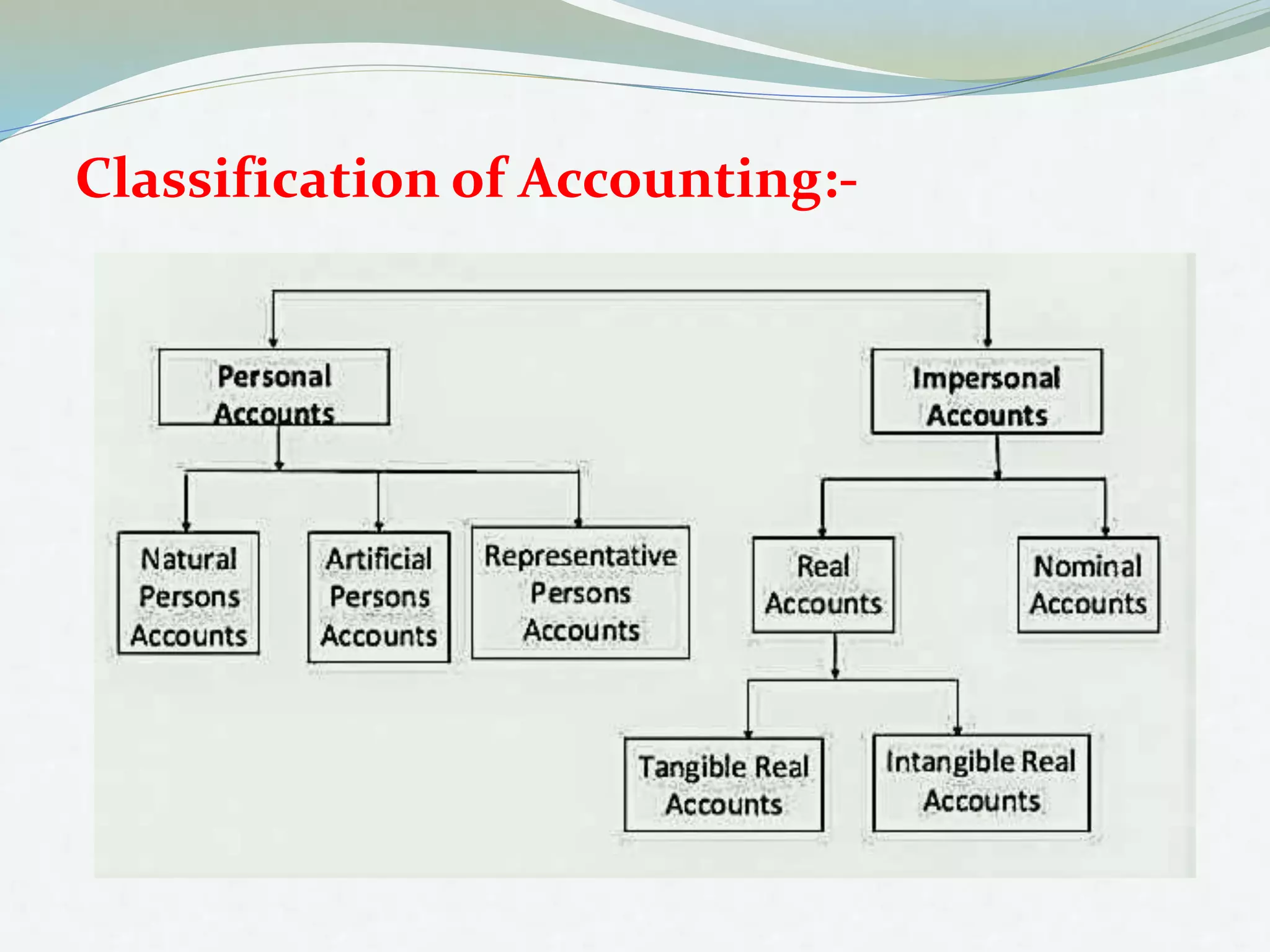
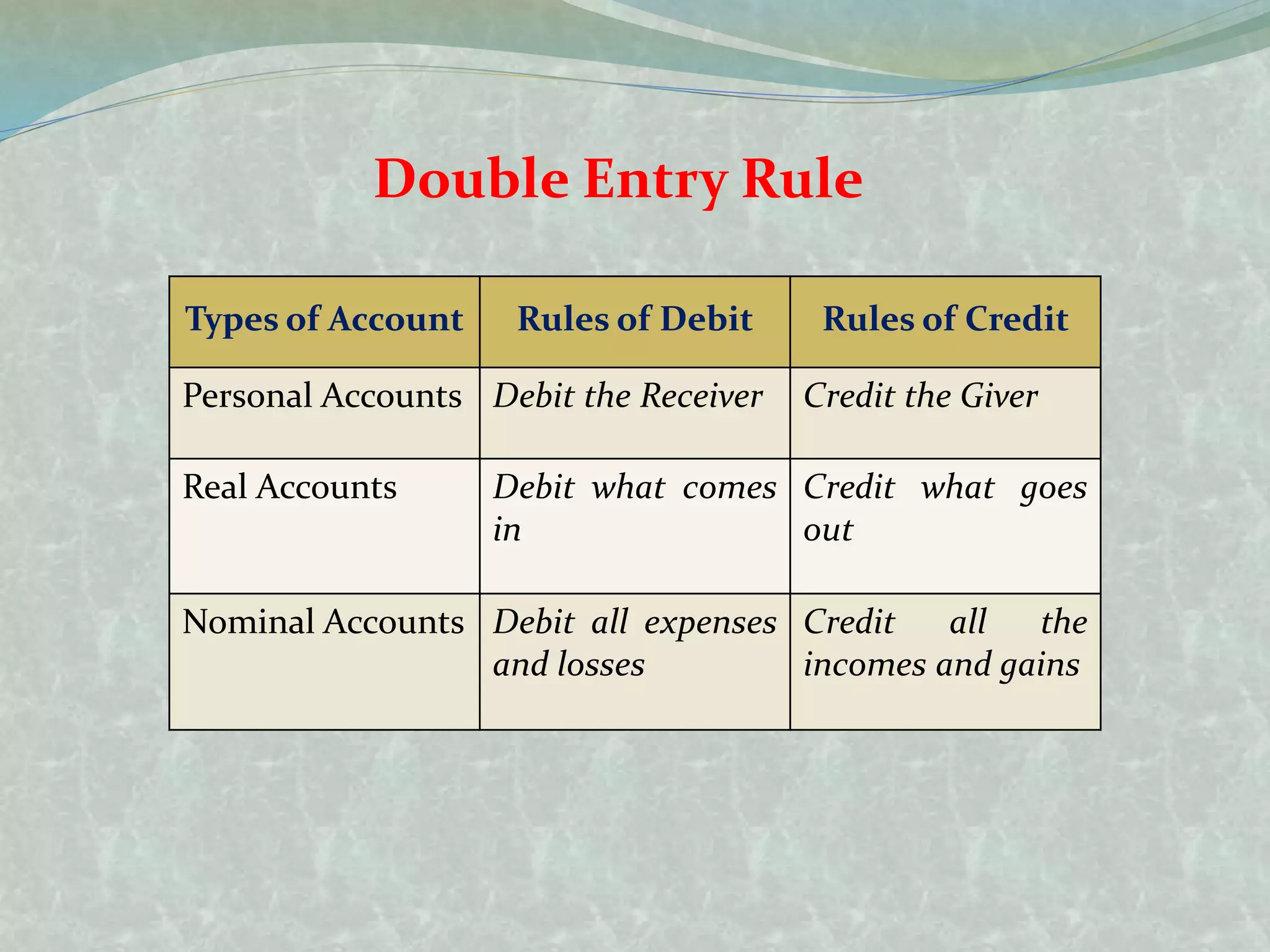
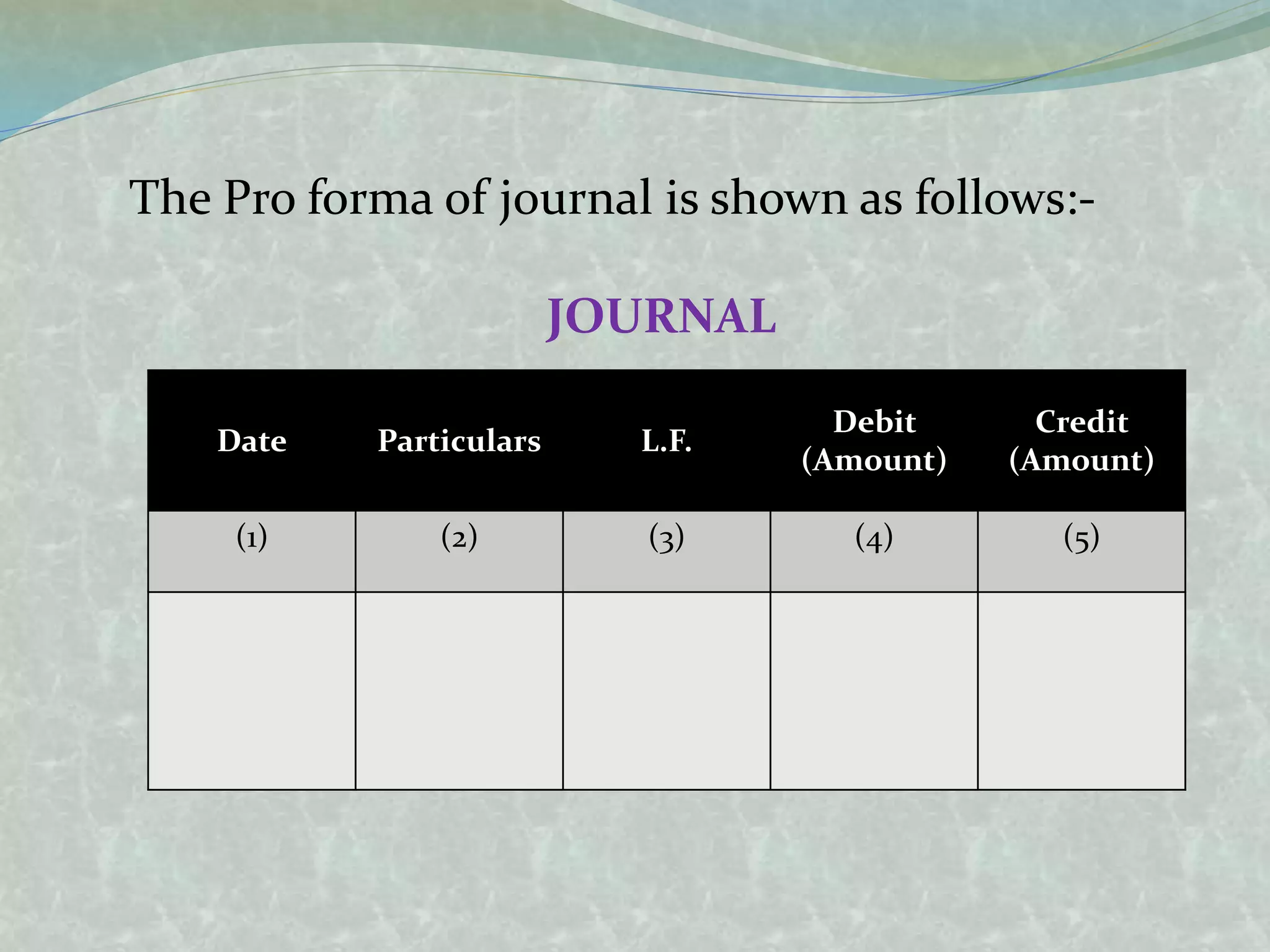
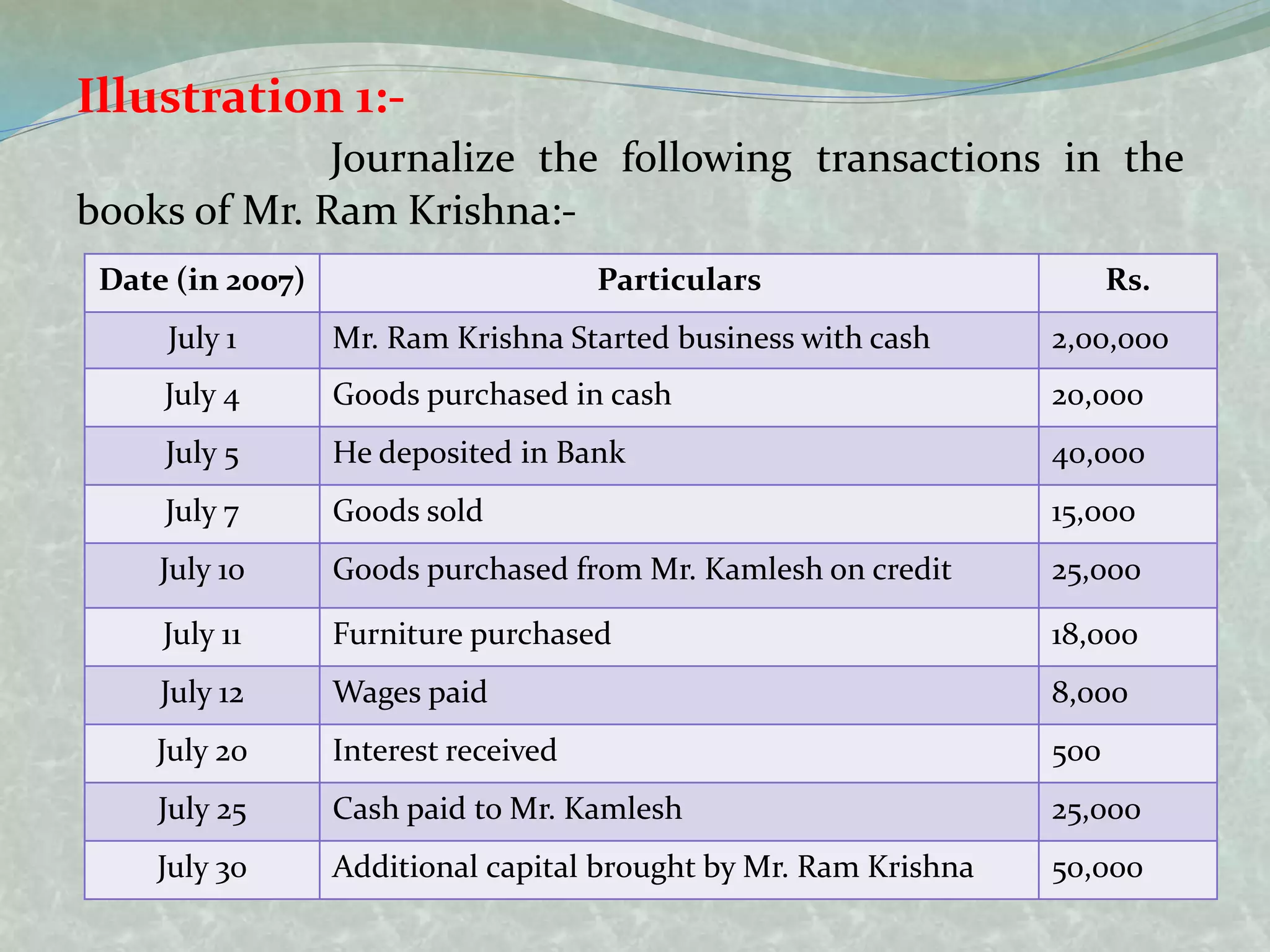
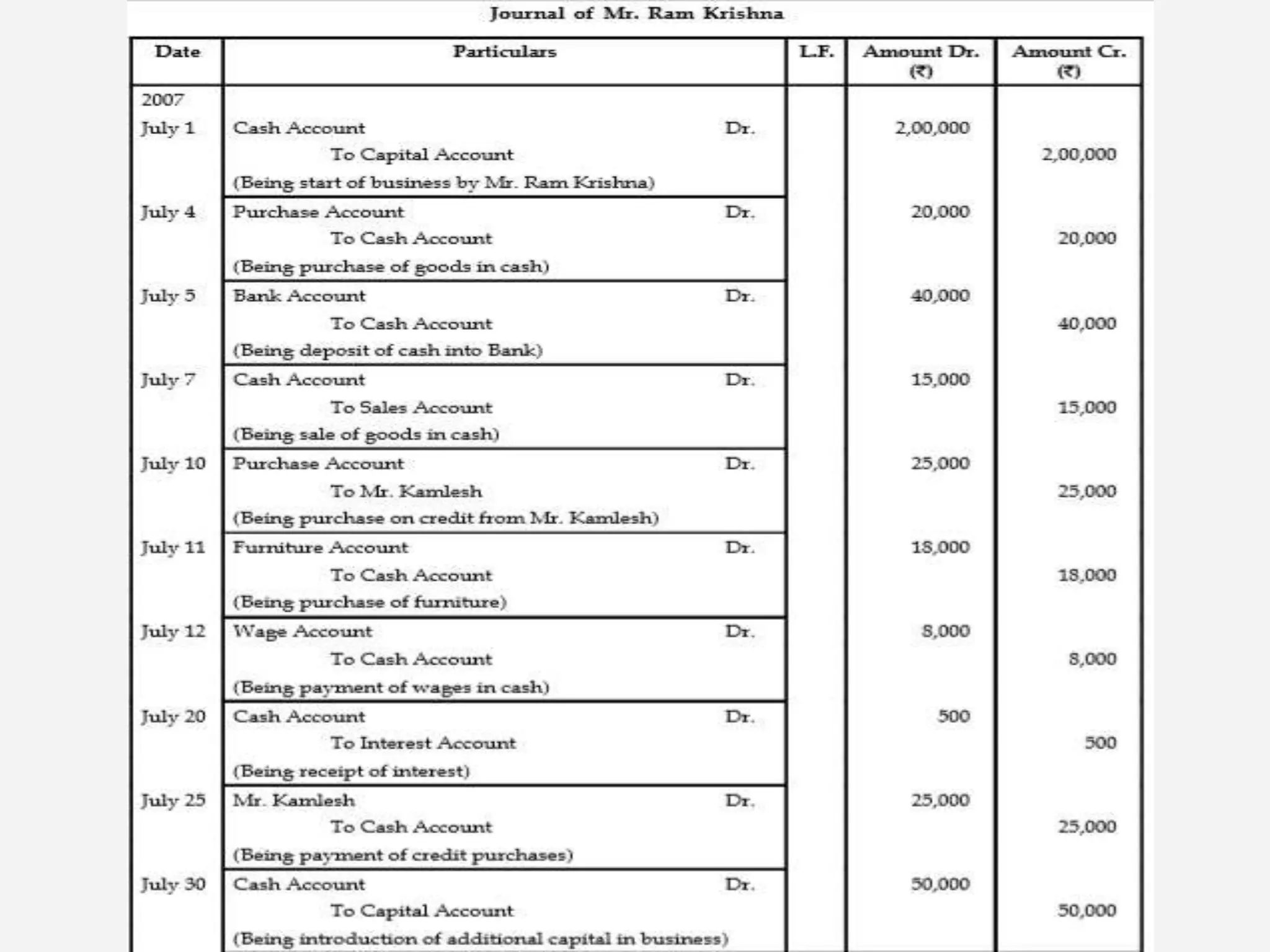
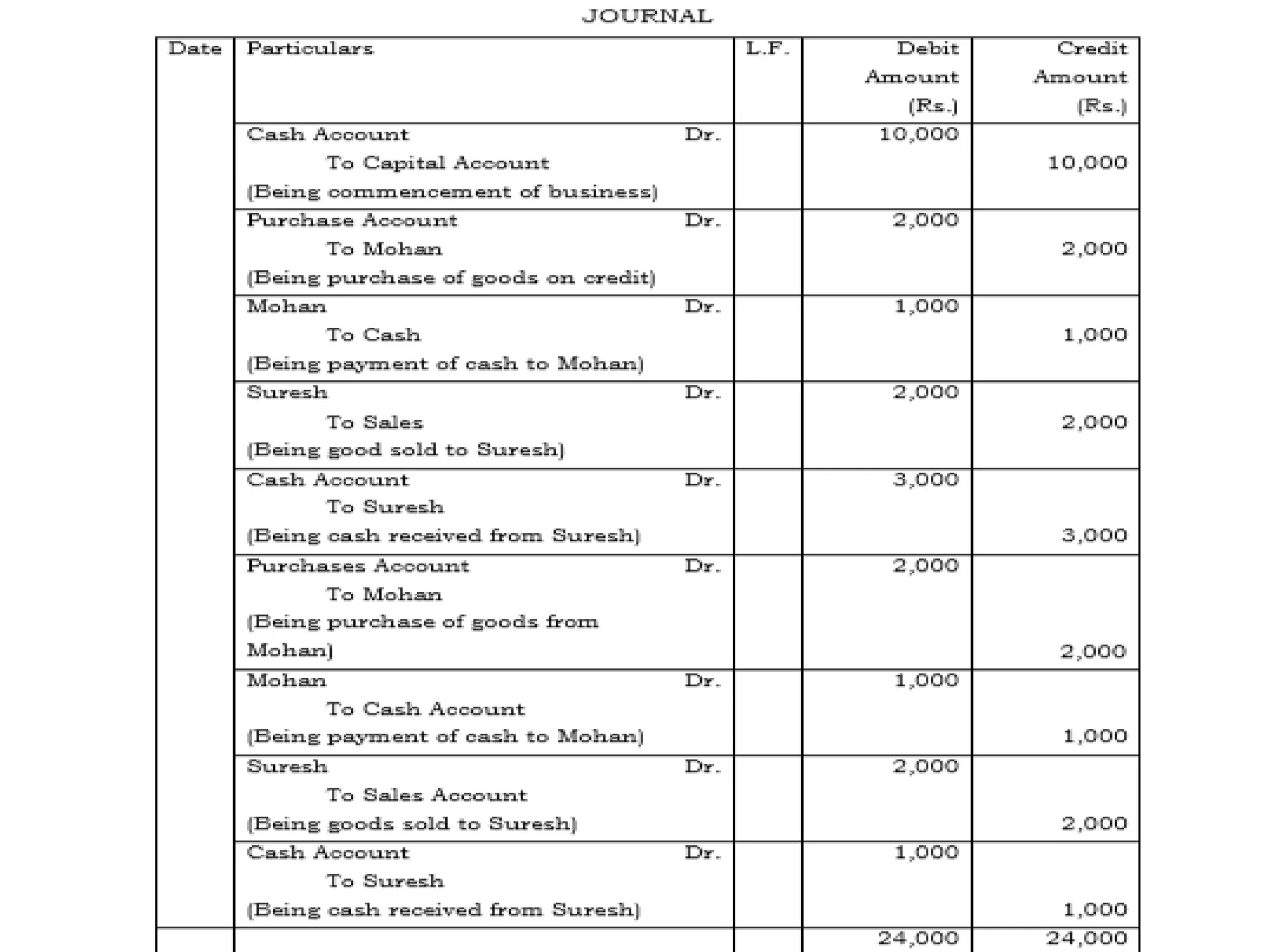
The document outlines the fundamentals of accounting, defining it as the language of business and a systematic process for recording and summarizing transactions. It covers key concepts such as the double entry rule, journal entries, and the steps involved in journalizing transactions. Additionally, it includes illustrations of journalizing various business transactions.