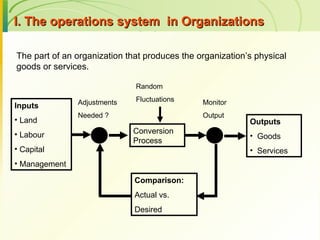
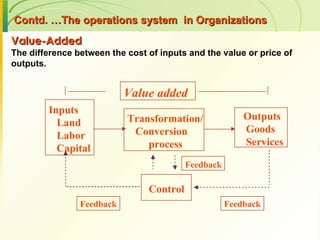
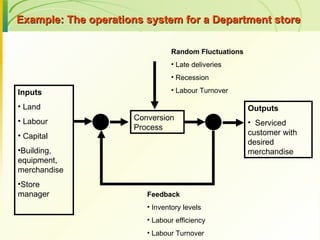
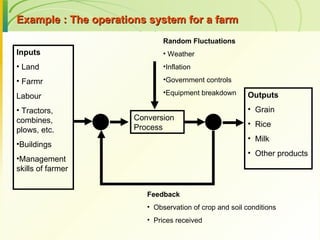
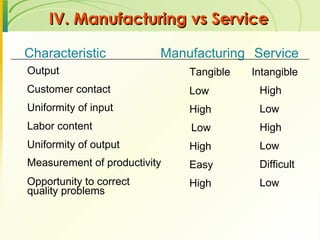
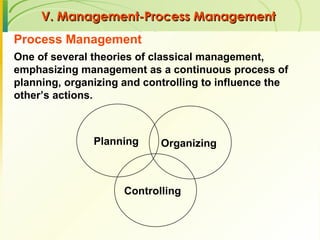
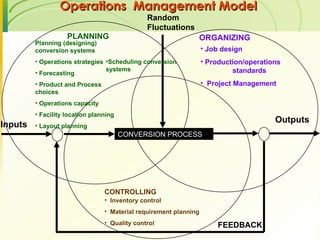
The document provides an introduction to operations management. It defines operations management as the management of the conversion process that transforms inputs like labor, capital, land and management into outputs of goods and services. It discusses the key components of an operations system including inputs, conversion processes, outputs, feedback and random fluctuations. It also distinguishes between manufacturing and service operations and explores different aspects of operations management like planning, organizing and controlling conversion processes.