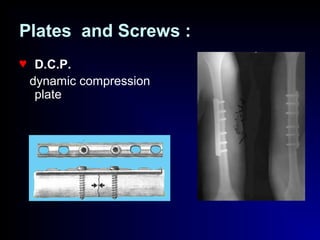
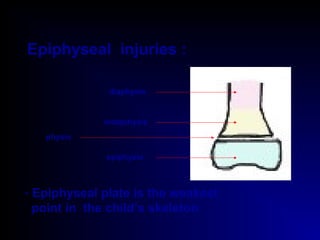
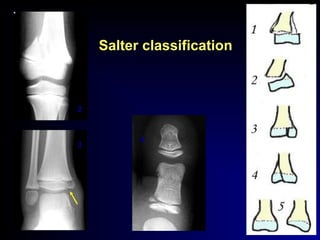
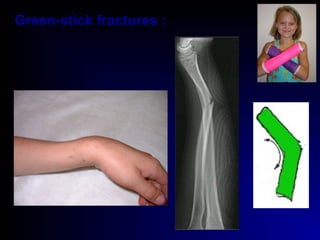
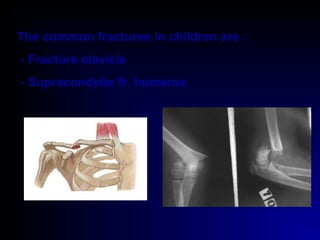
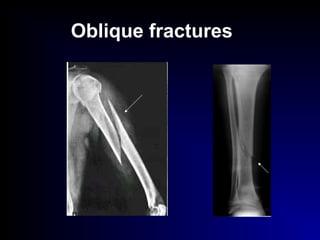
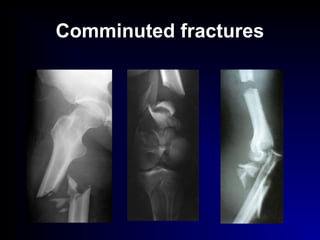
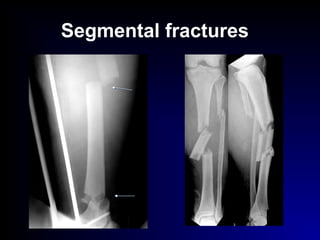
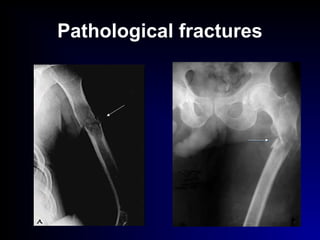
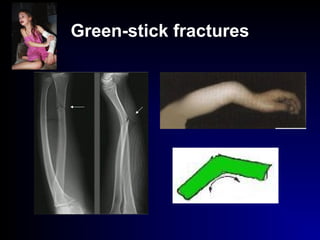
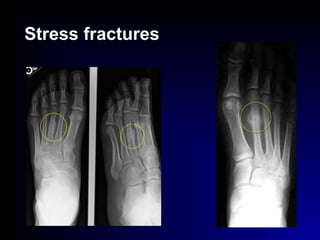
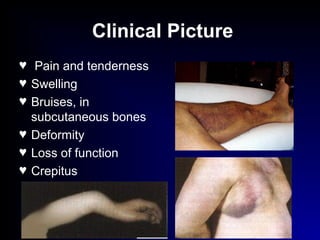
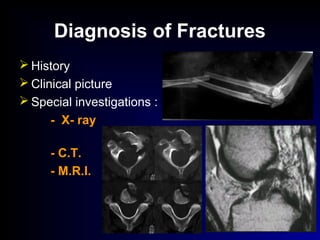
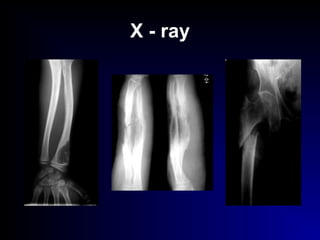
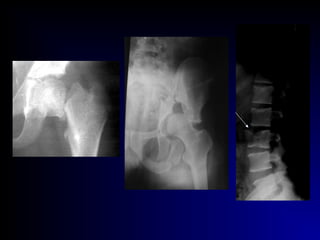
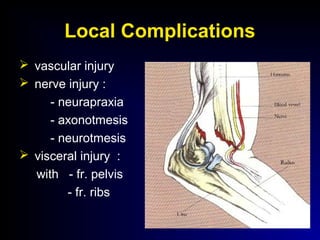
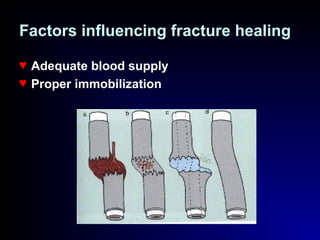
Fractures and joint injuries can range from simple closed fractures to more complex open or comminuted fractures. The aim of treatment is to save life and restore function. Diagnosis involves history, clinical exam, and imaging like x-rays. Treatment depends on the fracture type but generally involves closed or open reduction and fixation using conservative splinting or surgical methods like plates/screws. Factors like adequate blood supply and immobilization influence healing. Children's fractures have special considerations due to the physis.














![ complications of union :
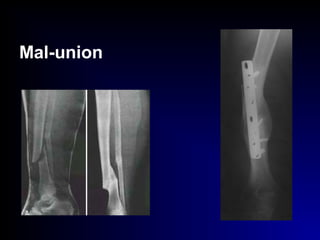
• Mal-union:
[angulation, shortening, rotation]
ttt. : corrective osteotomy + I.F.
• Delayed union
ttt. : further immobilization, then B.G.
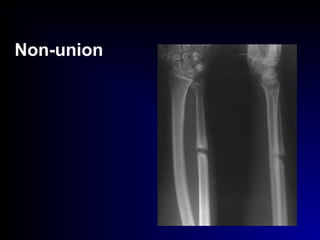
• Non-union :(pseudo-arthrosis)
ttt. : I.F. + B.G.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1-fractures-160410123753/85/Introduction-to-Fractures-27-320.jpg)
![Healing of Fractures
Fr. hematoma, invaded by fibroblasts and
osteoblasts from surrounding tissues and
periostium, forms soft woven bone [ callus],
precipitation of calcium salts enhances the
formation of hard lamellae of trabecular
bone.
Remodeling restores the
original contour .](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1-fractures-160410123753/85/Introduction-to-Fractures-30-320.jpg)

![Fixation of Fractures
♥ Conservative fixation [ Splintage ] :
- plaster
- traction
♥ Surgical fixation :
A - internal
B - external](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1-fractures-160410123753/85/Introduction-to-Fractures-34-320.jpg)
![Conservative Fixation ( Splintage)
♥ Plaster casts :
stable fr. in distal parts of the
limbs .
♥ Skin traction : [ Thomas splint ]
in fr. femur in children
and as a first aid in adults .
♥ Skeletal traction](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1-fractures-160410123753/85/Introduction-to-Fractures-35-320.jpg)