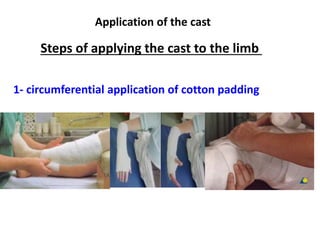
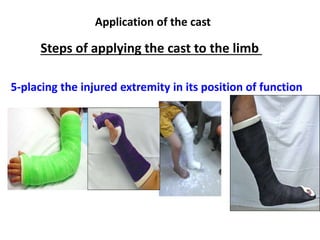
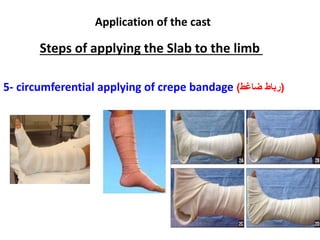
This document discusses casts and slabs for immobilizing musculoskeletal injuries. Casts fully surround the limb while slabs only partially surround. Casts provide better immobilization but have higher risks of complications like pressure sores. The document outlines indications, advantages, disadvantages and application steps for casts and slabs. It emphasizes the importance of monitoring for complications, starting physiotherapy early, and removing the cast or slab as soon as possible.