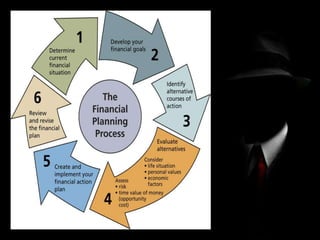
Financial planning and forecasting involves determining capital requirements, framing financial policies, and assessing future financial performance. Financial planning is the process of estimating needed capital and determining sources, while financial forecasting extends planning by making inferences about future sales, expenses, cash flows, and financial positions. Forecasting techniques include regression analysis of historical relationships, creating pro forma financial statements using past ratios or estimated expenses, and functional budgeting through cash, sales, and operational budgets.