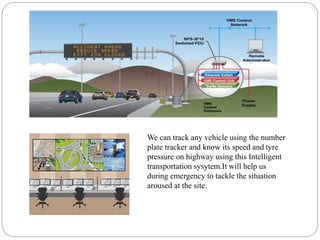
This document provides an overview of Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITS). It discusses the necessity of ITS in India due to rapid economic growth and increasing traffic. The main components of ITS include transportation infrastructure, vehicles, and traffic management. ITS aims to provide innovative services to different modes of transportation. Some applications of ITS mentioned are electronic toll collection, GPS, advanced traveler information systems, and automatic passenger counters. While ITS can improve safety, traffic flow and reduce costs and pollution, challenges include high equipment costs and potential hacking of control systems.