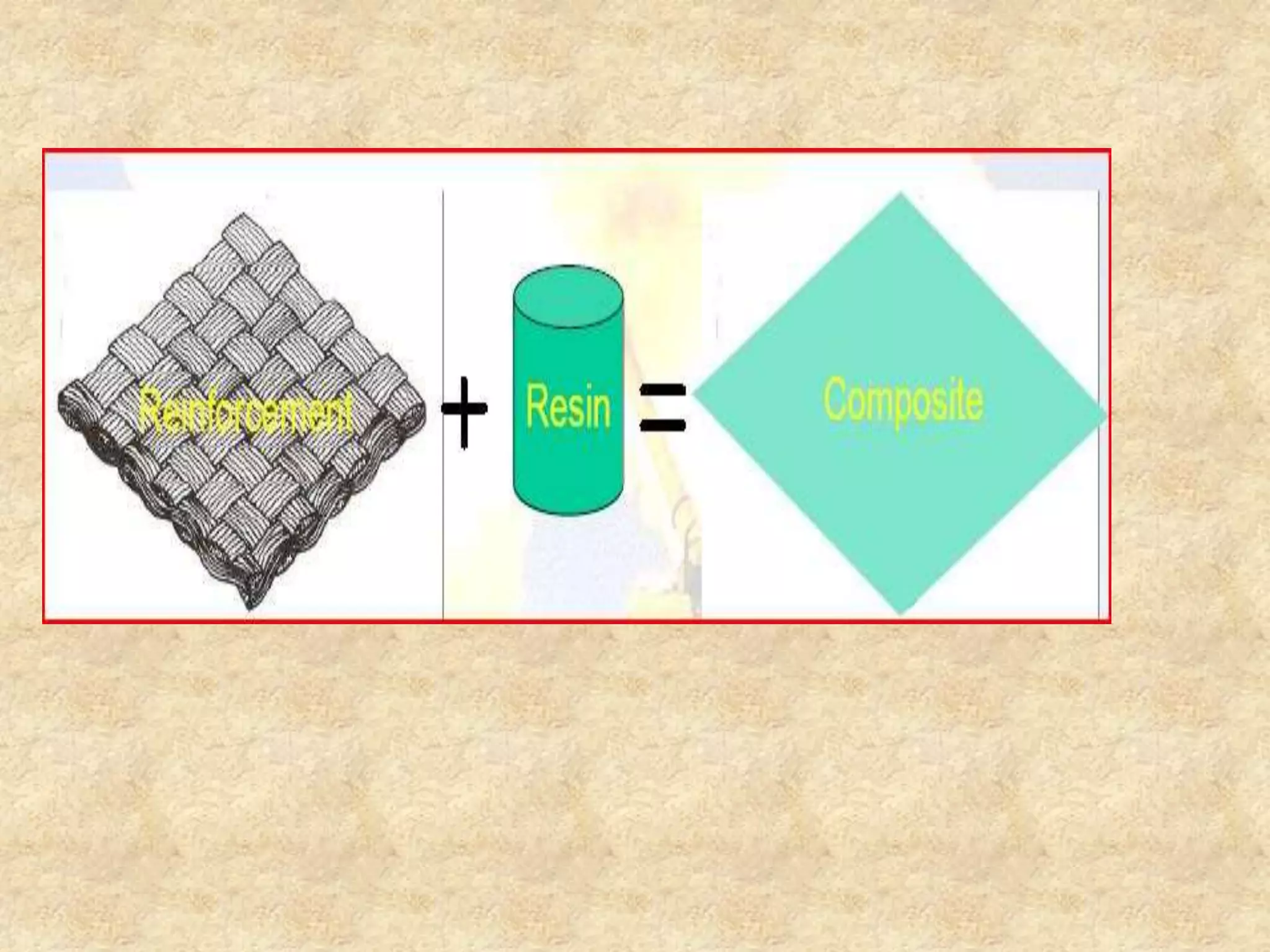
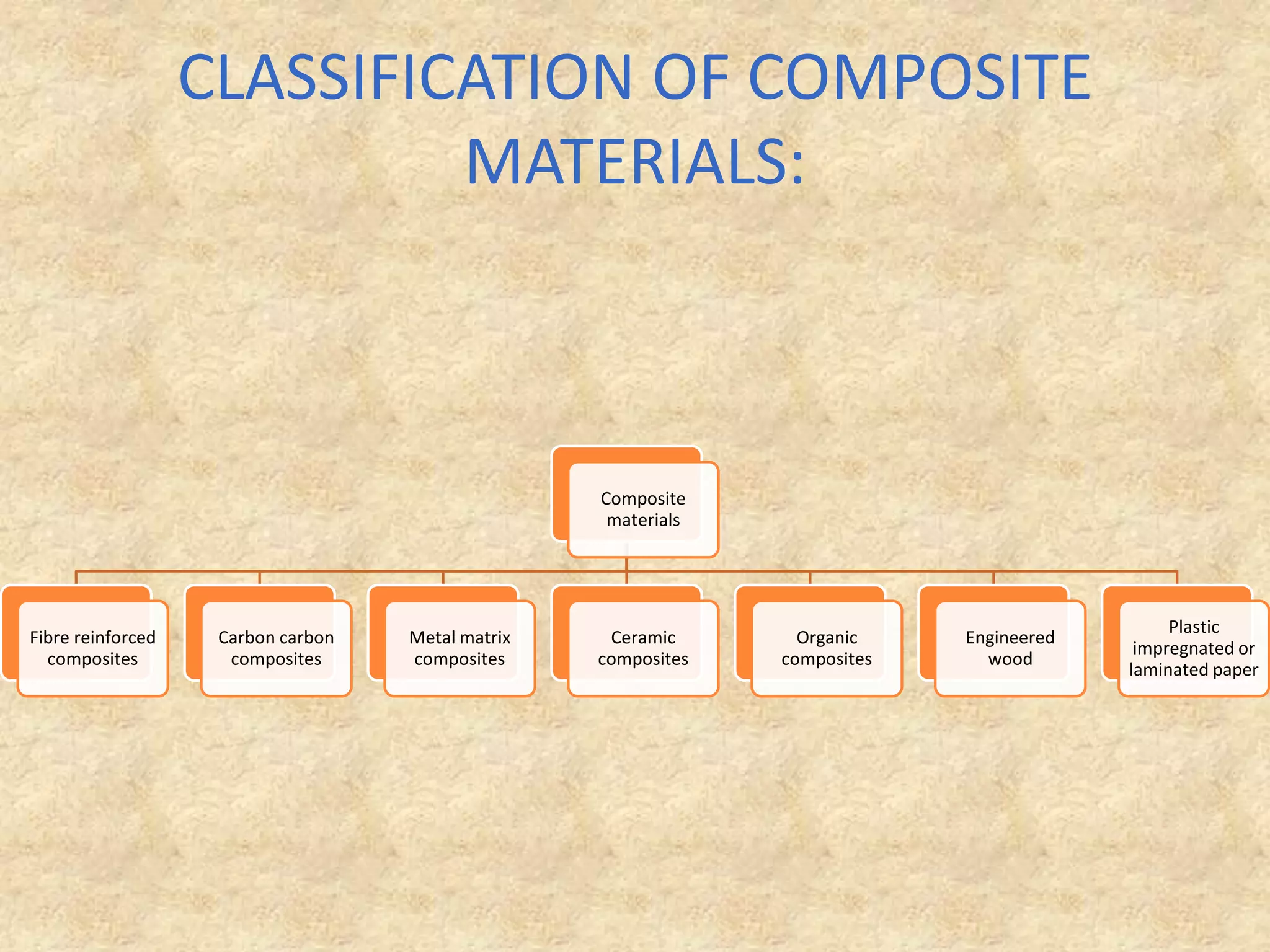
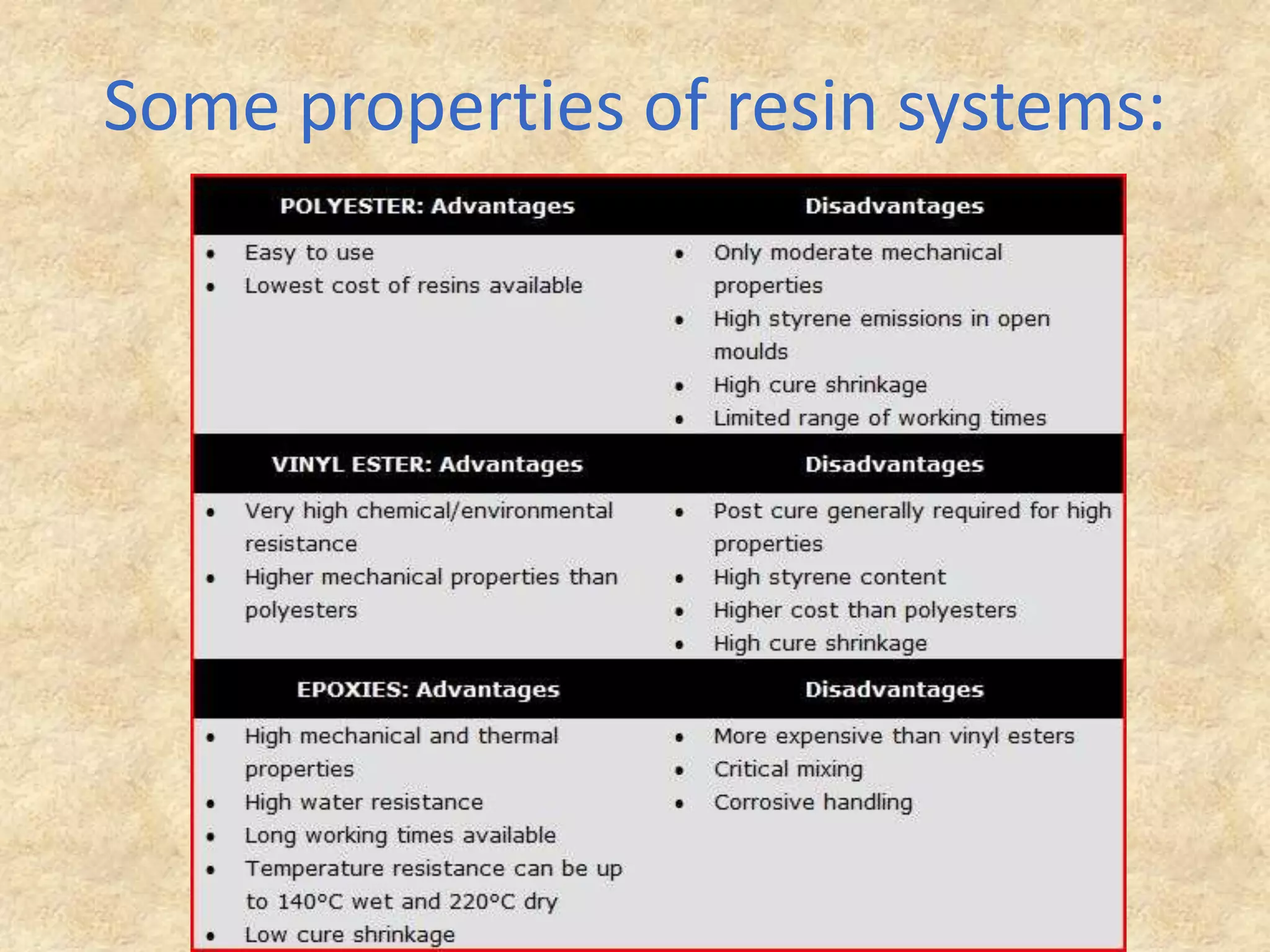
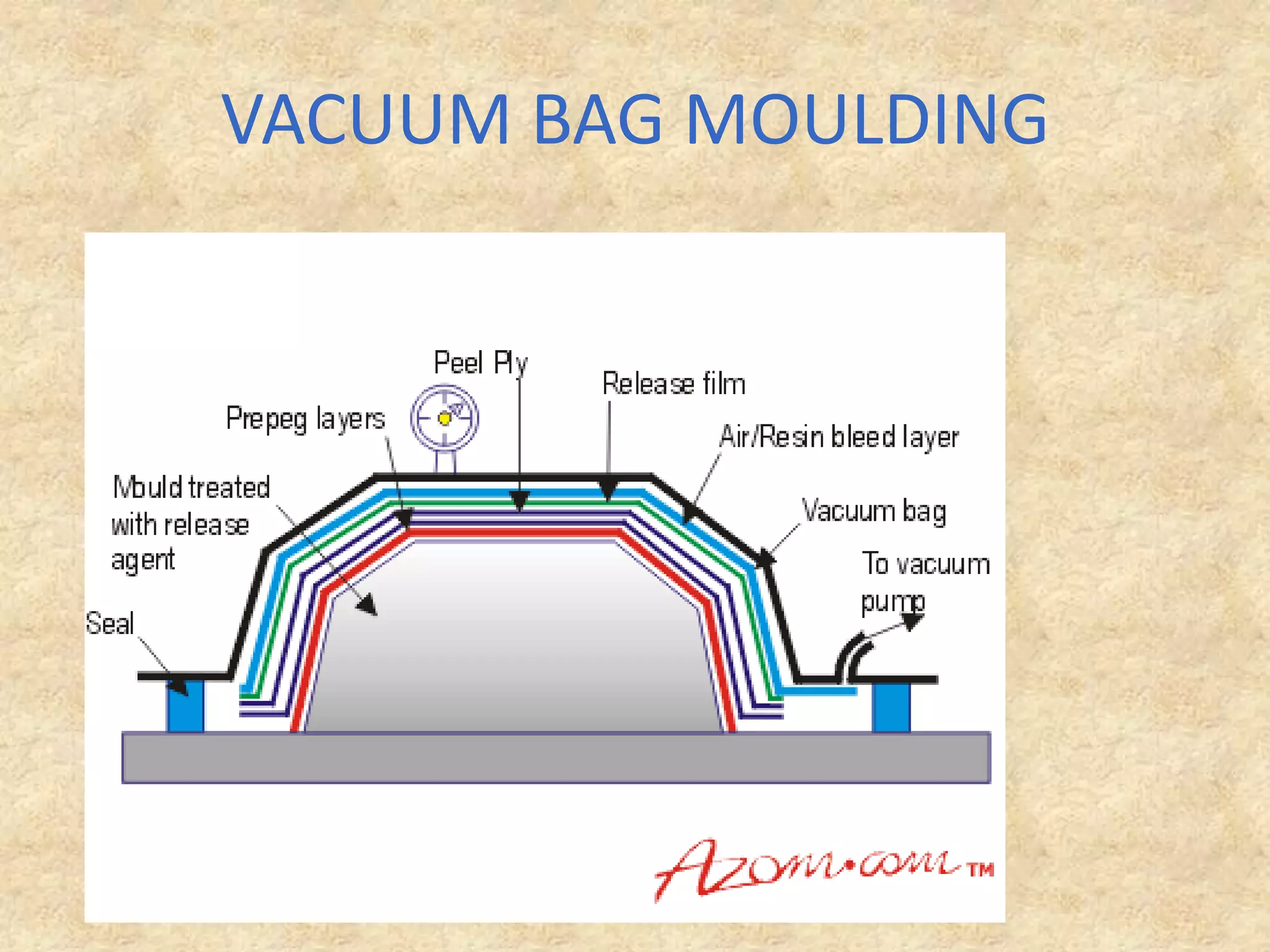
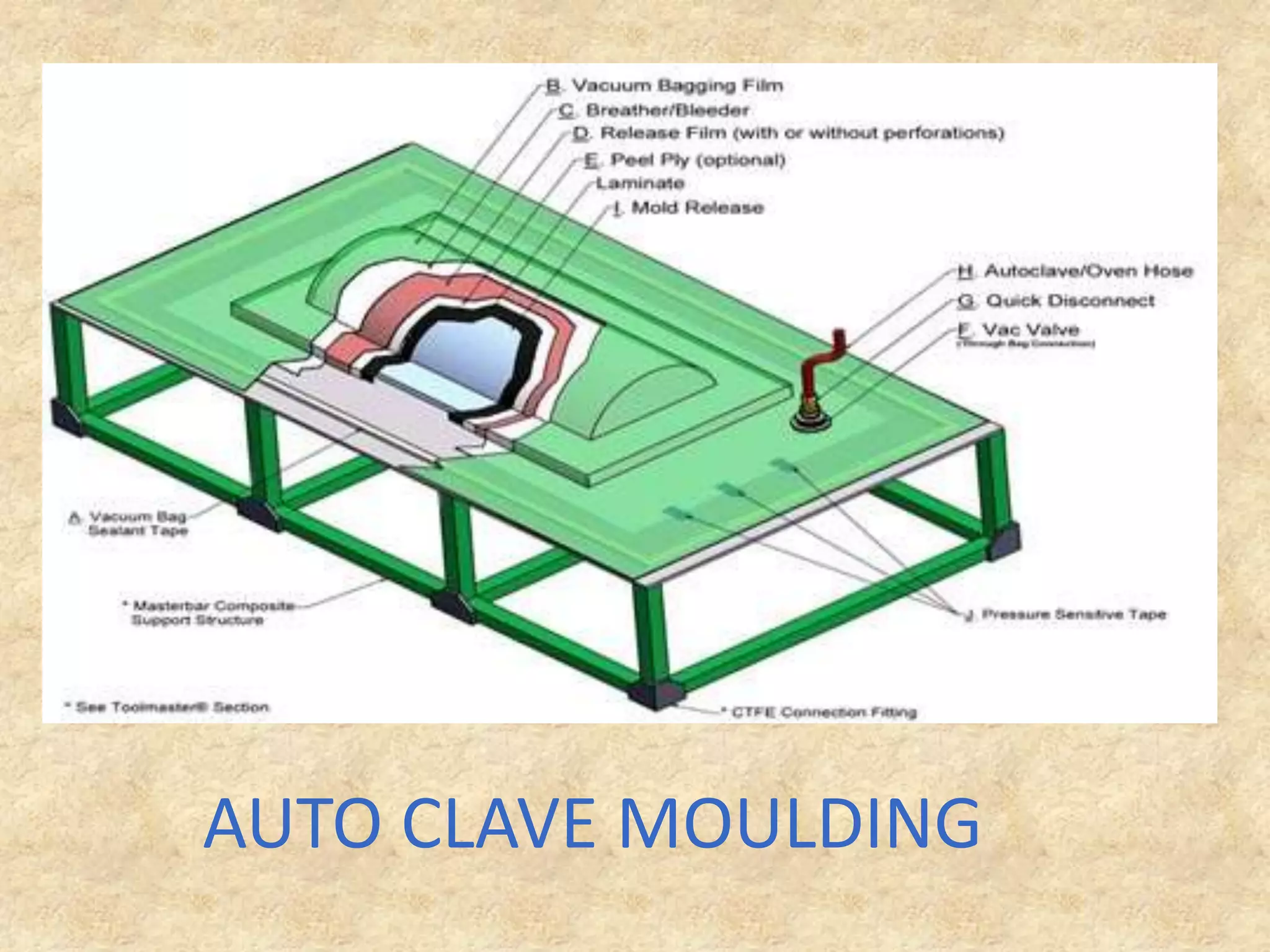
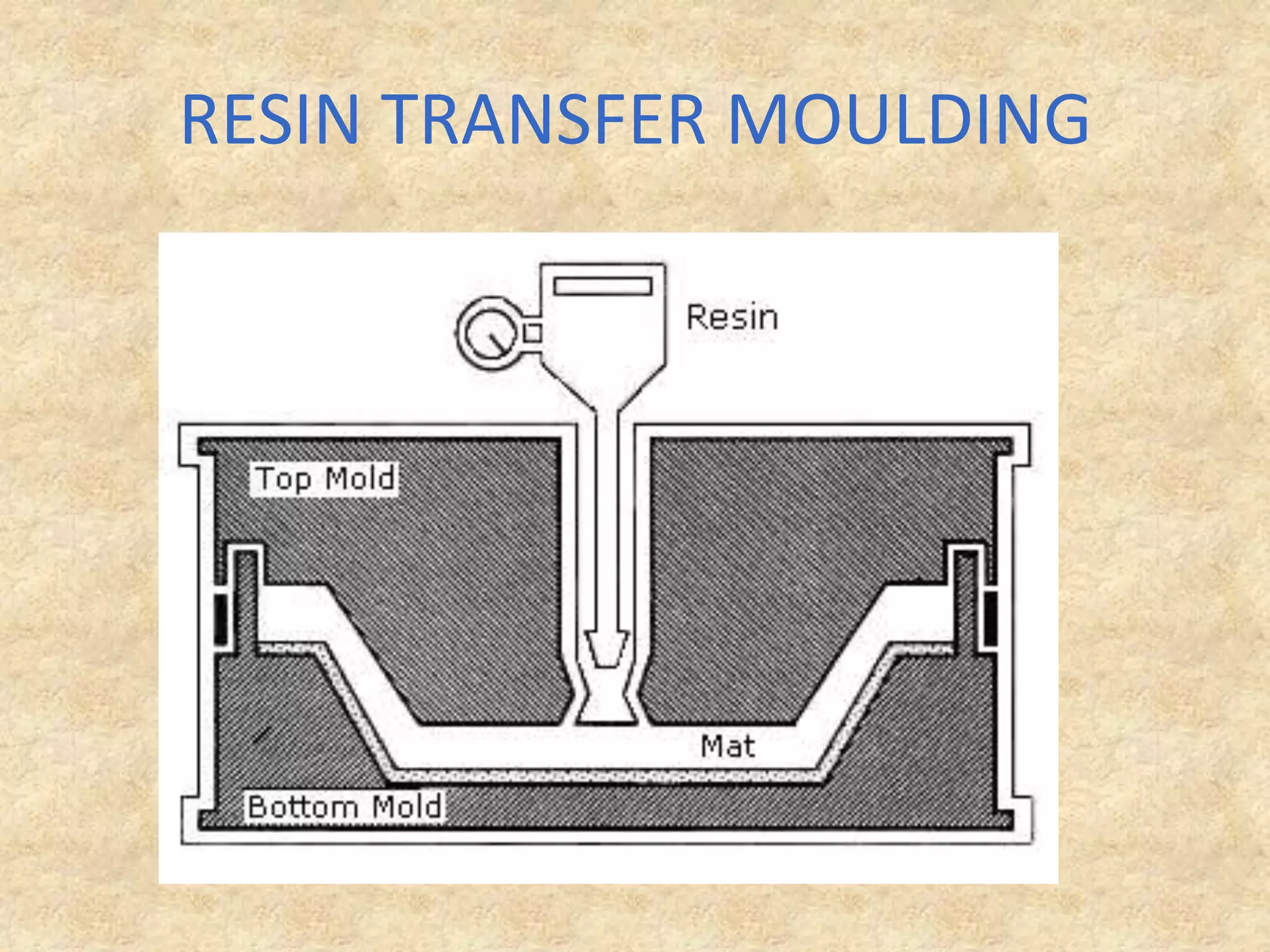
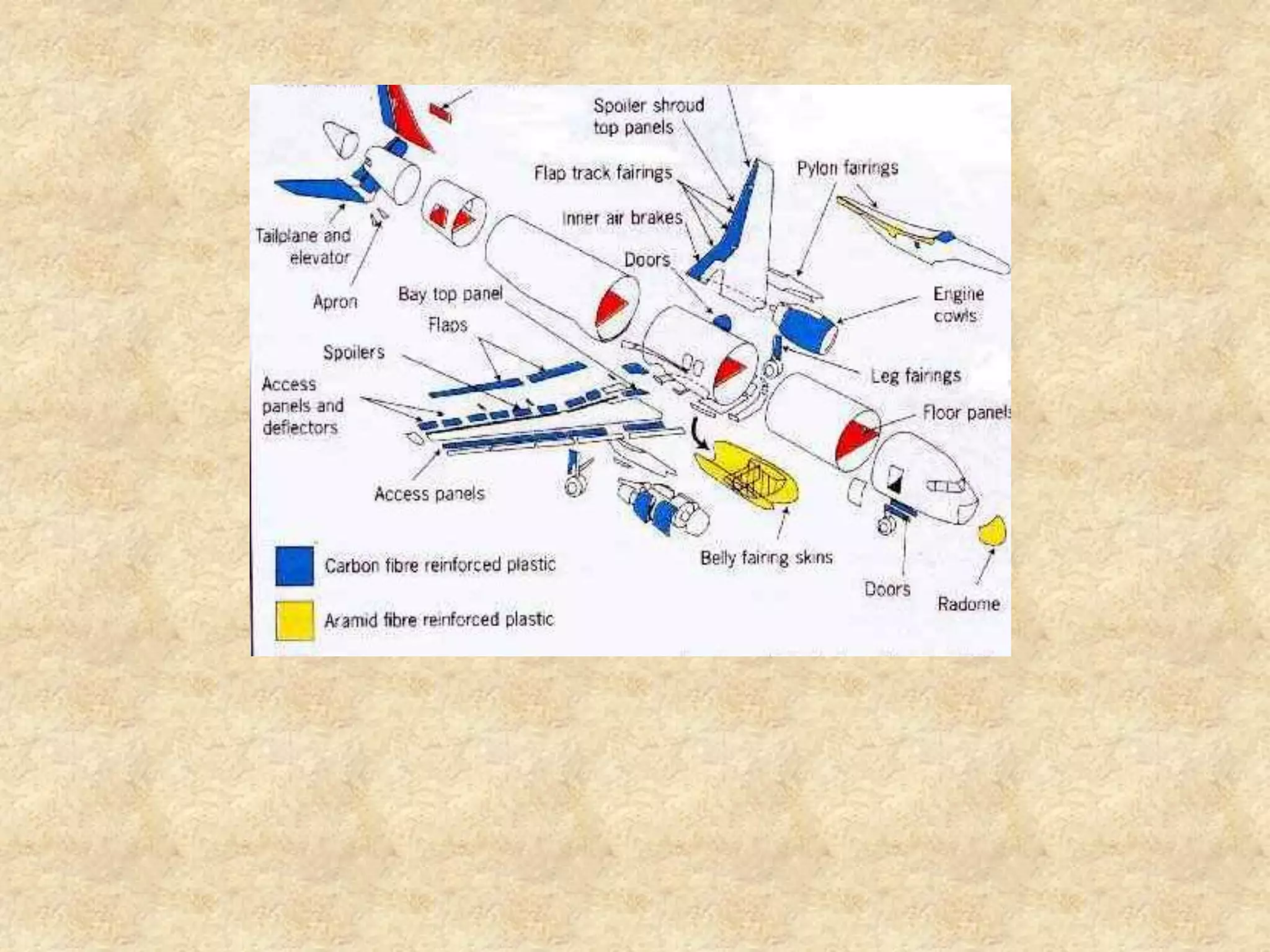
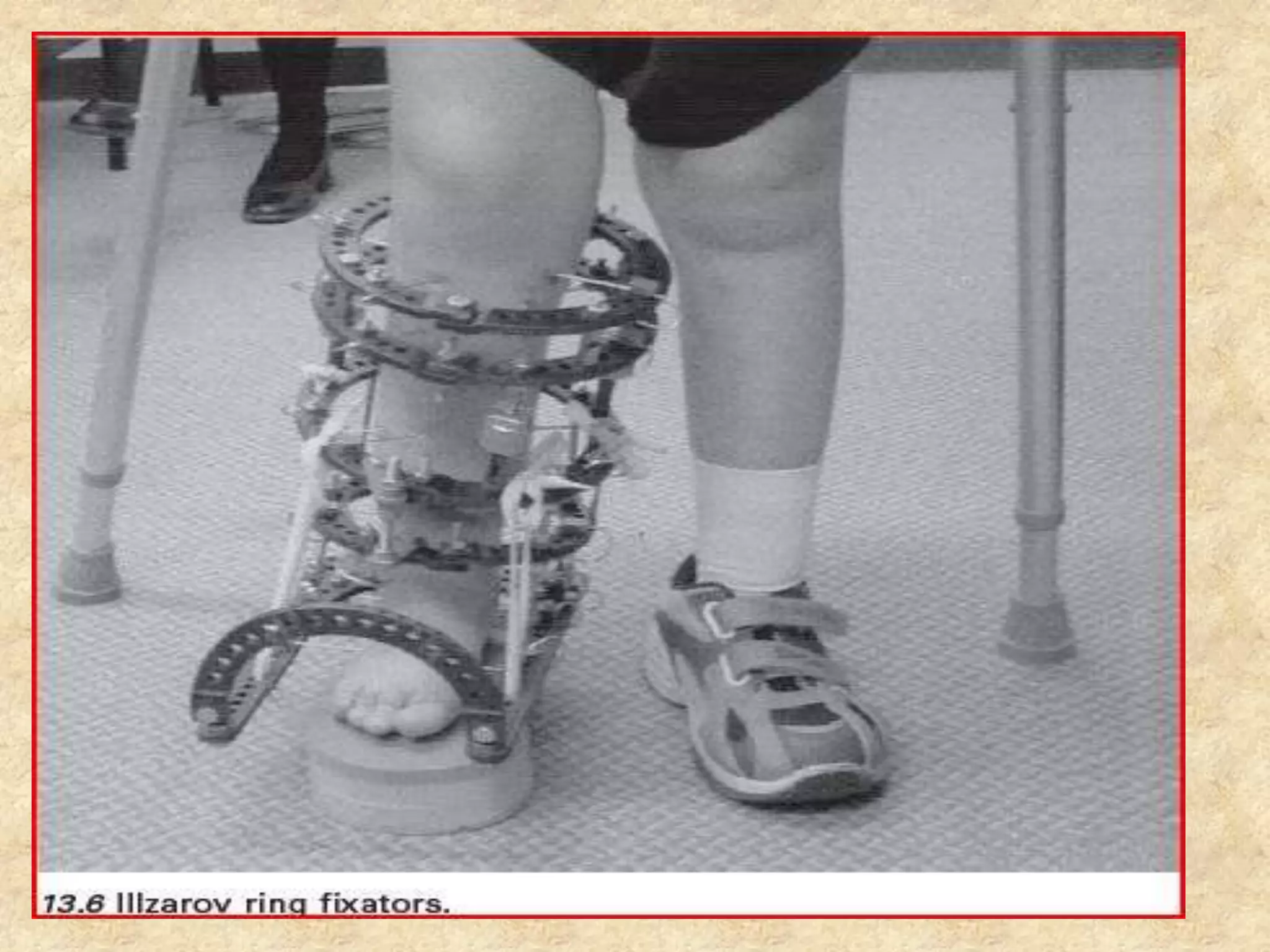
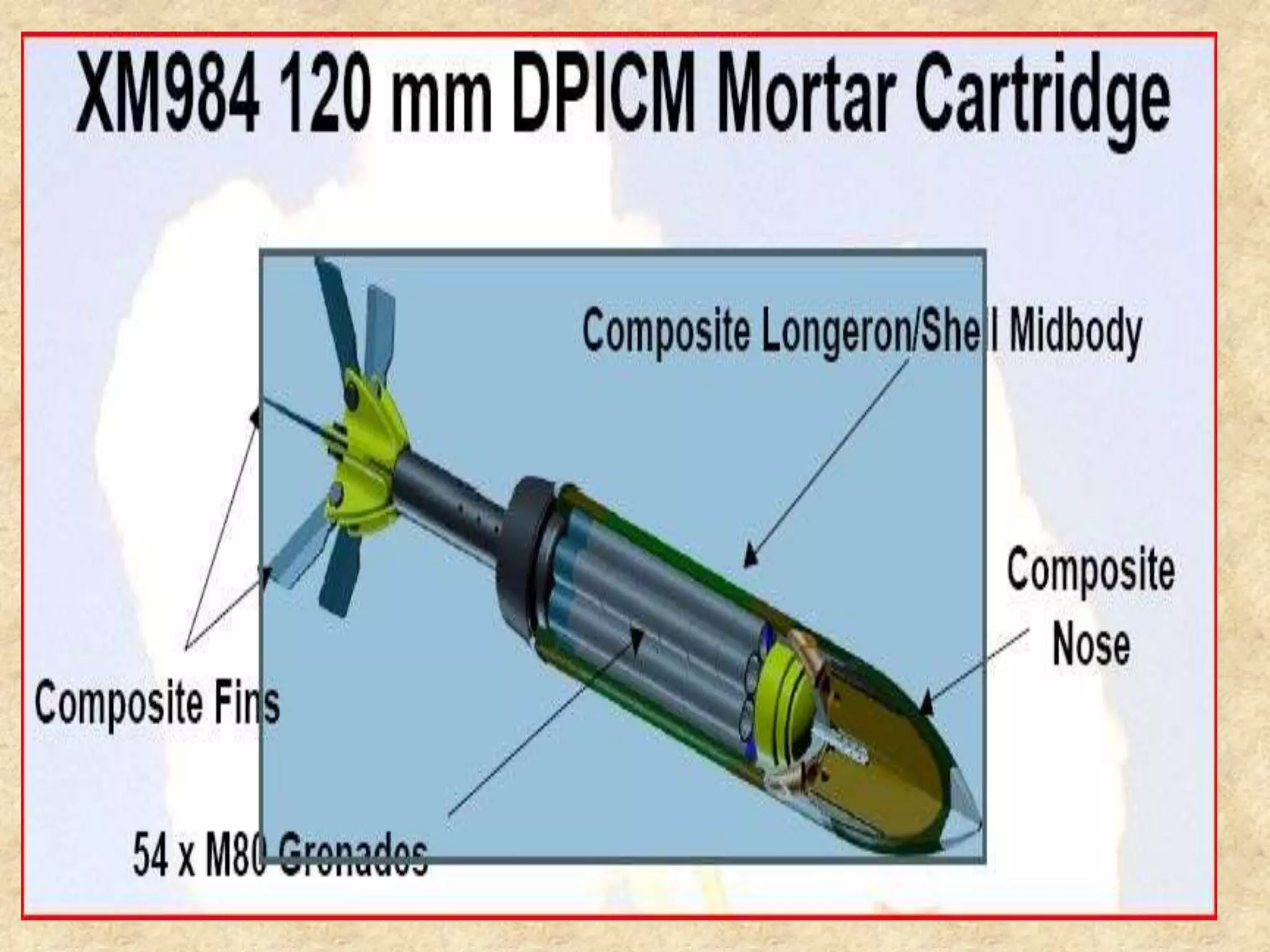
Composite materials are engineered materials made from two or more constituent materials with different properties. The matrix, such as plastic, holds reinforcements like fibers or particles in place. Common reinforcements include glass, carbon, and Kevlar fibers. Composites have been used for thousands of years in materials like straw-reinforced bricks, but modern composites use fibers in fabrics arranged before resin cures. Composites are manufactured using processes like vacuum bag molding, resin transfer molding, and autoclave molding. They have applications in industries like aerospace, construction, medical, sports, and defense due to properties like high strength and low weight.