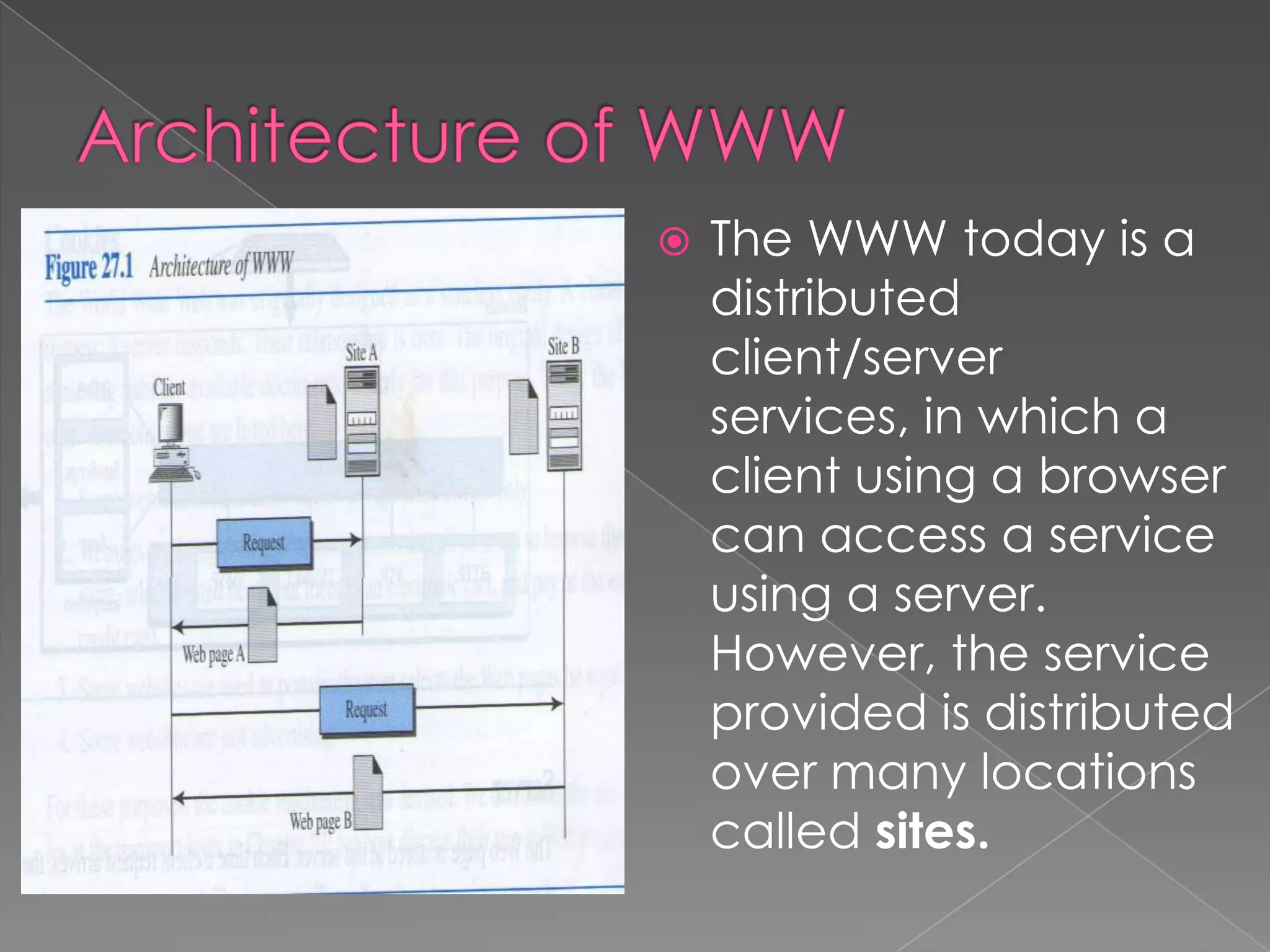
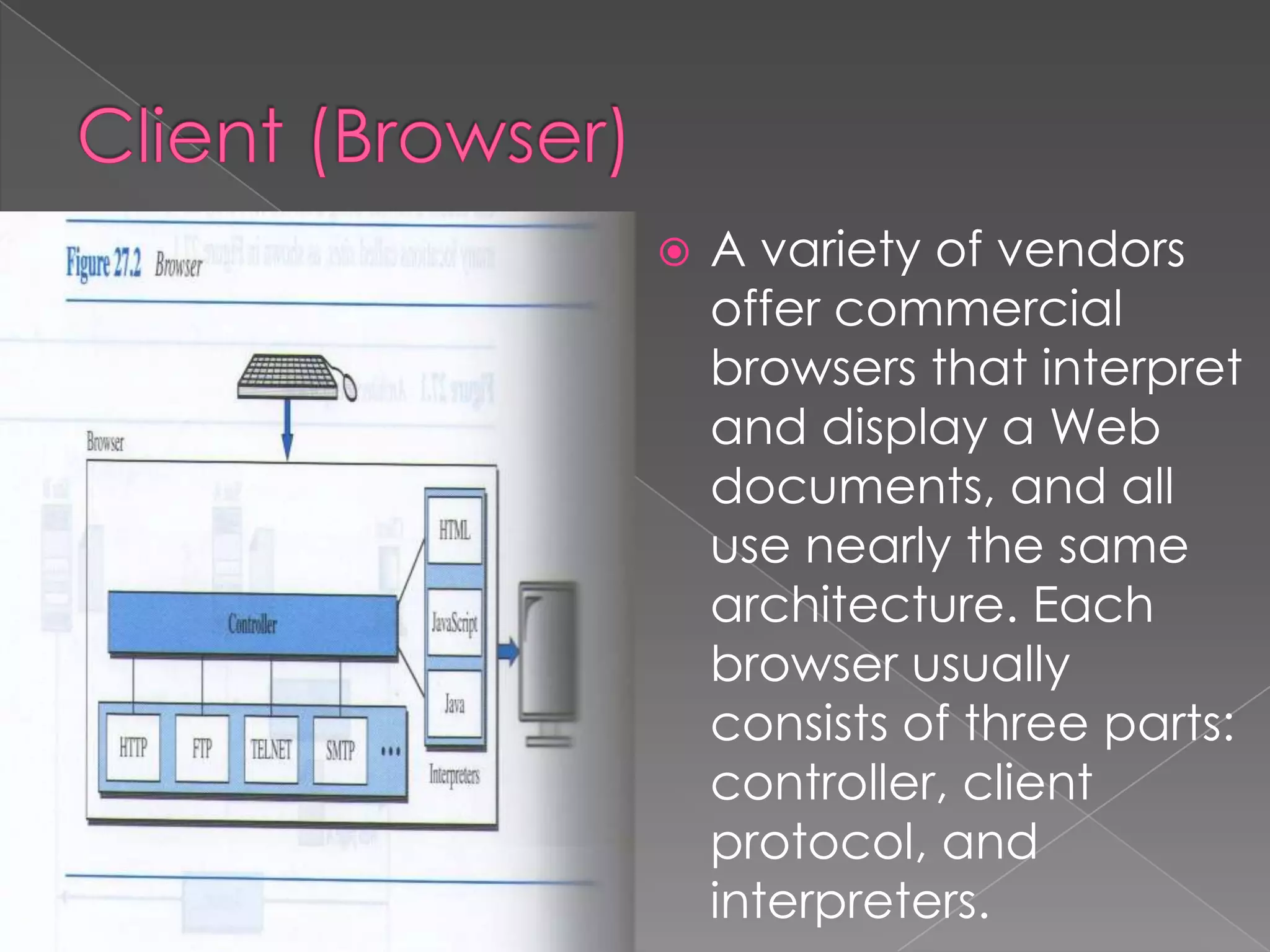
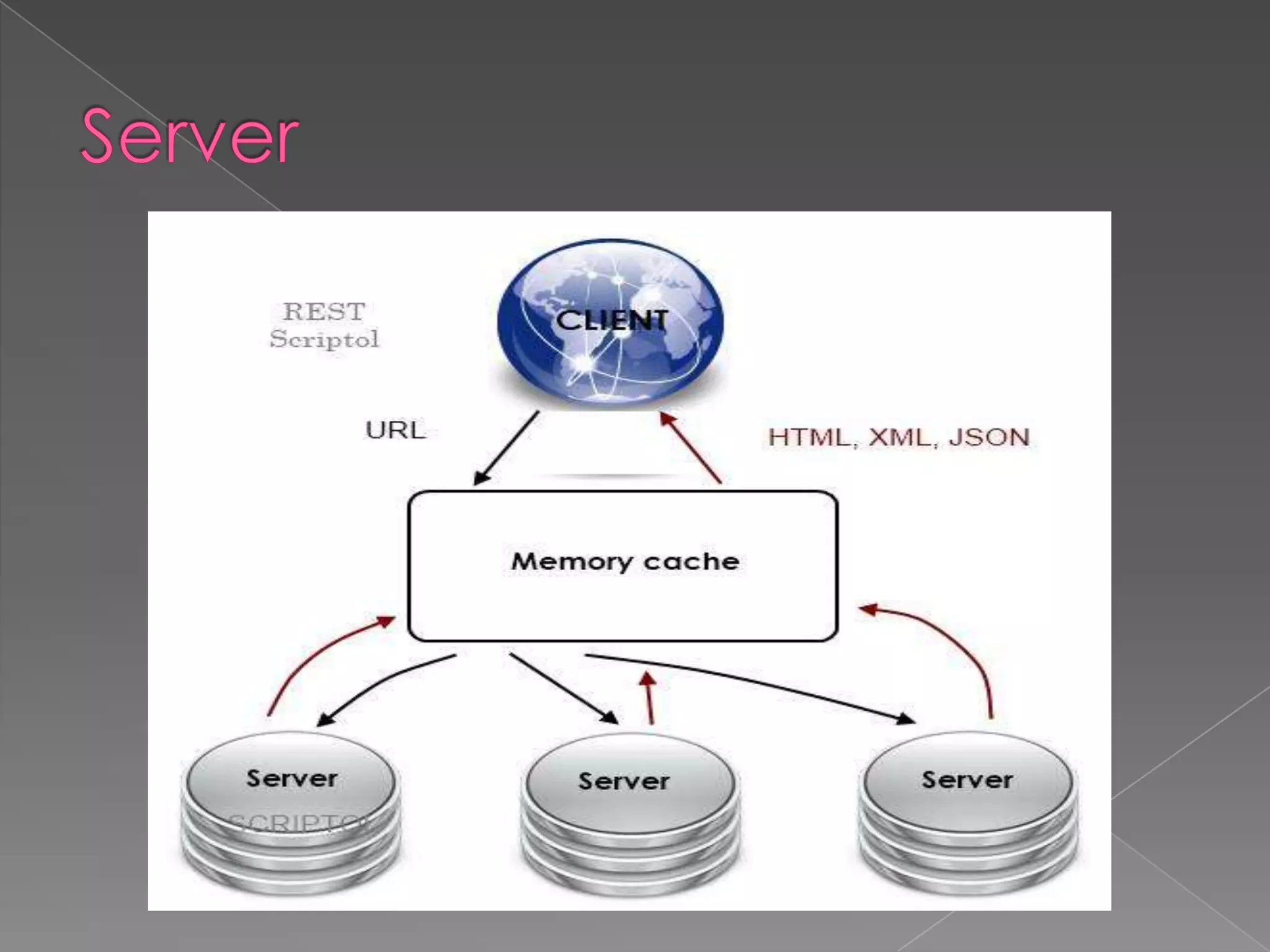
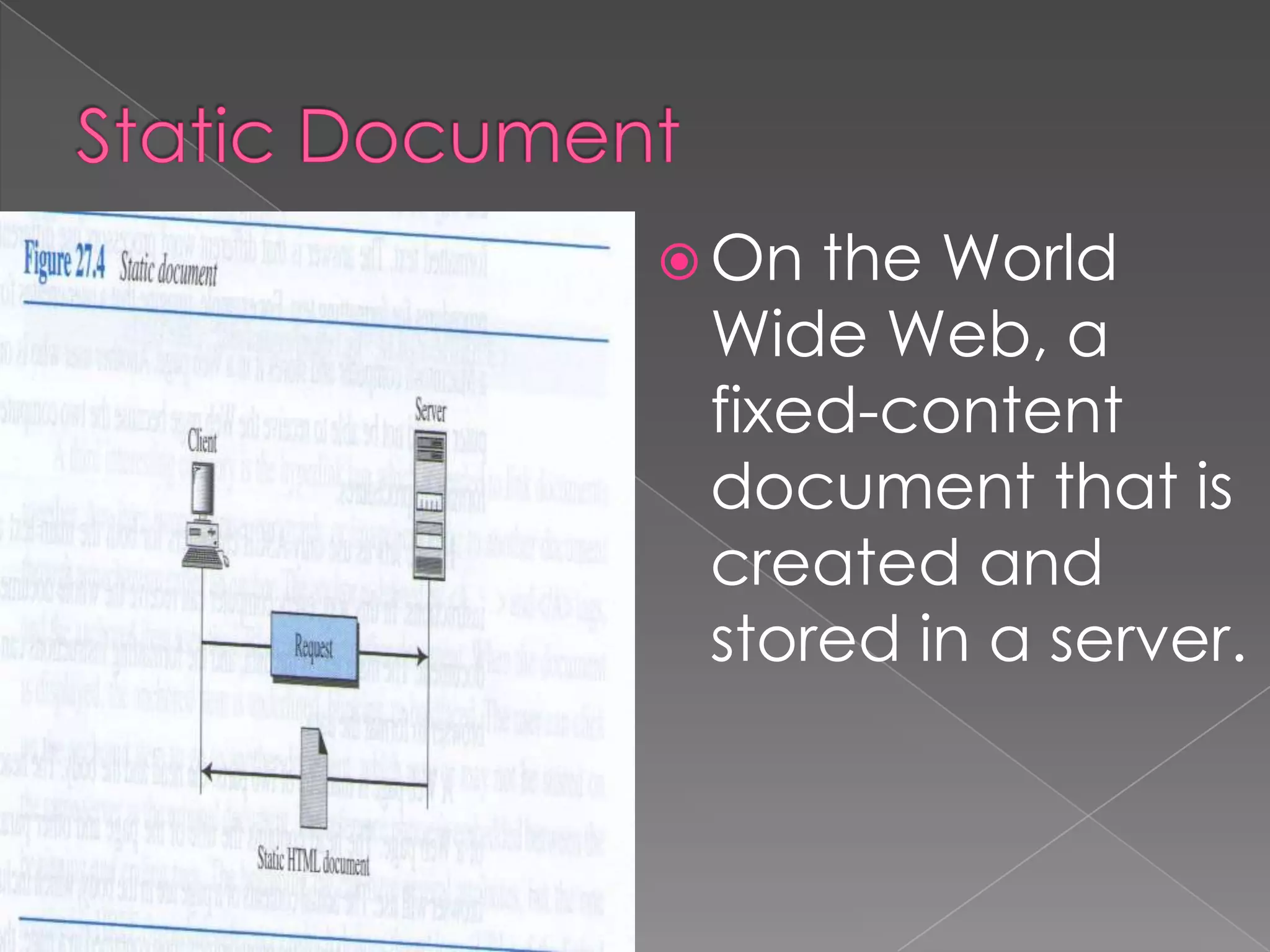
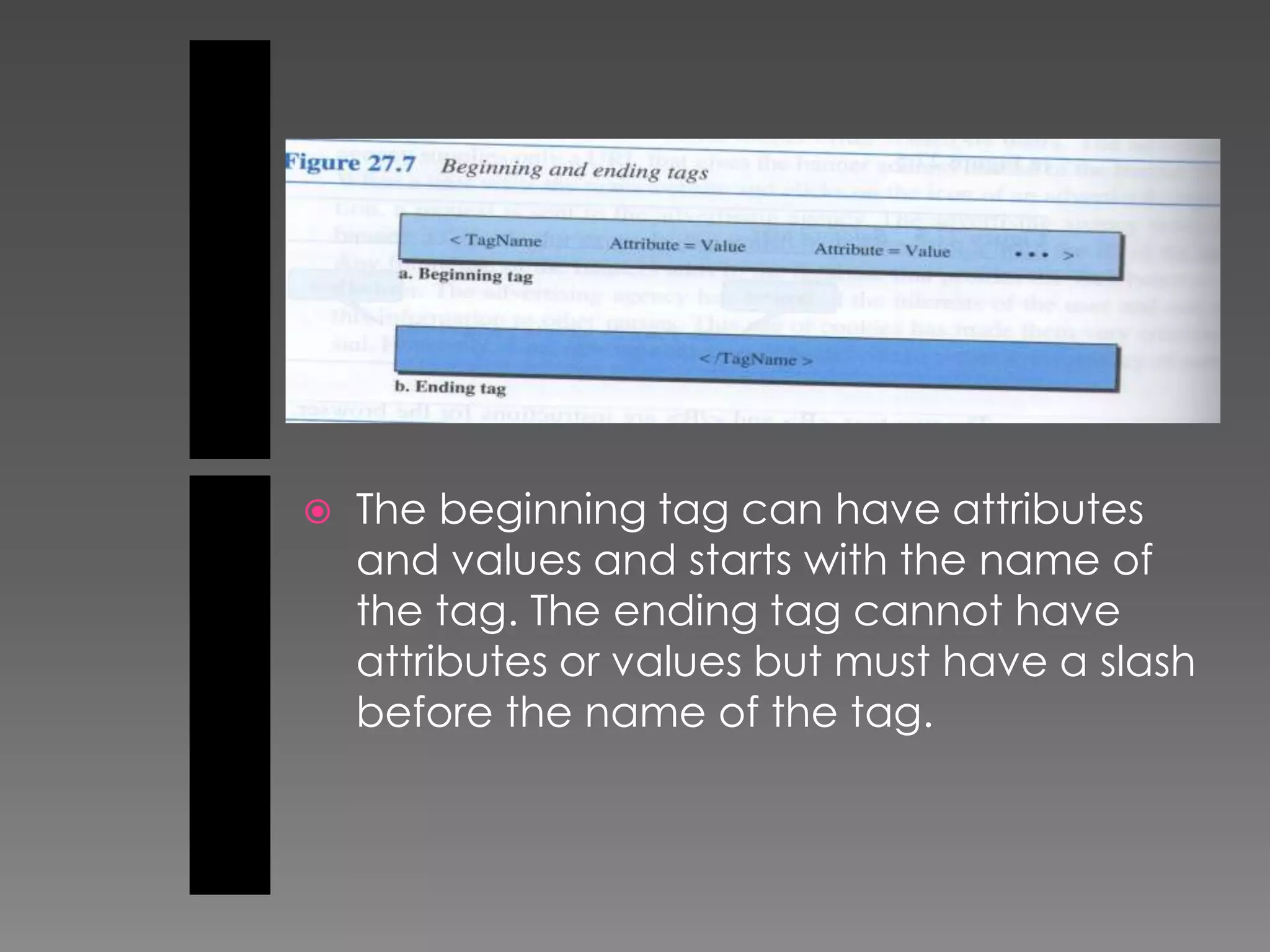
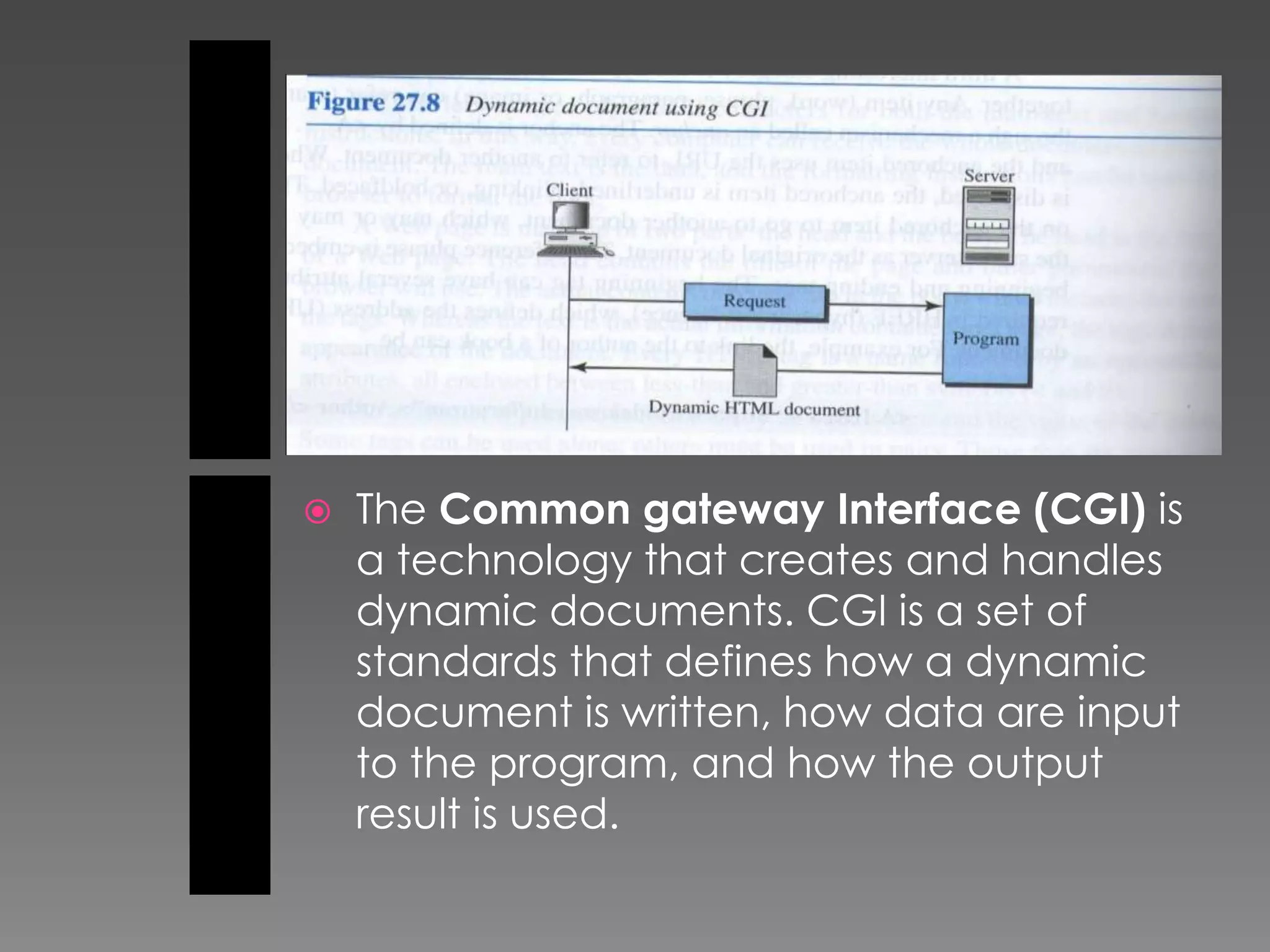
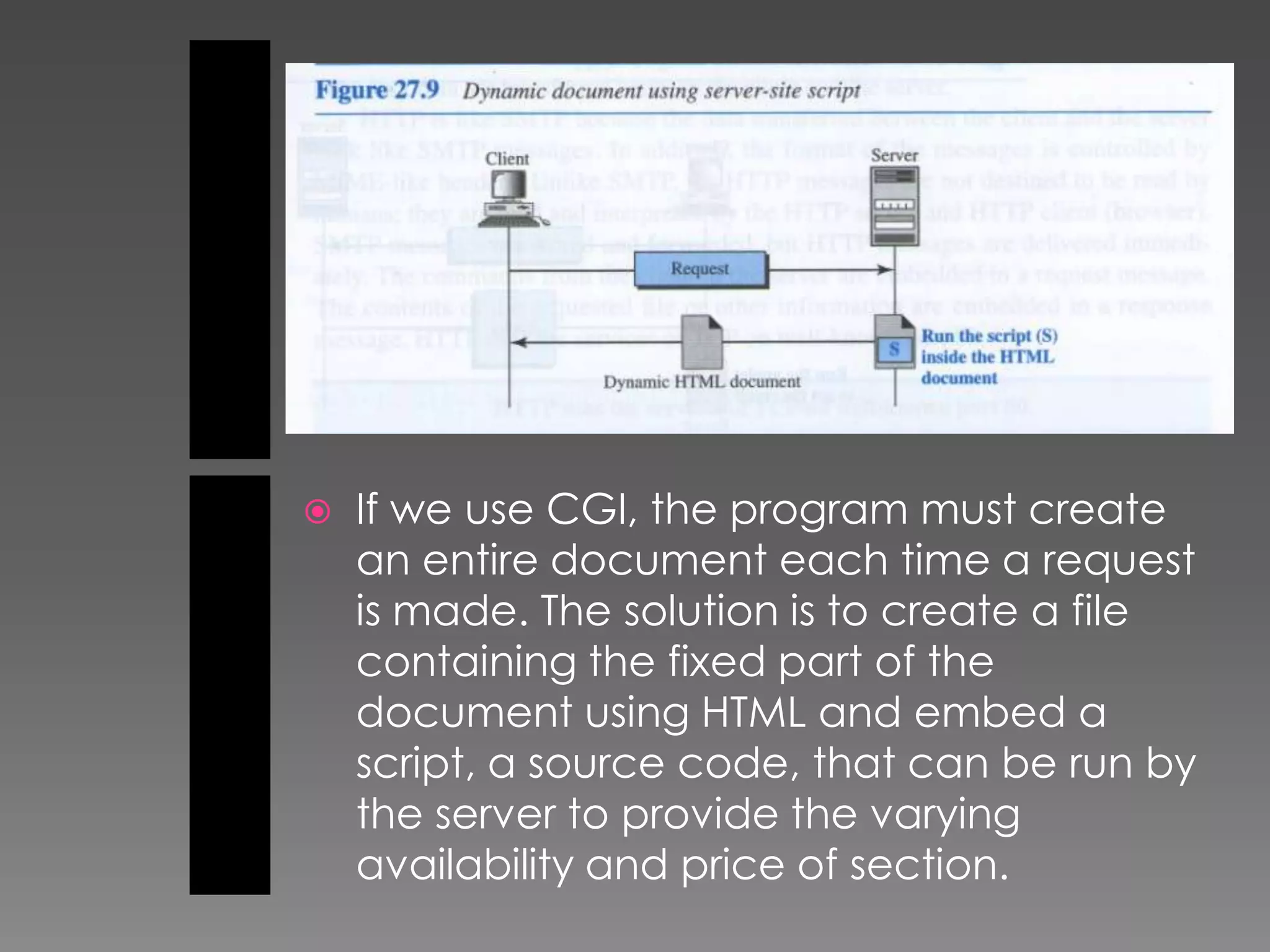
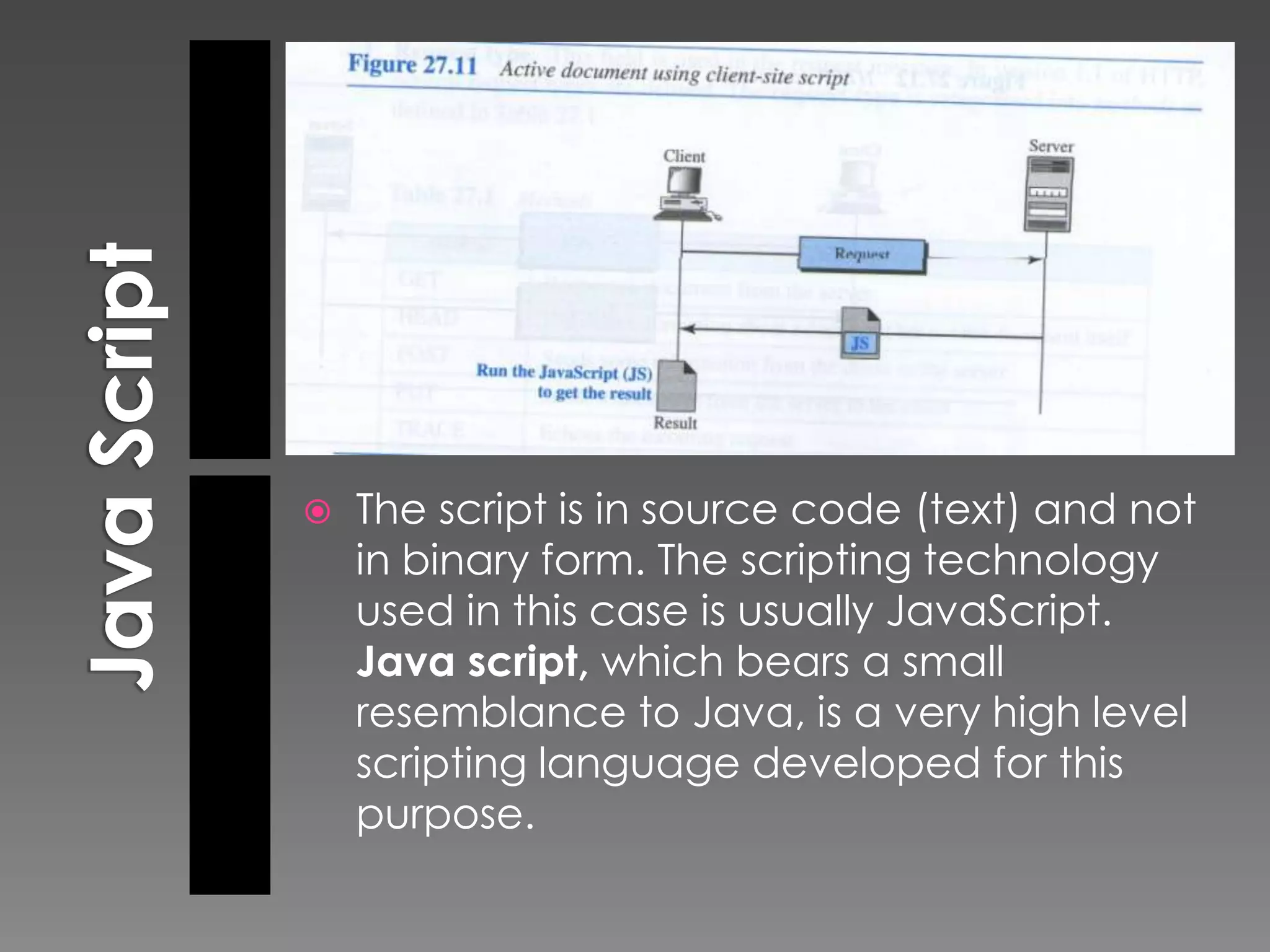
The document discusses the history and development of the World Wide Web from its origins in the 1980s to its modern implementation. It describes Sir Tim Berners-Lee's 1989 proposal that laid the foundations for the Web as a system of interlinked hypertext documents accessed via the HTTP protocol. The document then provides details on key Web technologies like browsers, servers, URLs, HTML, and how static, dynamic and interactive content is implemented and delivered over the Web.