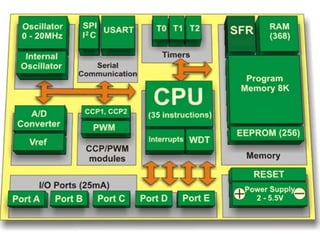
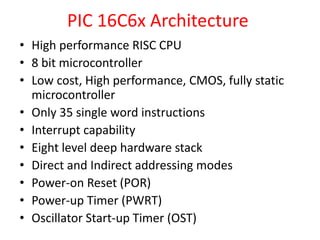
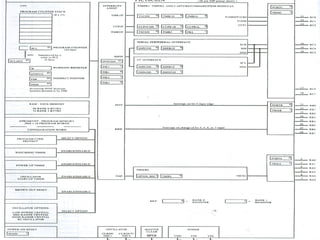
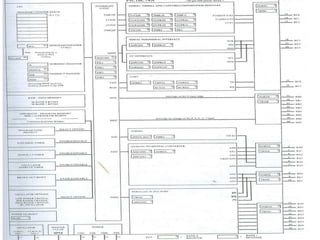
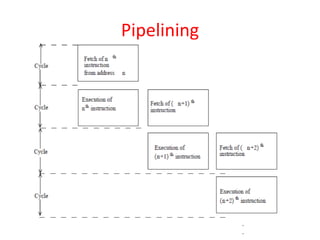
This document provides an introduction to PIC microcontrollers. It discusses why PICs have become popular, including their low cost, wide availability, and support tools. It then describes the basic architecture of PIC microcontrollers, including their Harvard architecture, RISC design, and peripheral features like timers and serial communication. Finally, it discusses the architecture of the PIC16C6x line specifically, outlining its registers, addressing modes, and peripheral modules.