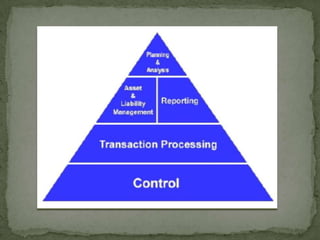
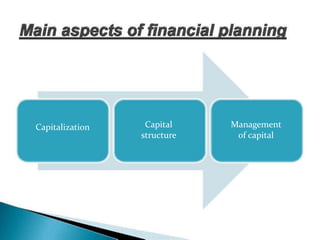
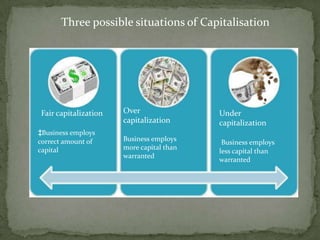
Financial management involves planning, acquiring, and managing assets to achieve business goals. It entails decisions around long-term investments, working capital, and financing assets. Financial management also aims to generate profits to finance growth while ensuring safety of funds. It encompasses functions like planning, reporting, processing transactions, and control.