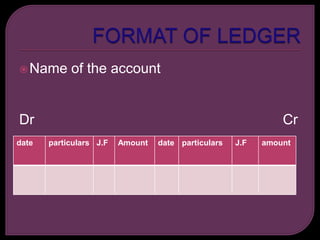
The ledger is the principal book of accounting that contains accounts where transactions are recorded. It collects all accounts from the journal and special journals. The ledger is useful for ascertaining the net result of transactions in an account on a given date. It organizes accounts by debit and credit sides, records journal folio references, and amounts. Ledger accounts are classified into five categories: assets, liabilities, capital, revenues/gains, and expenses/losses. Temporary accounts are closed at period end by transferring them to trading and profit and loss, while permanent accounts appear on the balance sheet.