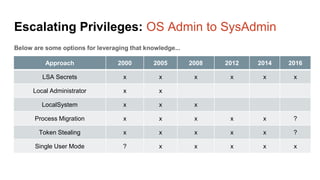
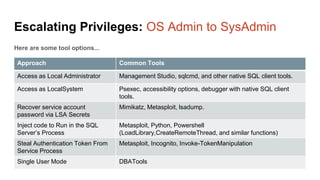
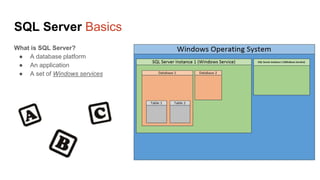
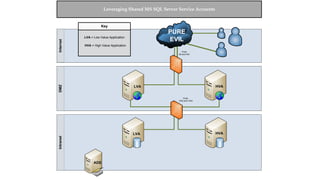
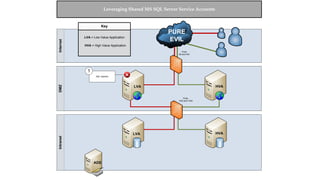
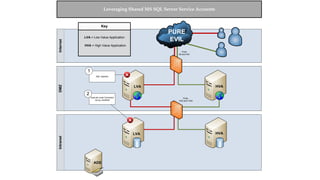
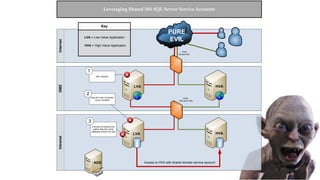
The document presents an overview of a presentation by Scott Sutherland on hacking SQL Server using PowerShell, highlighting topics such as privilege escalation, post-exploitation activities, and the use of the PowerUpSQL toolkit. It details various techniques for discovering and exploiting SQL Server vulnerabilities, emphasizing the risks associated with shared service accounts and the ease of escalating privileges in enterprise environments. General recommendations for securing SQL Servers are also provided to mitigate such vulnerabilities.



























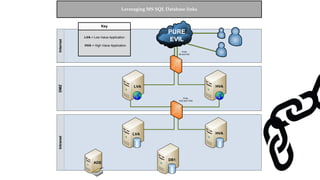
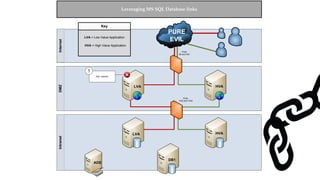
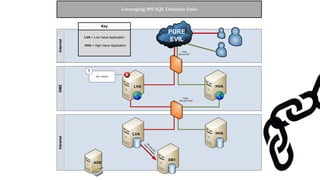
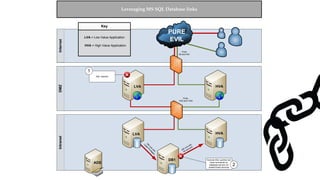
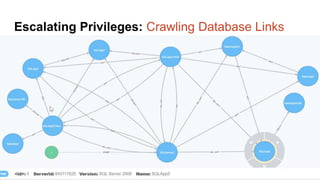
![Escalating Privileges: Crawling Database Links
What’s a database link?
● Database links are basically persistent database connections for SQL Servers.
Why should I care?
● Short answer = privilege escalation
● Public role can use links to execute queries on remote servers (impersonation)
SELECT * FROM OpenQuery([SQLSERVER2],’SELECT @@Version’)
● Stored procedures can be executed (xp_cmdshell)
● Links can be crawled](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2016derbycon-hackingsqlserversonscalewithpowershell-final-160921193358/85/DerbyCon2016-Hacking-SQL-Server-on-Scale-with-PowerShell-42-320.jpg)