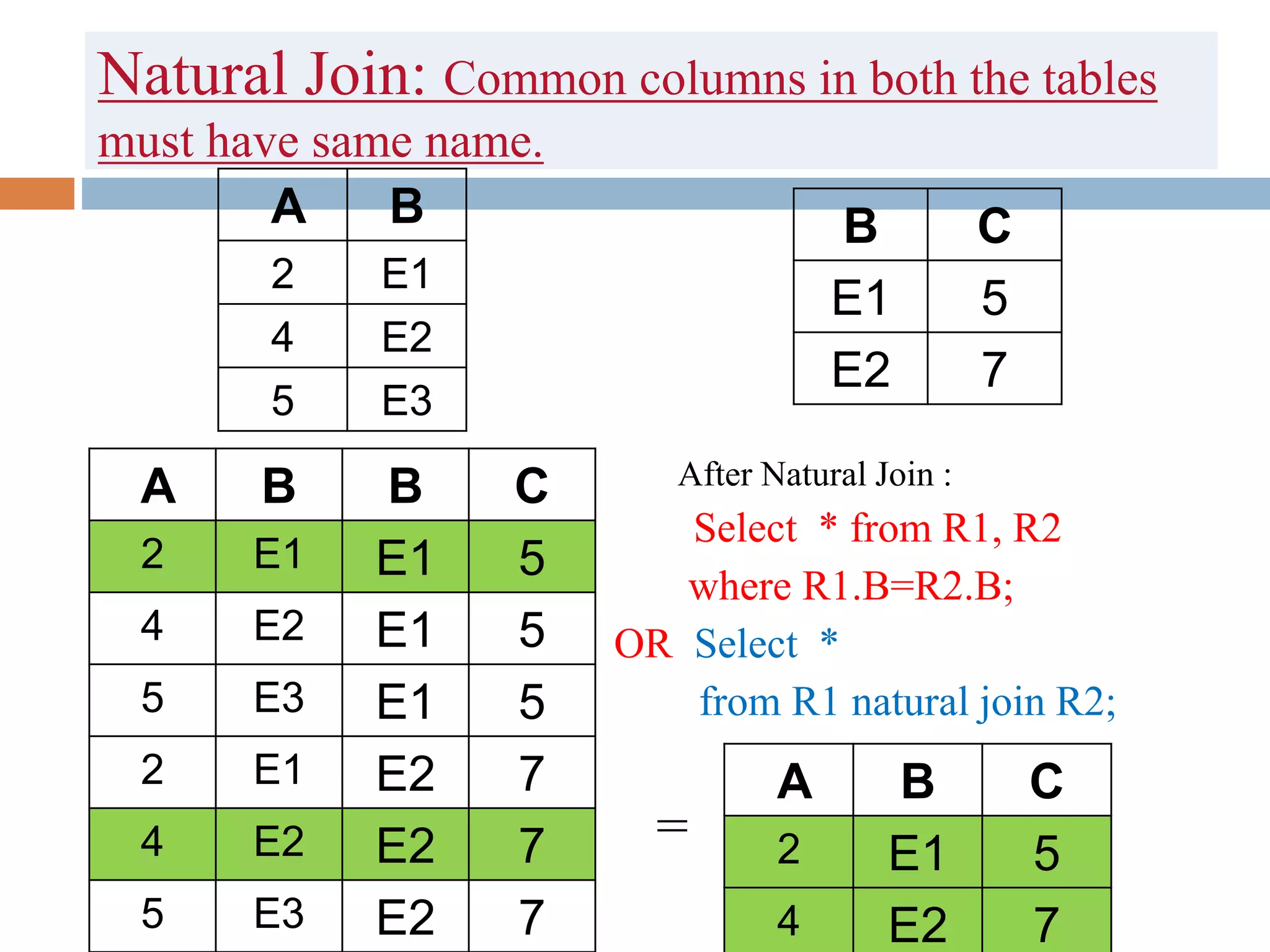
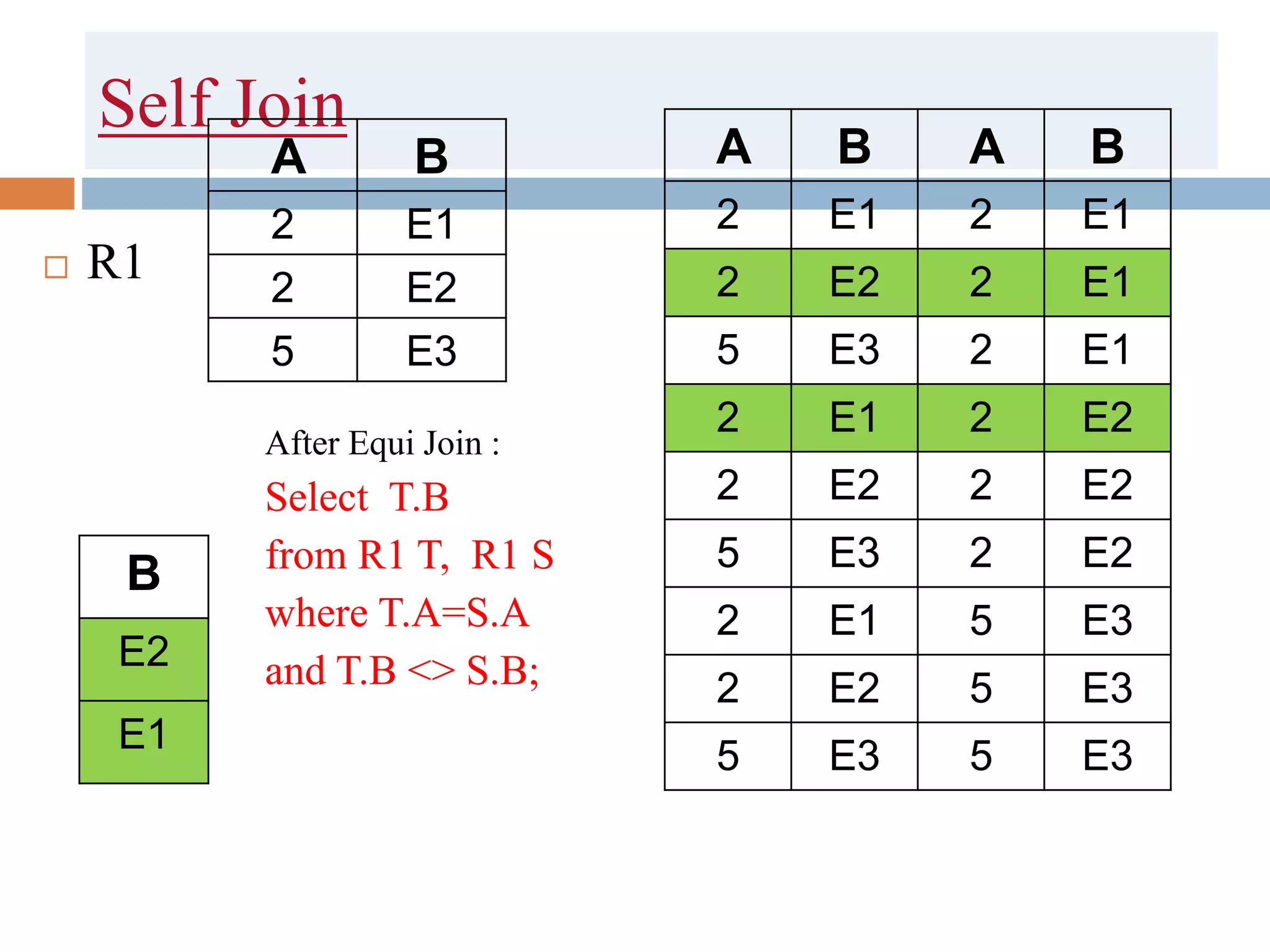
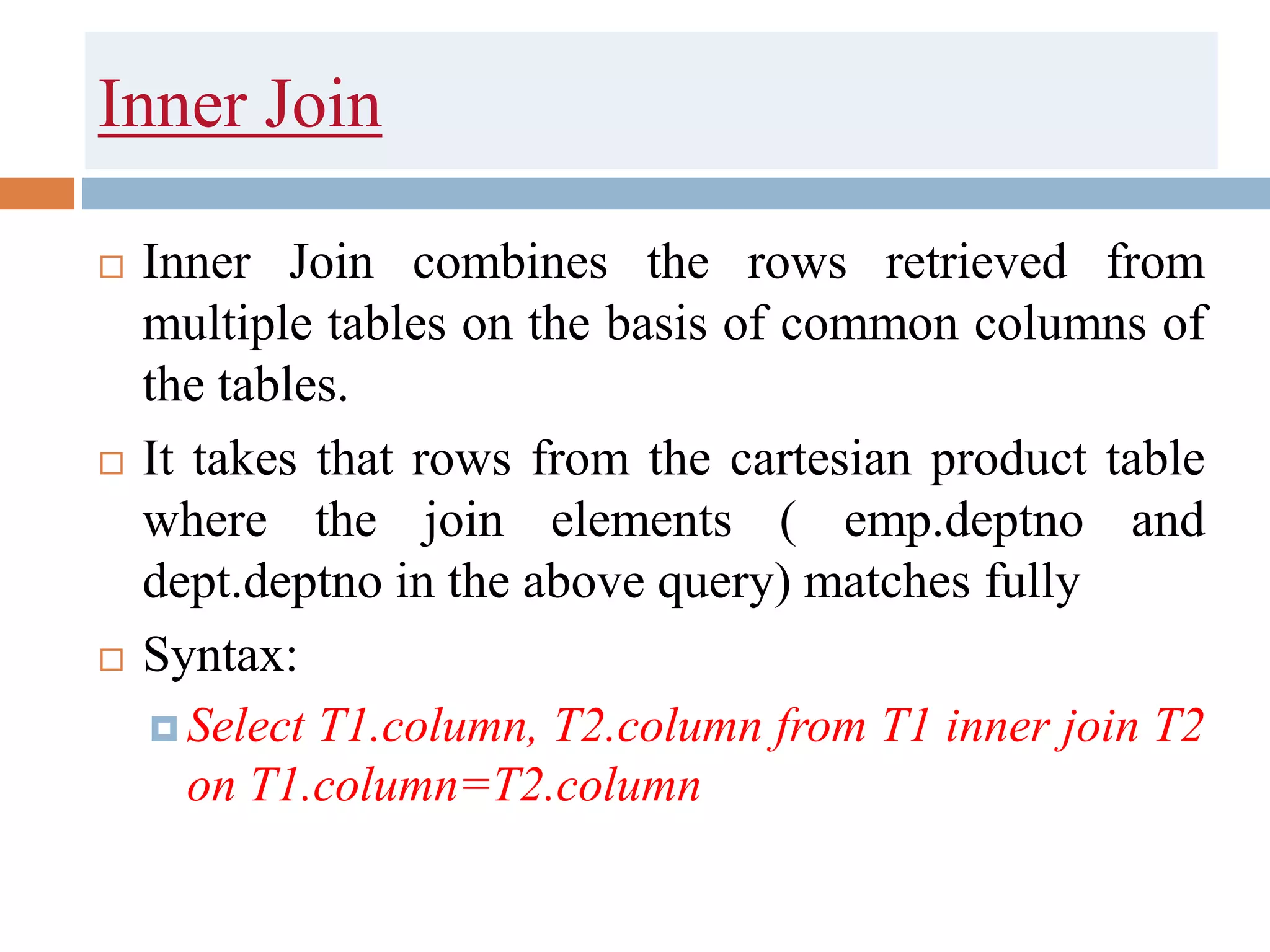
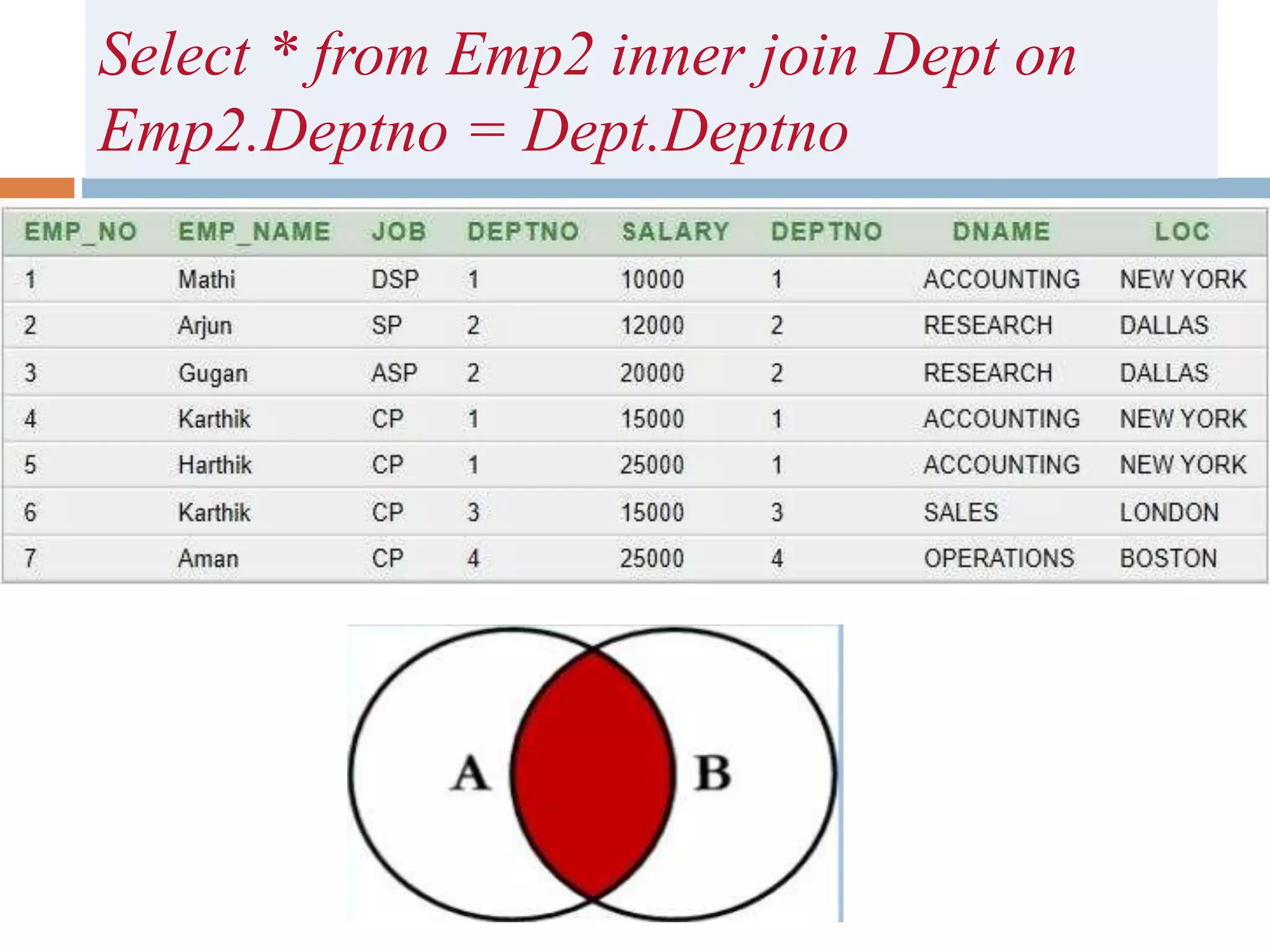
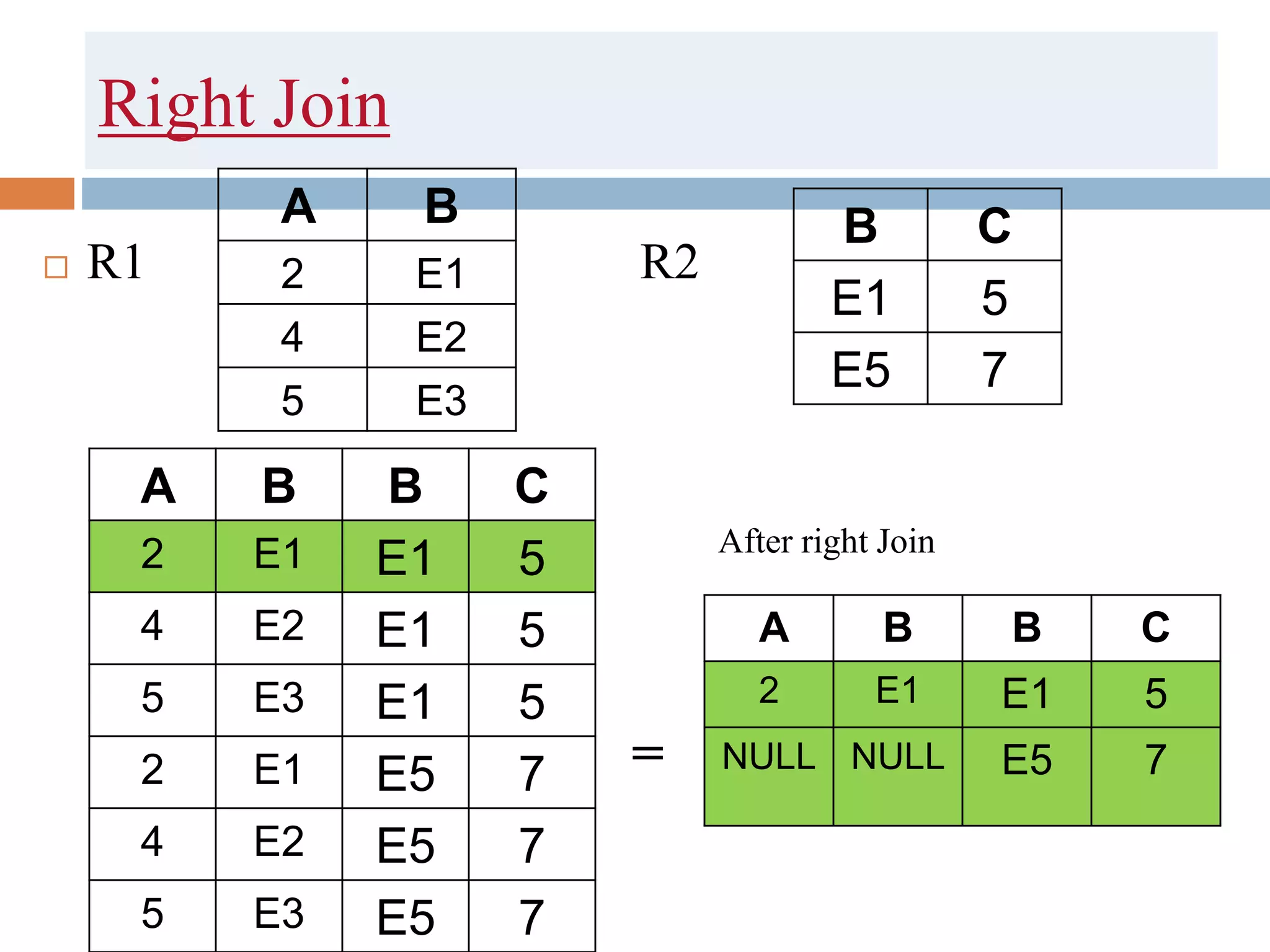
The document discusses different types of joins in SQL including Cartesian product, natural join, equi join, self join, inner join, left join, right join, and full outer join. It provides examples of each join type using sample tables and describes the key characteristics of each join.