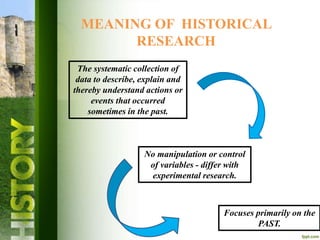
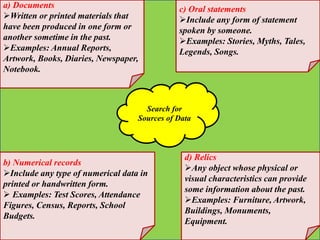
Historical research is the critical inquiry into past events to produce accurate descriptions and interpretations. It relies on existing records and materials without manipulating variables, focusing on issues, movements, and accomplishments of individuals or institutions. The research involves identifying topics, sourcing data, evaluating sources, and writing reports while adhering to rigorous analytical and evaluation methods.