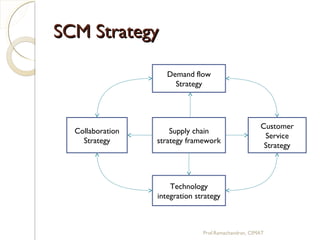
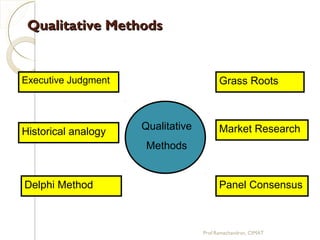
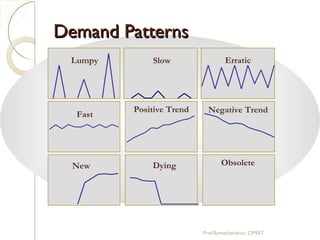
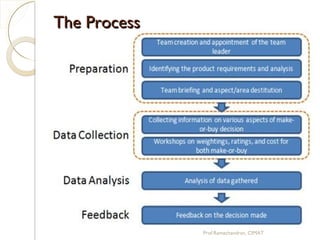
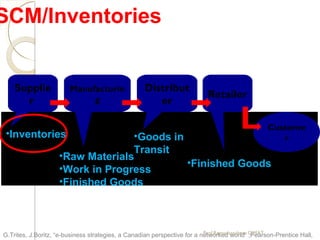
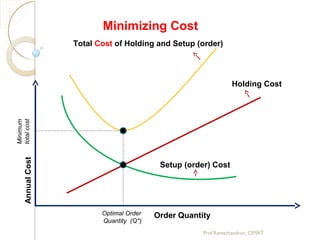
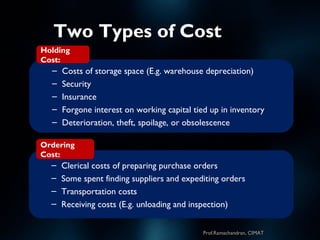
The document discusses supply chain management (SCM) strategies including collaboration strategy, demand flow strategy, customer service strategy, and technology integration strategy. It covers topics such as demand forecasting, demand planning, purchasing, inventory management, and cost management. Key points include defining demand planning as a process to create reliable forecasts that reflect constraints, and describing inventory management as overseeing the flow of units in and out of inventory to meet customer service goals in an efficient manner.