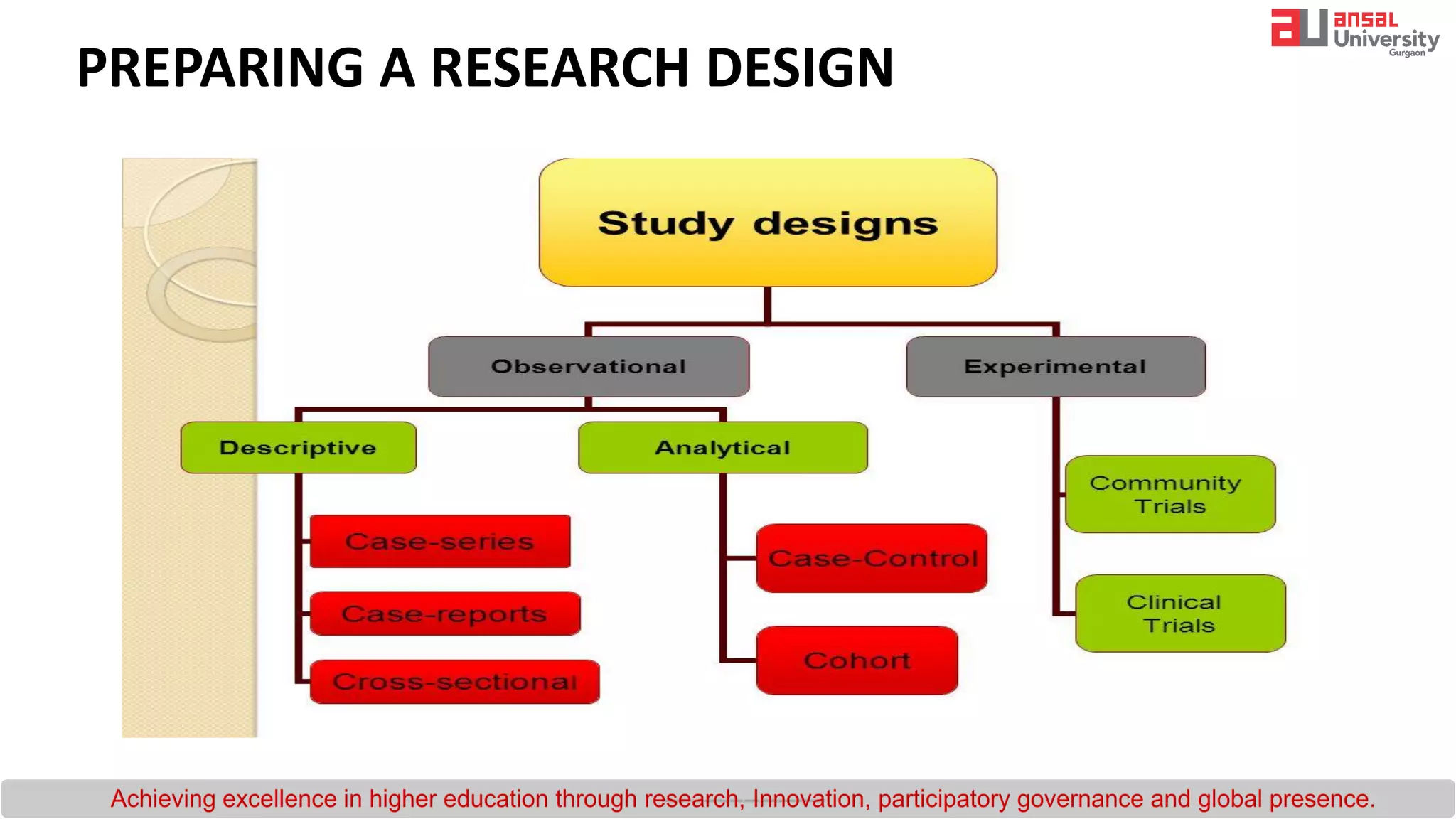
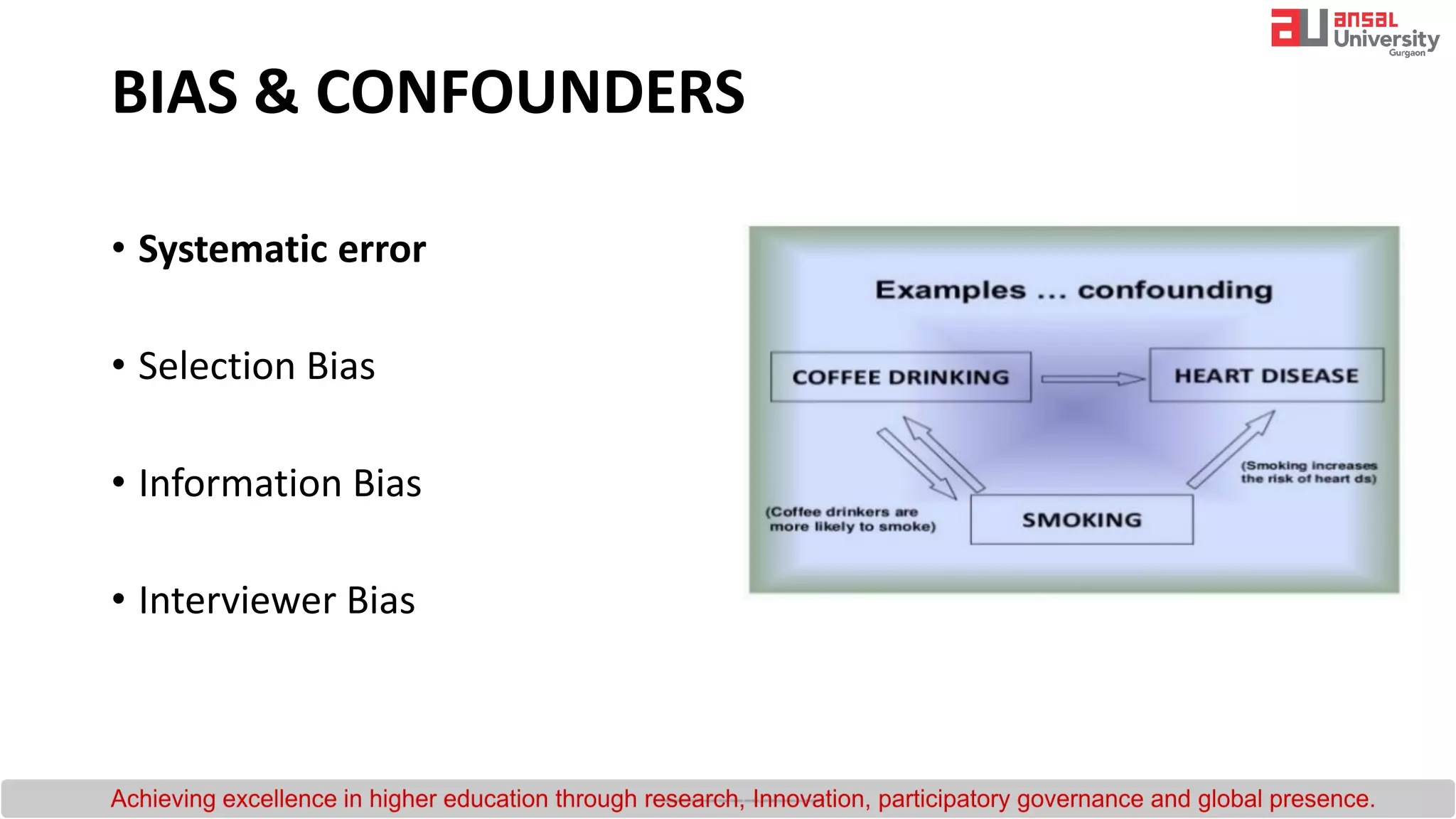
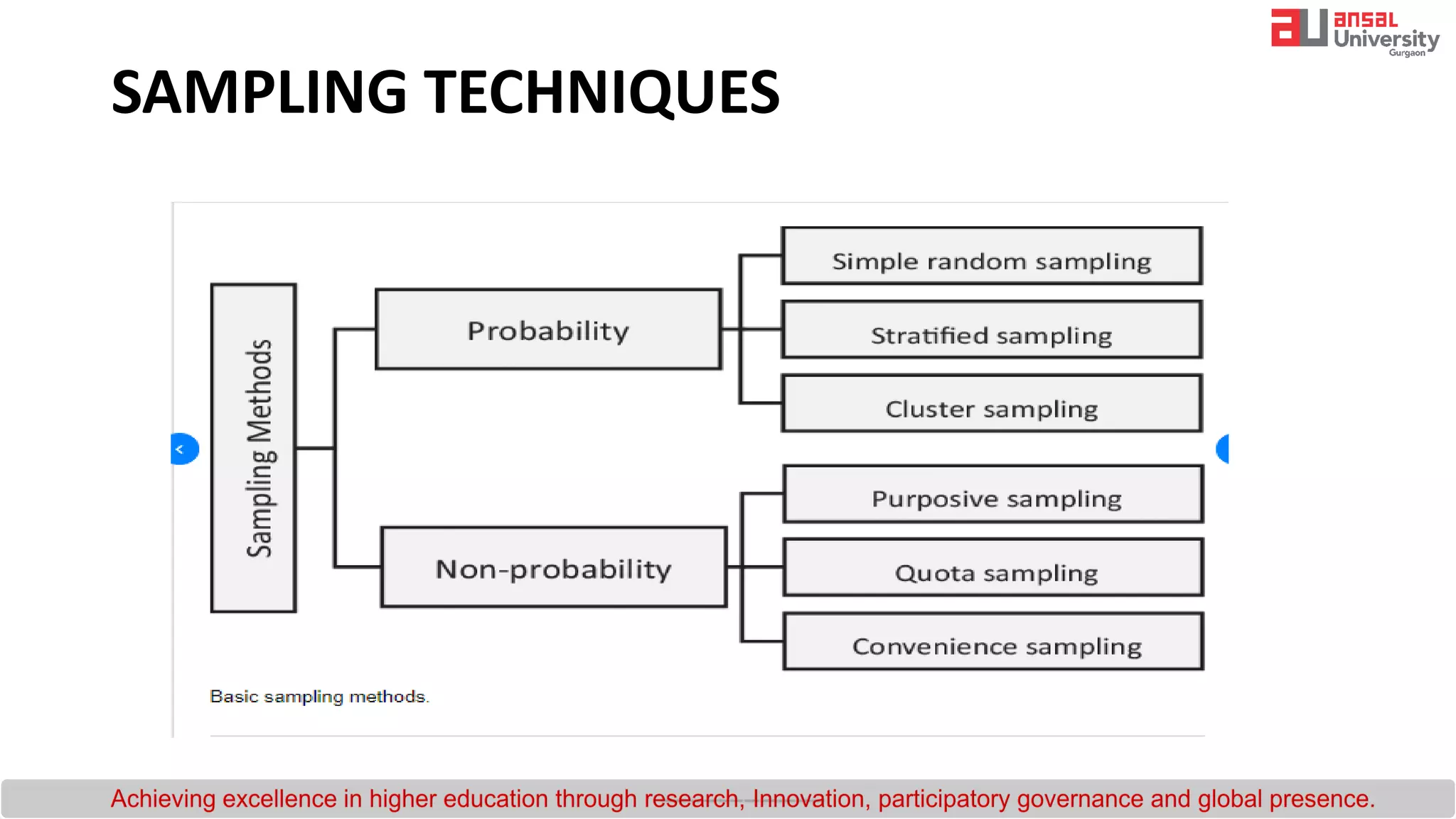
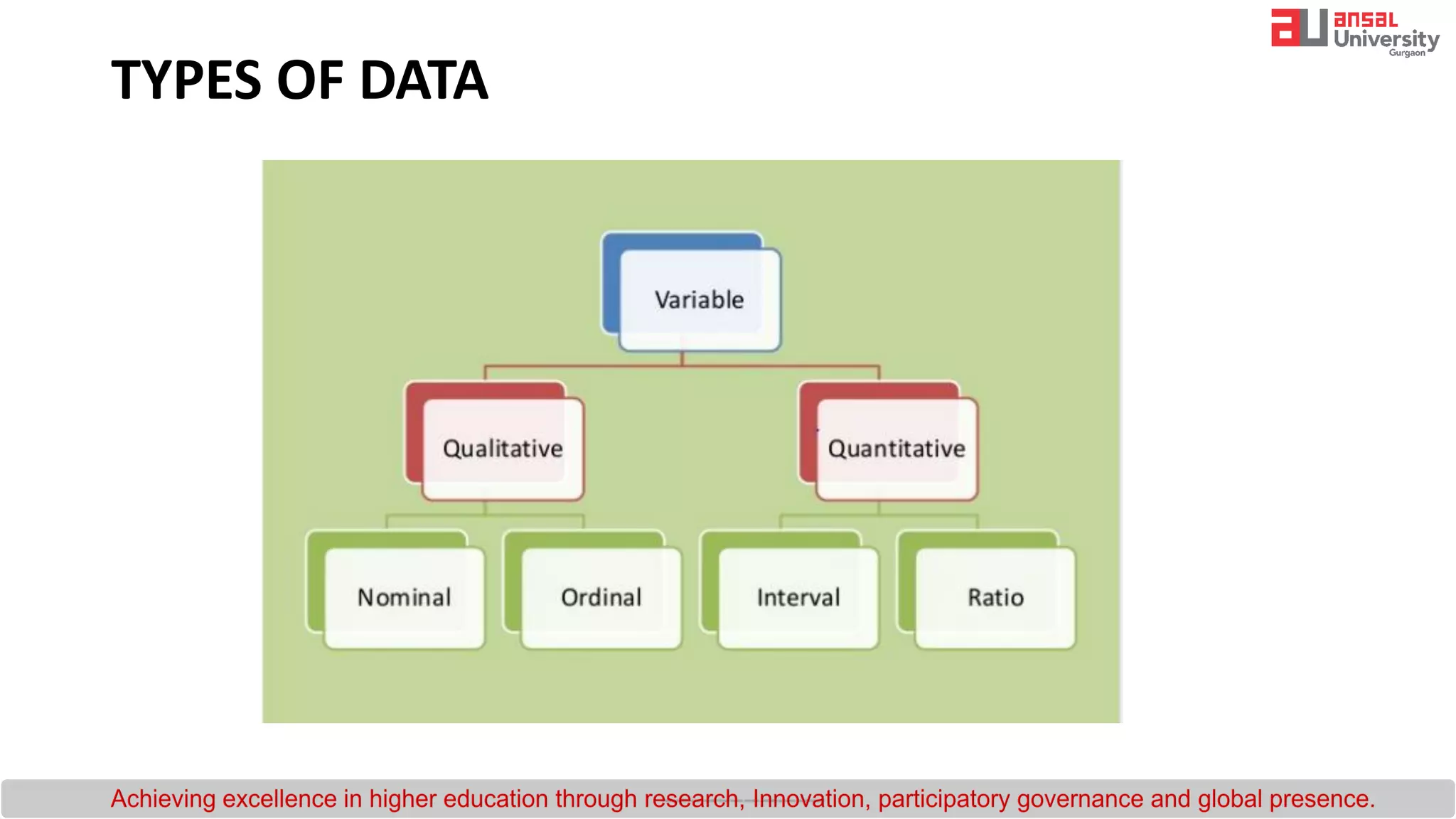
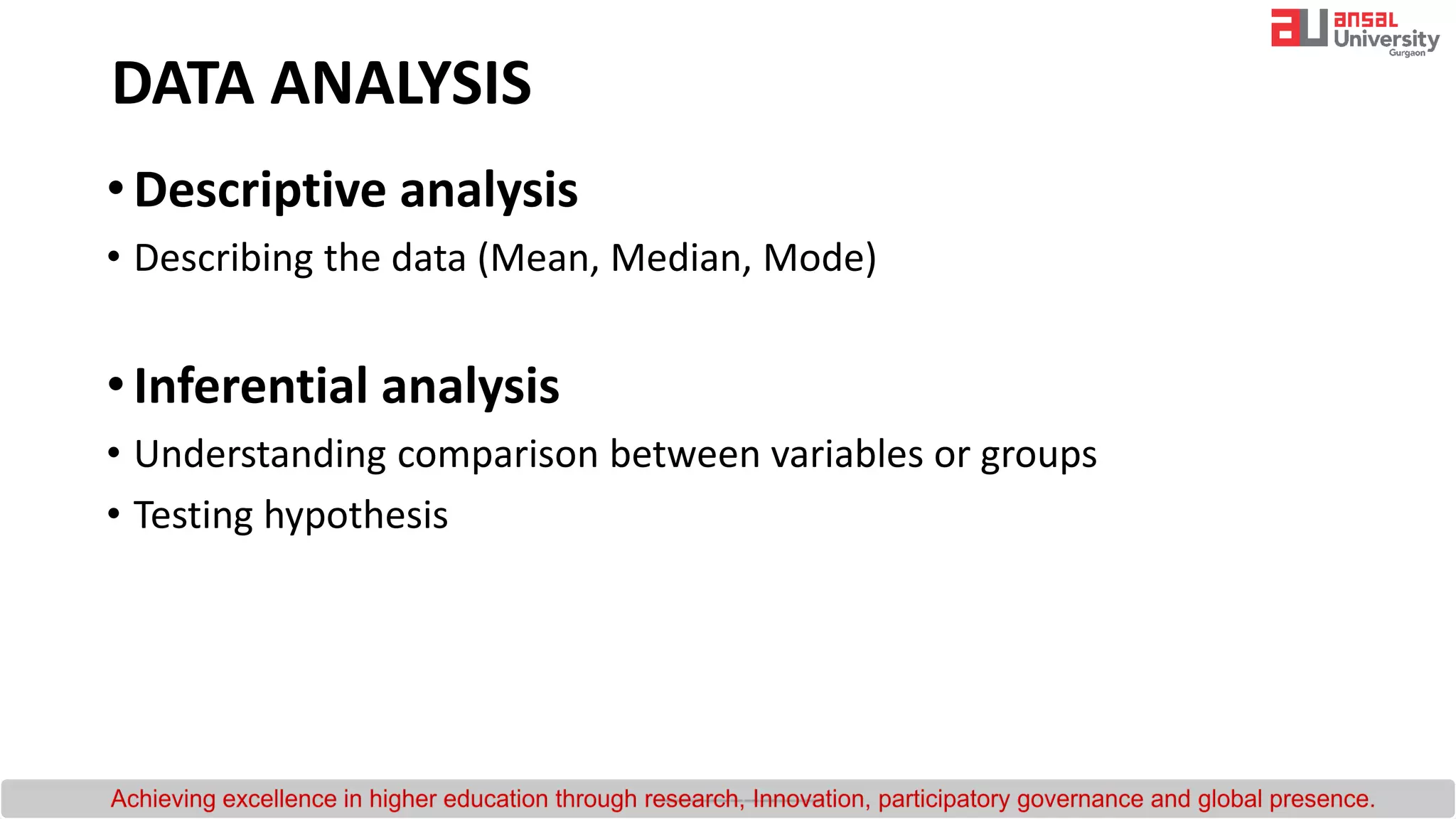
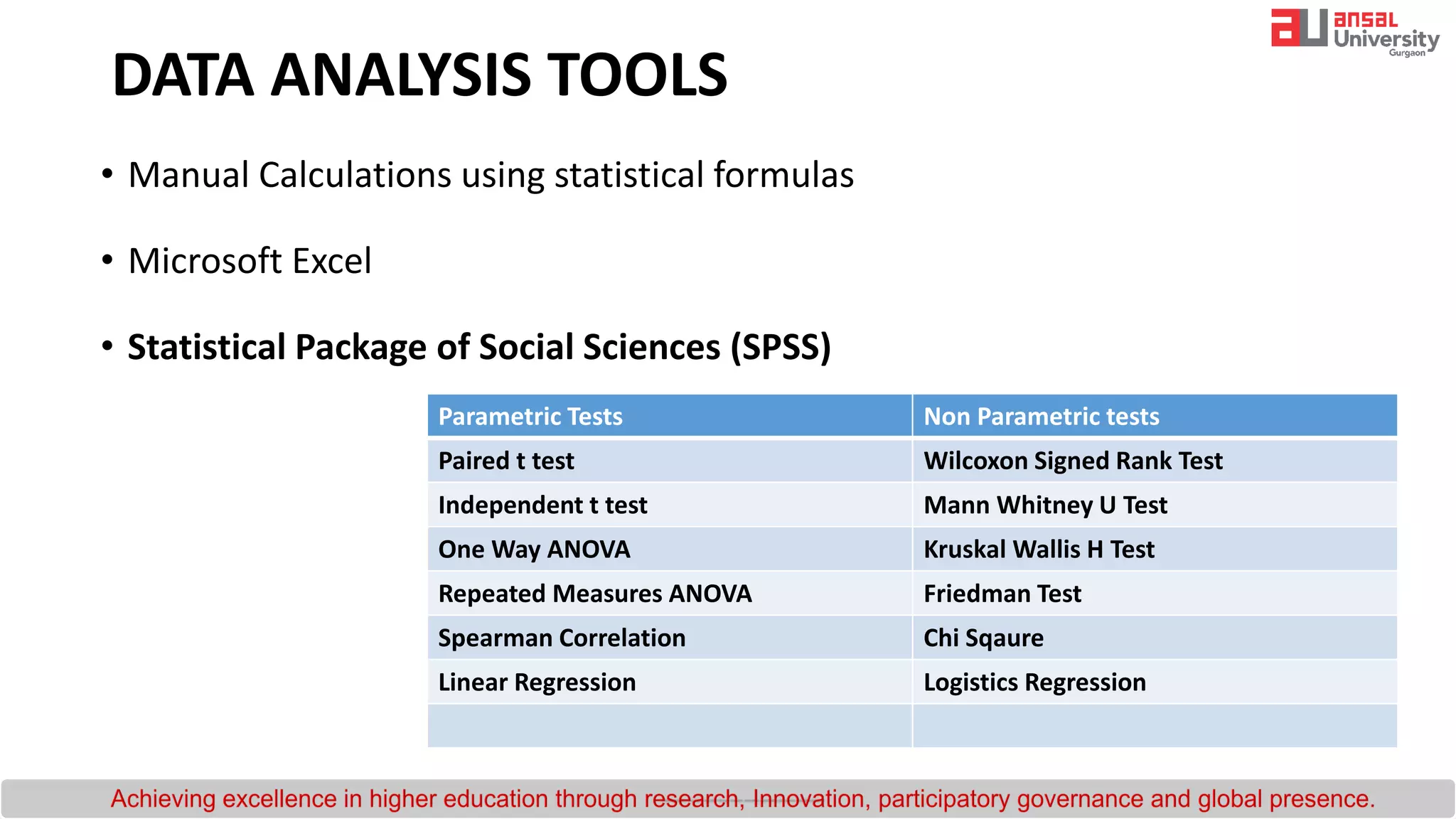
The document provides an introduction to research methodology. It outlines the key steps in the research process as: (1) formulating the research question by identifying gaps in existing literature through a literature review; (2) developing hypotheses and objectives; and (3) preparing a research design that includes determining the sample, data collection methods, and data analysis plan. It also discusses important qualities of good research such as being controlled, rigorous, systematic, valid and verifiable.