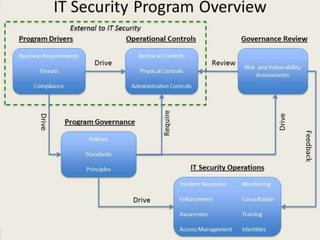
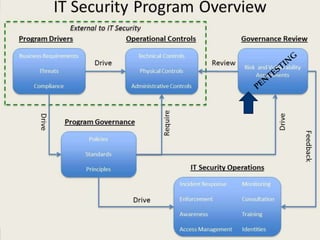
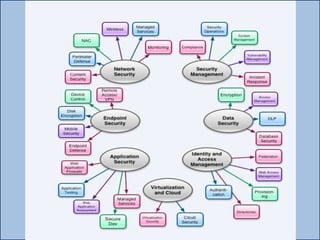
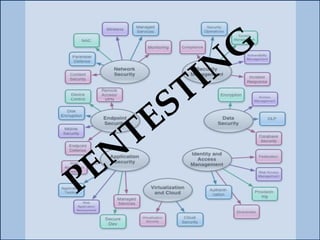
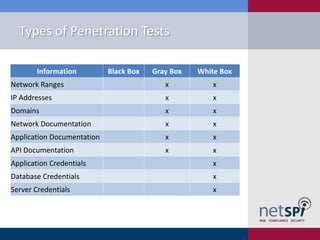
The document provides an overview of penetration testing, its definitions, and its importance for companies in evaluating security risks and compliance. It discusses various types of penetration tests, methodologies, tools, and the skills required for penetration testers, along with ethical considerations and rules of engagement. The document also touches on pathways to a career in penetration testing and emphasizes the need for continuous learning and community involvement.