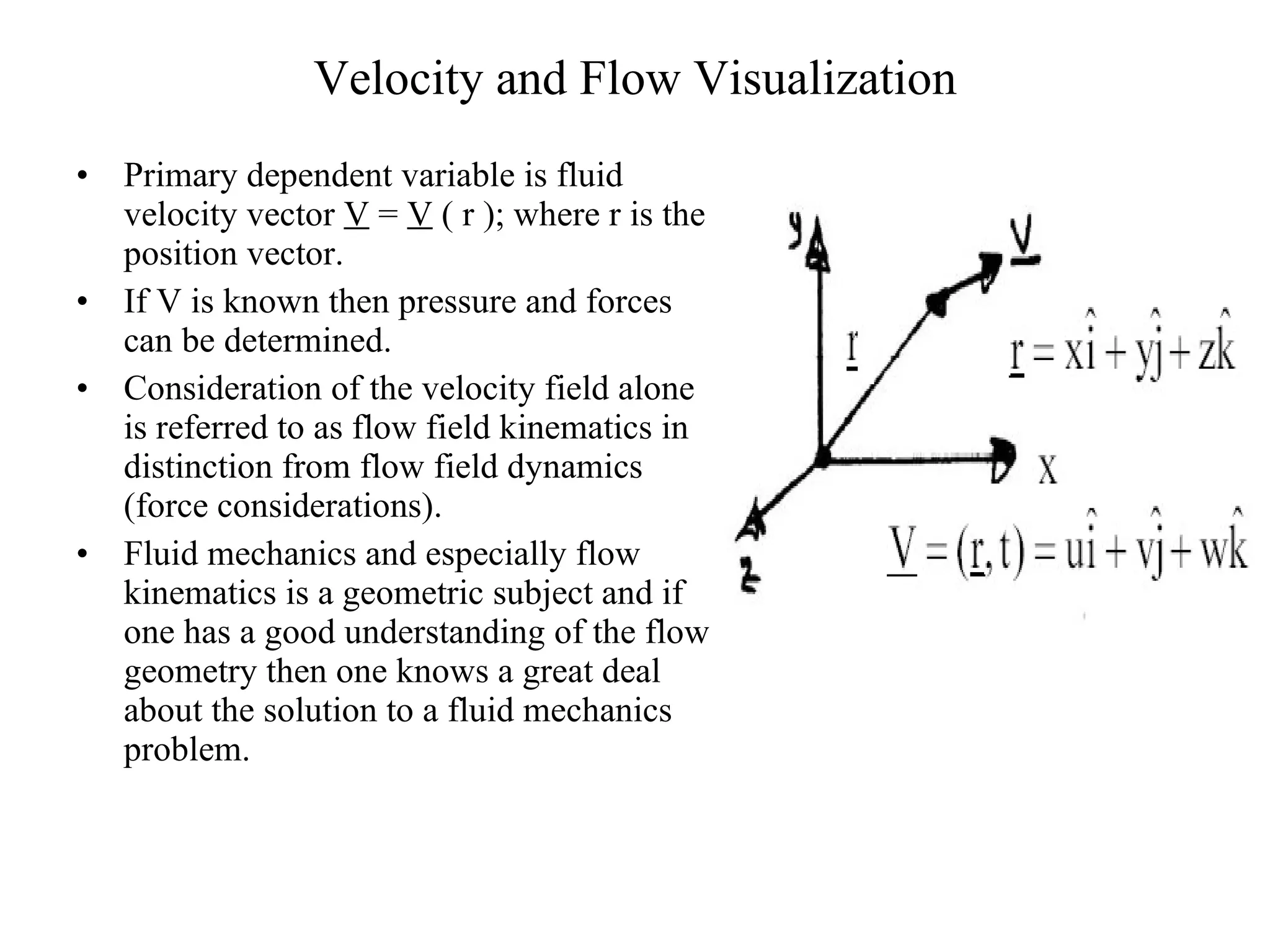
The document discusses fluid mechanics concepts relevant to power generation, including:
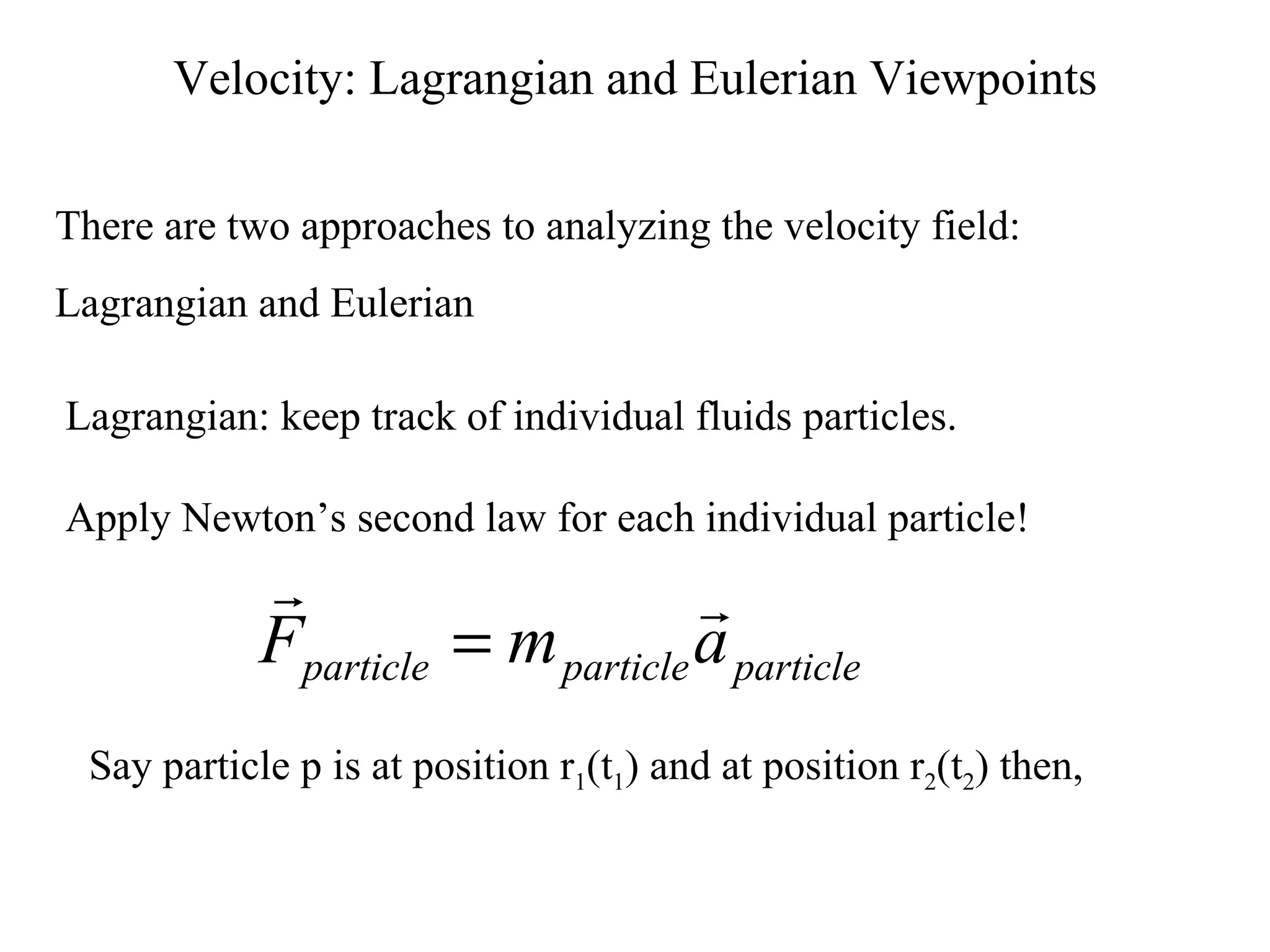
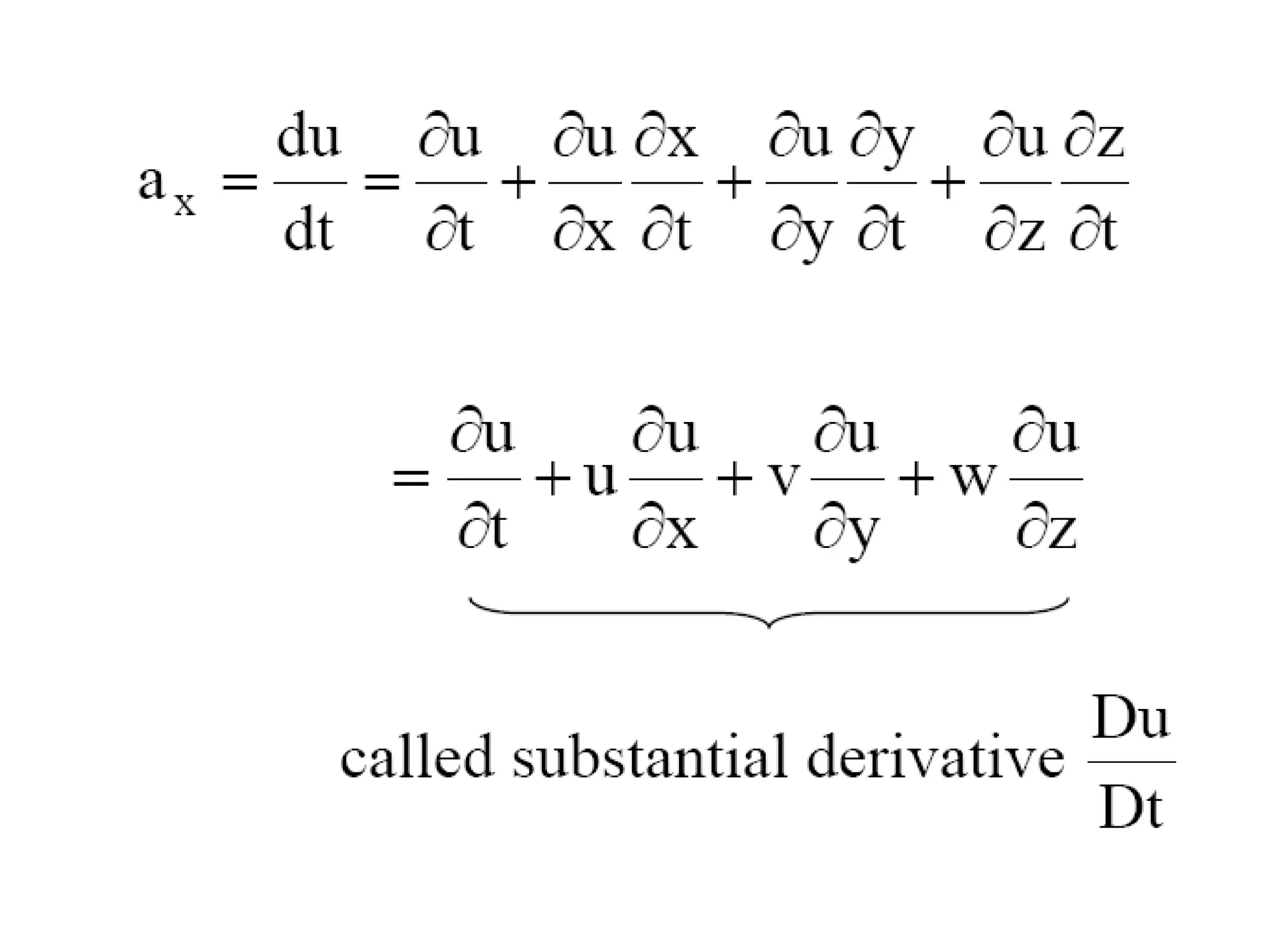
1. It describes Lagrangian and Eulerian approaches to analyzing velocity fields in fluids, with the Eulerian approach being more useful as it focuses on velocity at fixed points rather than tracking individual particles.
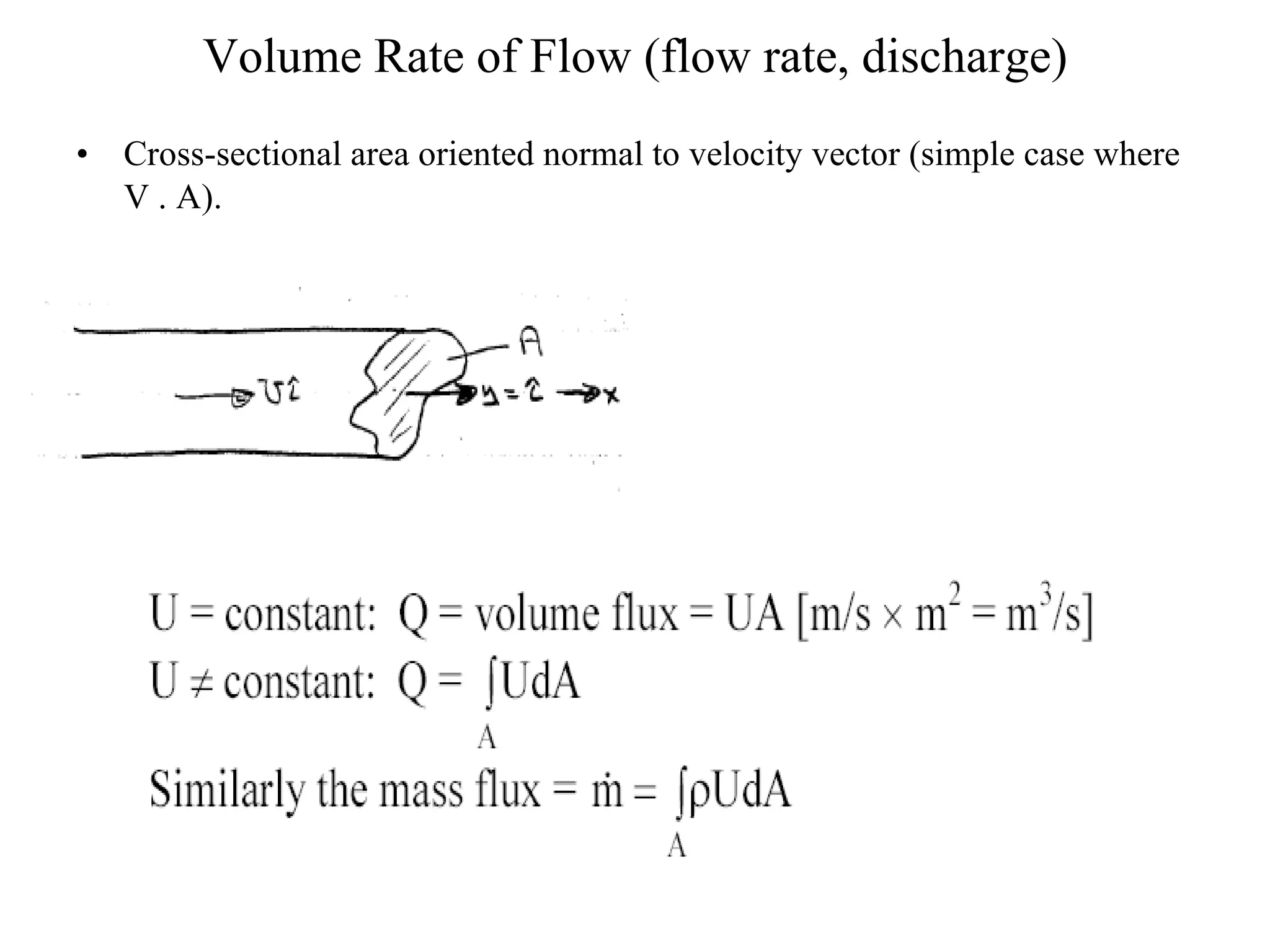
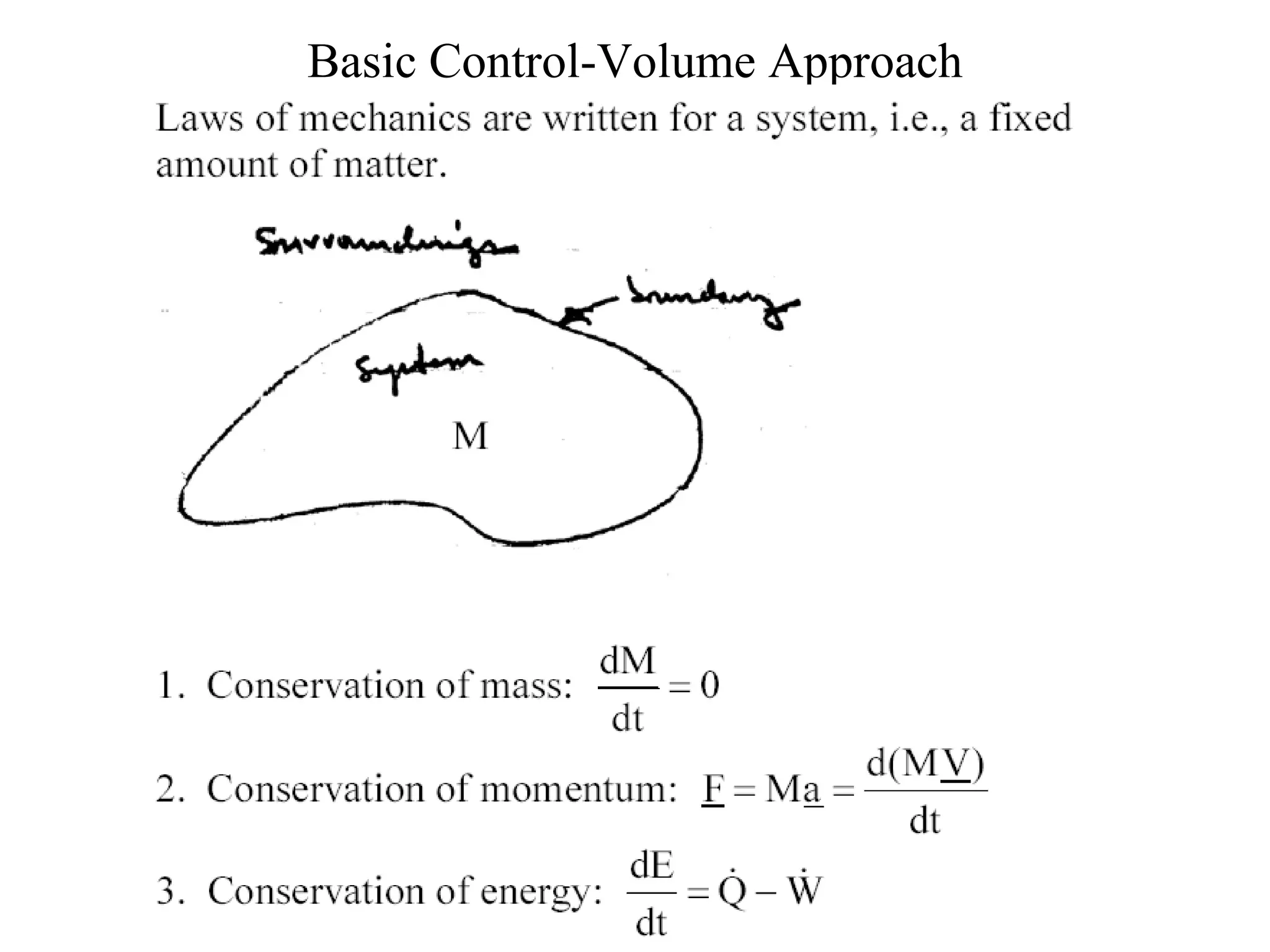
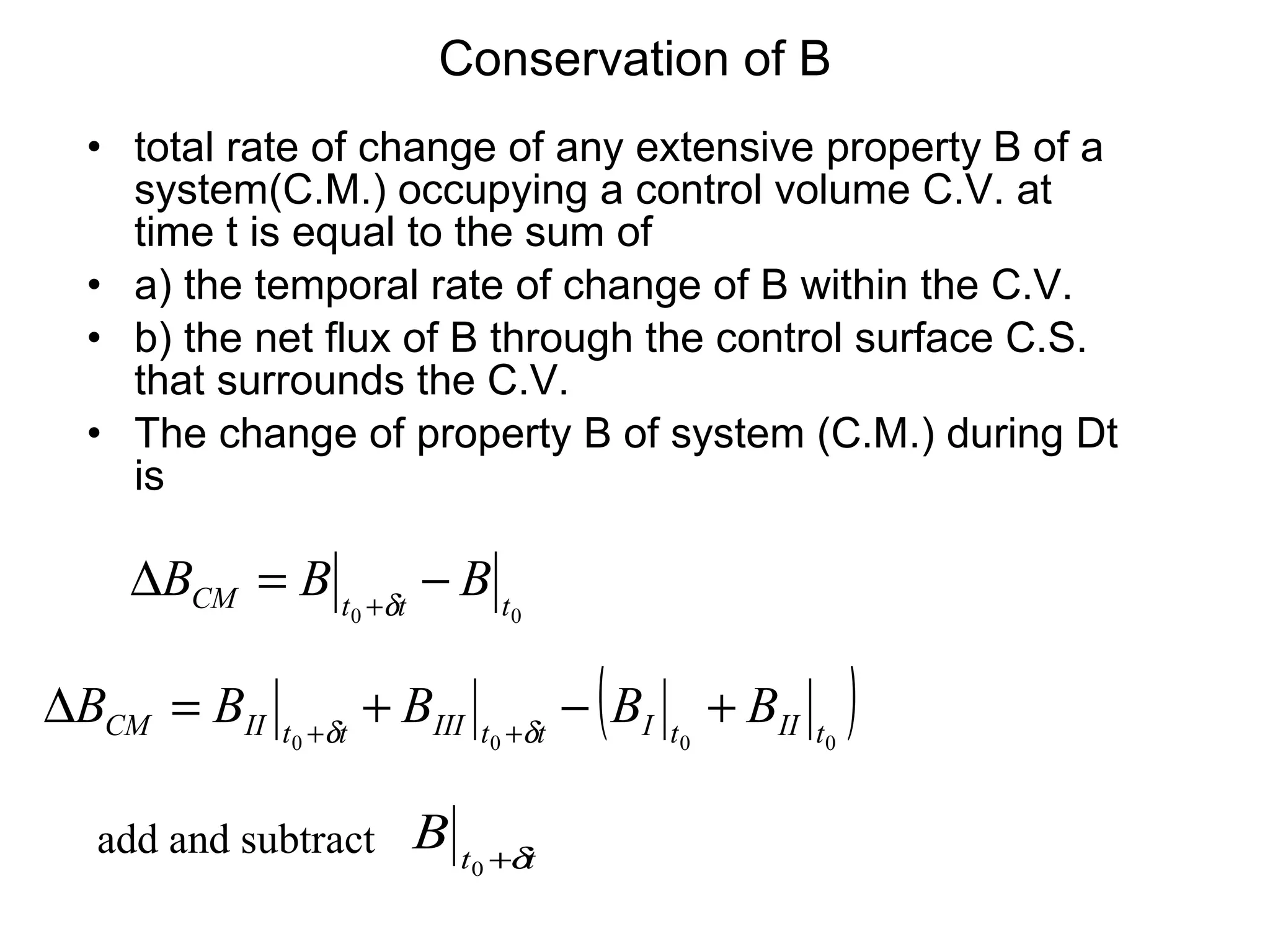
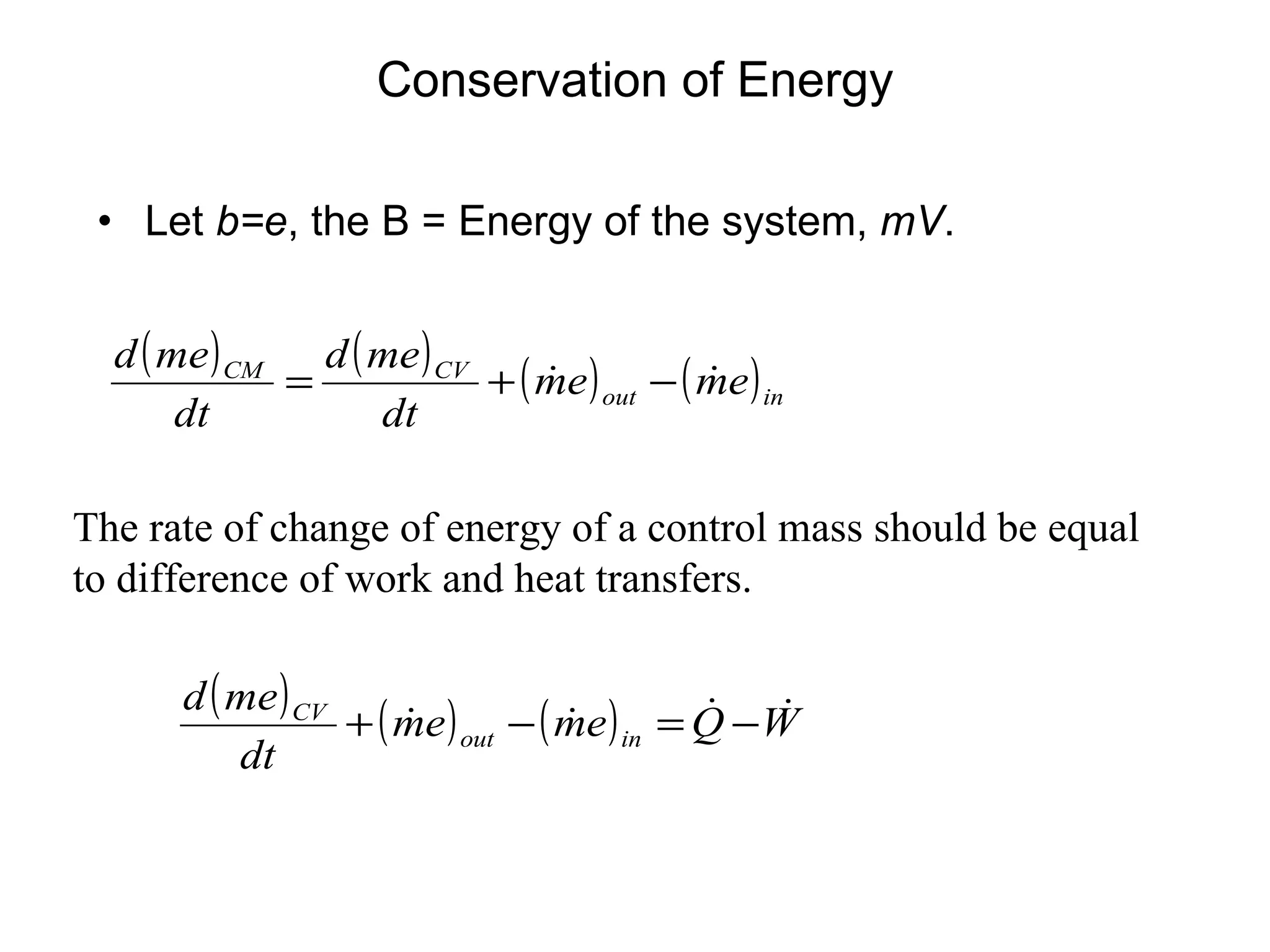
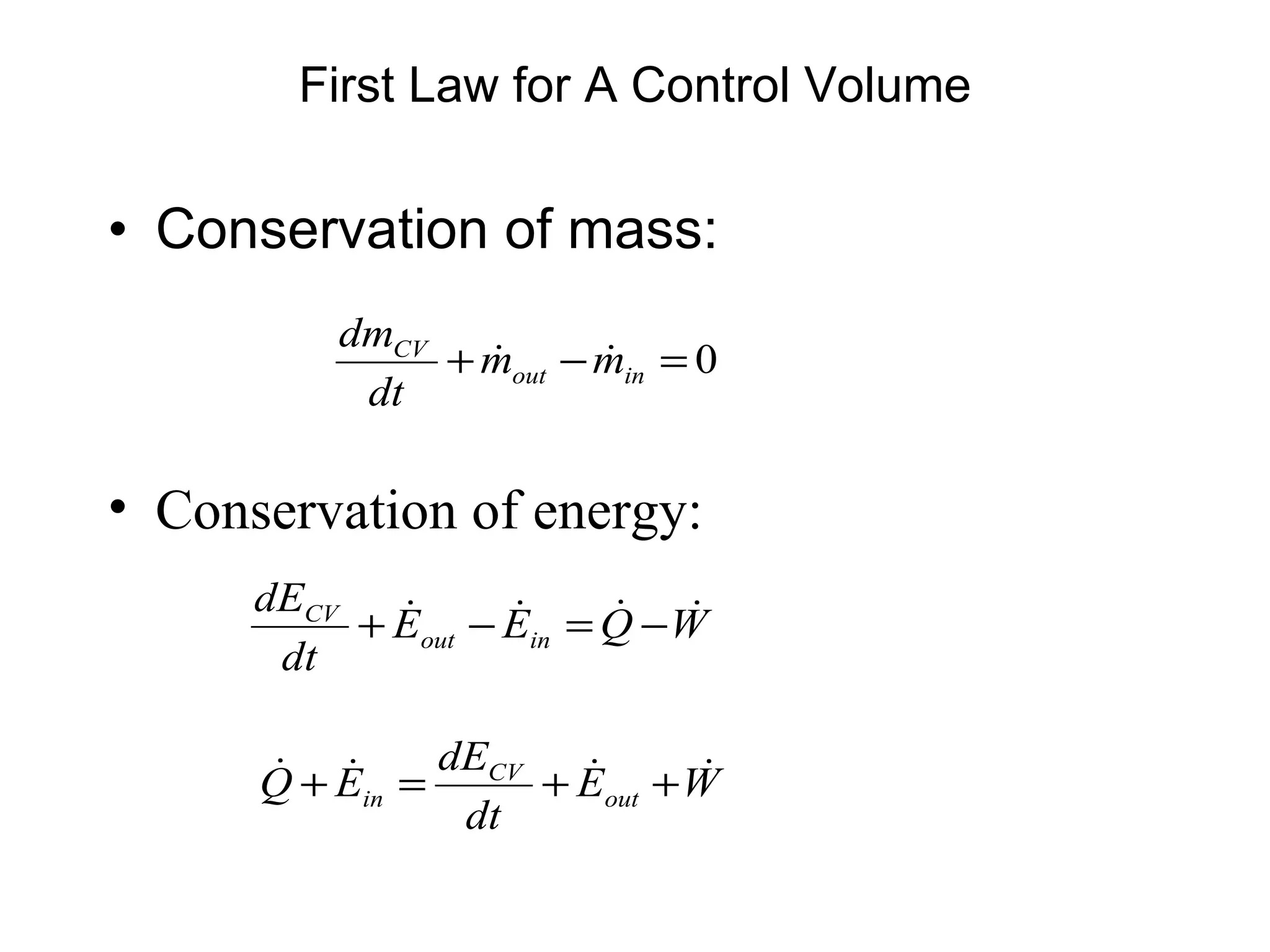
2. Conservation laws for mass, momentum and energy are presented using the control volume approach, with the Reynolds Transport Theorem relating changes in an extensive property within a control volume to flux of that property across its boundaries.
3. Complex flows encountered in power generation equipment are classified, with turbulent internal pipe flows and external flows around bodies requiring both viscous and inviscid analyses highlighted.