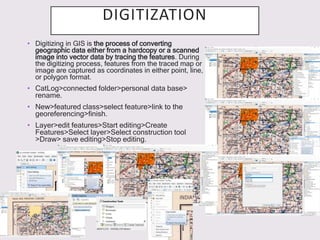
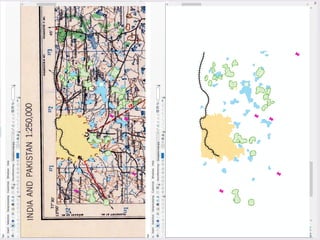
The document introduces Geographic Information Systems (GIS) and its applications in various fields such as urban planning, agriculture, disaster management, and telecommunications. It highlights the importance of GIS in architectural education and its role in analyzing spatial data for effective decision-making. Additionally, the document discusses the process of creating contour maps, georeferencing, and digitization in GIS.