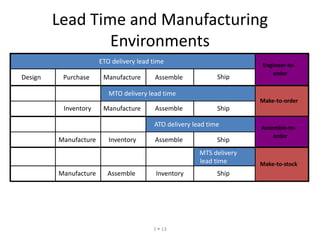
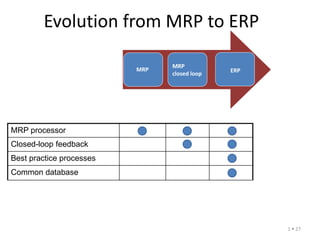
The document provides an introduction to supply chain management and manufacturing. It discusses the components of the manufacturing business model including defining products and customers, designing products and processes, managing material flow, and providing customer service. It also covers manufacturing environments like engineer-to-order, make-to-order, assemble-to-order, and make-to-stock. Additionally, it presents an overview of manufacturing planning and control including objectives like meeting customer demand and ensuring availability of materials and capacity. Finally, it discusses the evolution of systems from MRP to ERP and the impact of new philosophies like lean, total quality management, and six sigma.