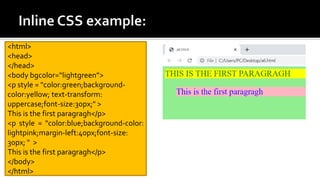
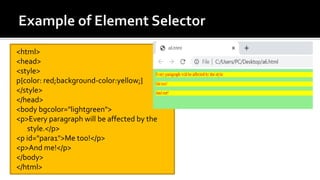
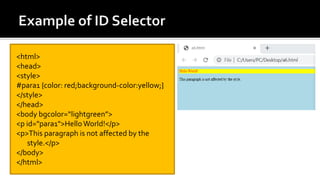
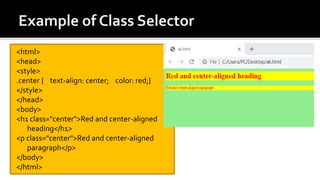
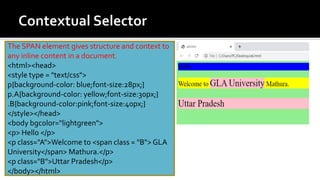
The document discusses Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) and provides examples of common CSS properties and selectors. It covers topics such as CSS syntax, the different types of CSS stylesheets (internal, external, inline), common selectors like element, id, class selectors, and properties for fonts, text, colors, backgrounds, borders, margins and more. Examples are provided throughout to demonstrate how to apply various CSS rules and properties.