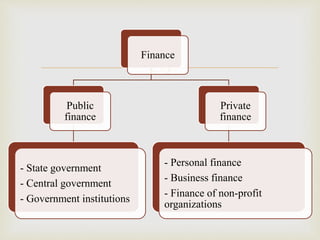
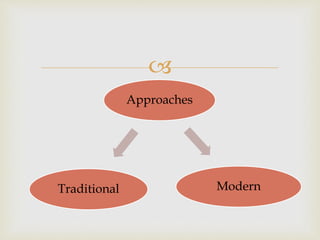
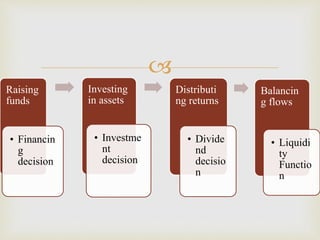
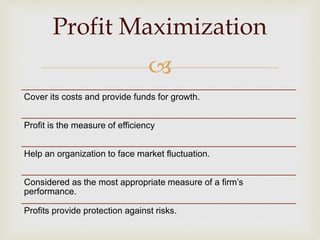
This document discusses the concepts of finance, financial management, and the objectives of financial management. It provides an overview of the evolution of financial management from traditional to modern approaches. The key functions of financial management - investment, financing, dividend and liquidity decisions - are explained. Both profit maximization and wealth maximization are discussed as objectives of financial management, along with their respective advantages and disadvantages.