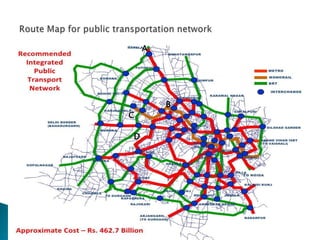
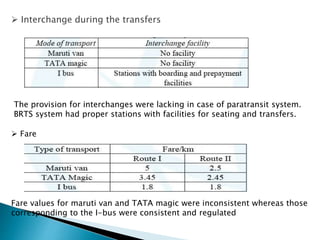
The document discusses the necessity and evaluation of an Integrated Multi-Modal Transportation System (IMMTS) in India, emphasizing the importance of improved transport infrastructure for economic growth and reduced traffic congestion. It presents a study on the performance of transportation systems in Indore and Delhi, noting key performance measures such as travel time, passenger satisfaction, and waiting times. The findings highlight the dominance of paratransit systems in Indore, issues with service quality, and the need for better integration of transport modes.