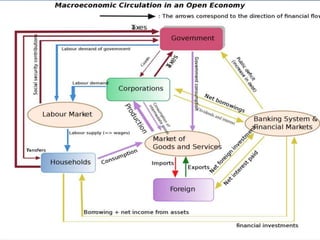
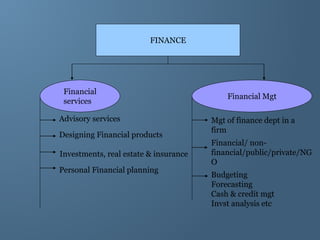
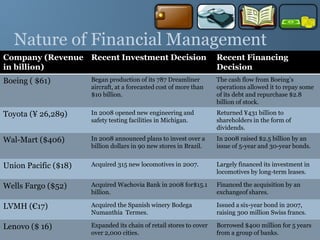
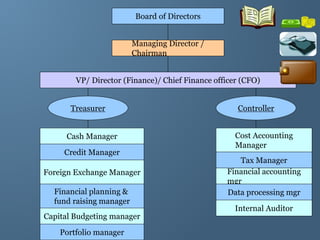
The document provides a comprehensive overview of financial management, outlining its definition, processes, objectives, and the roles of financial managers. It emphasizes the importance of managing funds efficiently to maximize profits while balancing risk and costs, and discusses various financial decisions including investments, financing, and dividend policies. Additionally, it highlights the evolving challenges faced by financial managers in a dynamic economic environment.