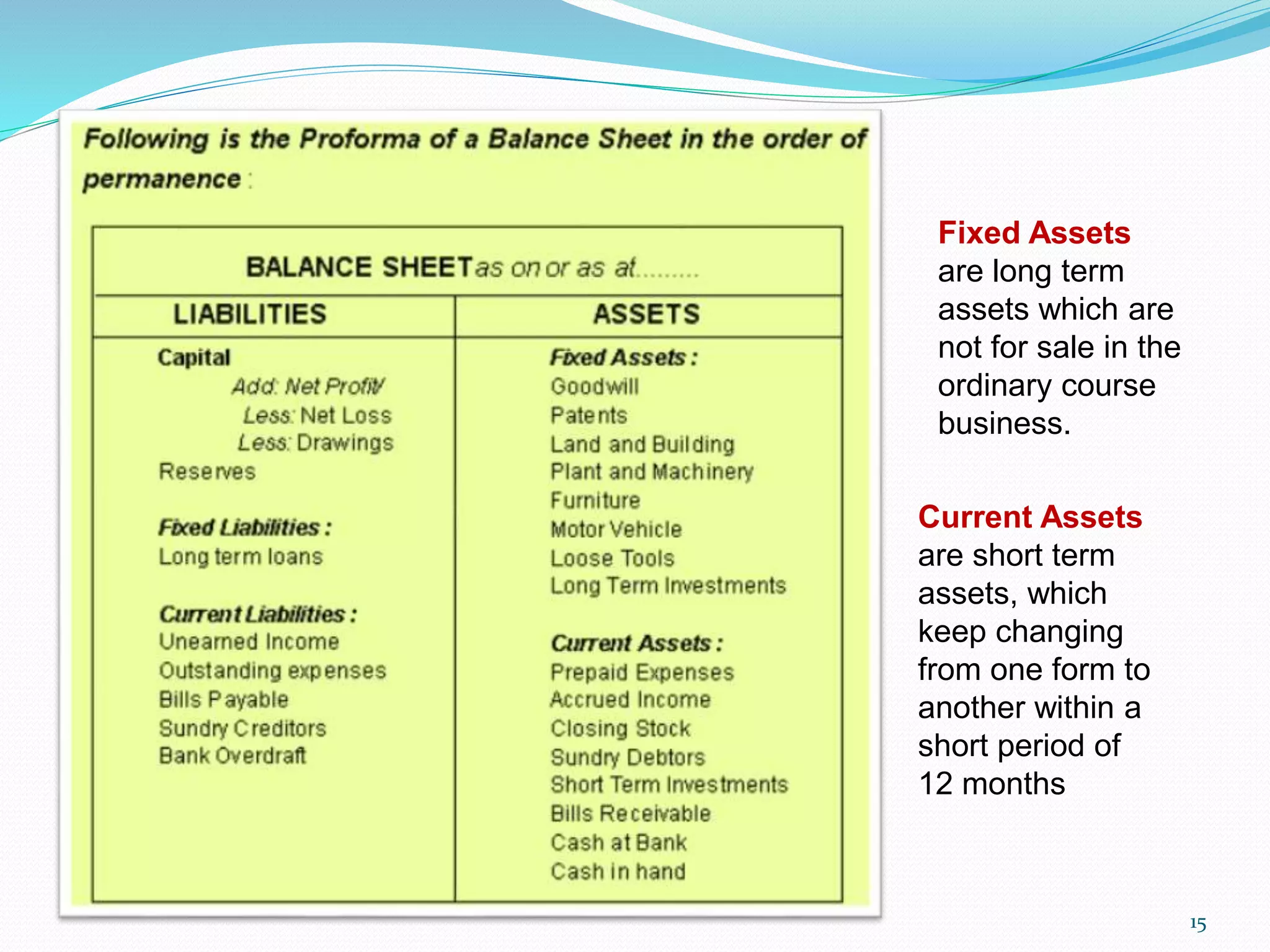
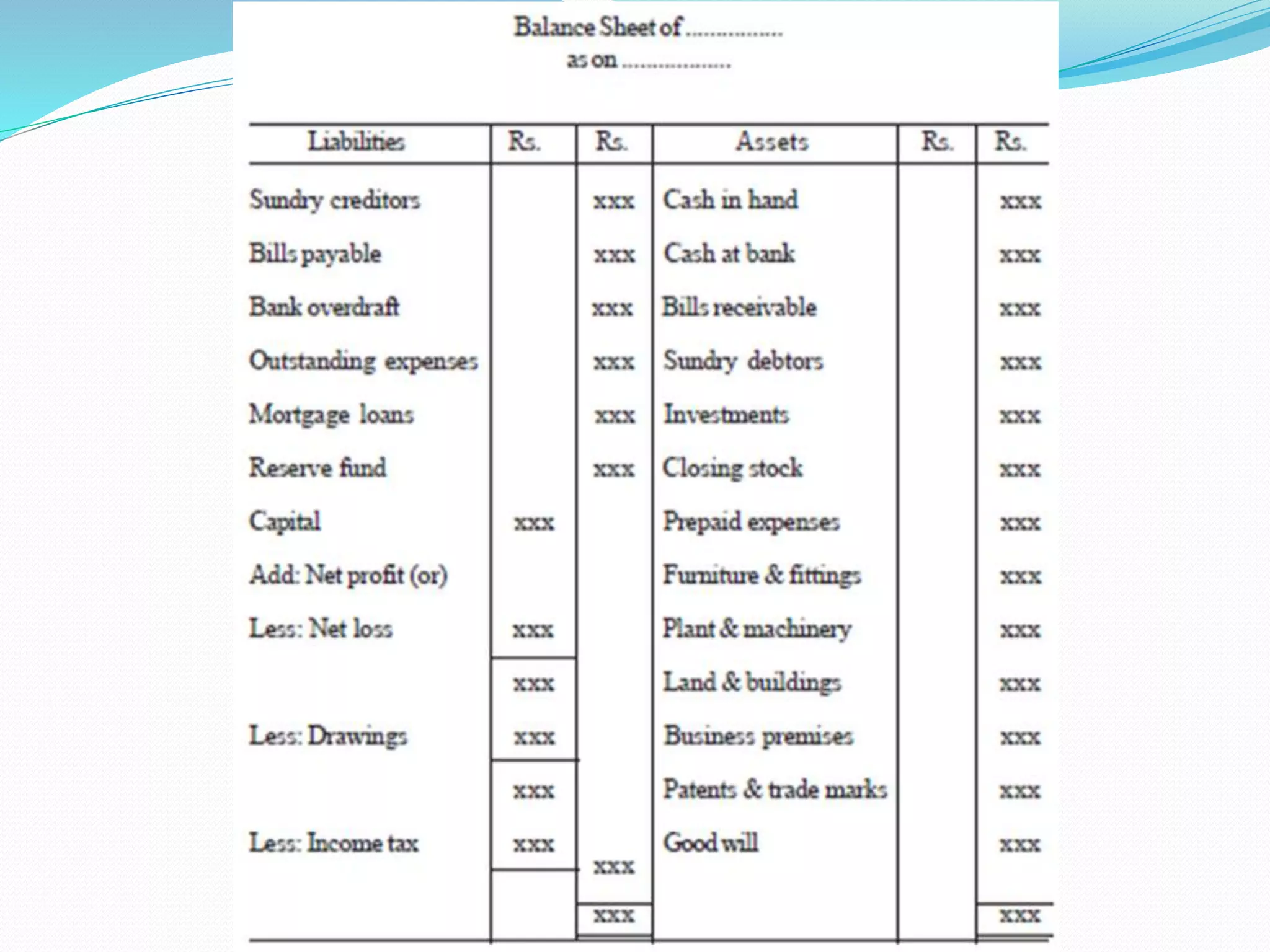
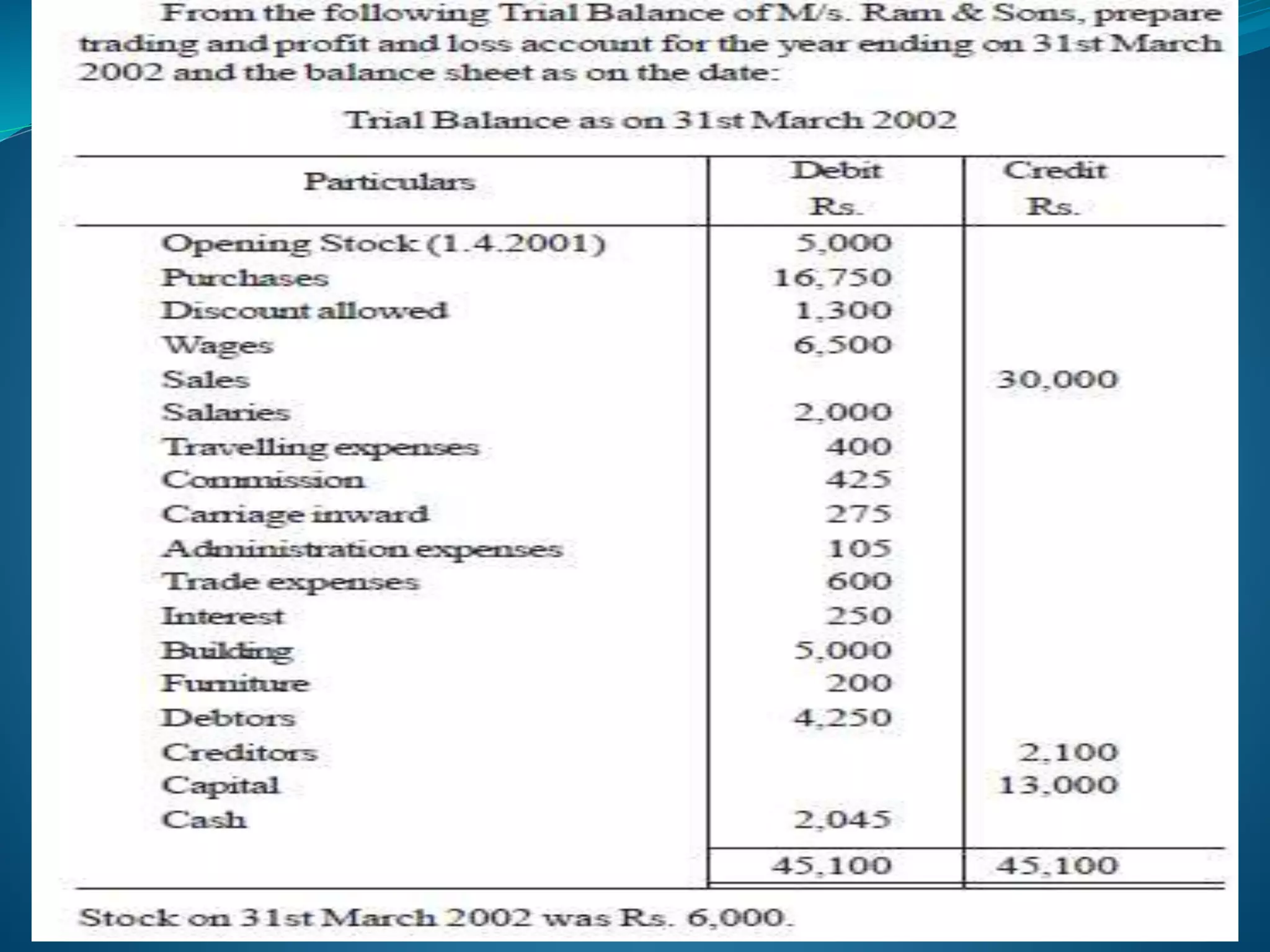
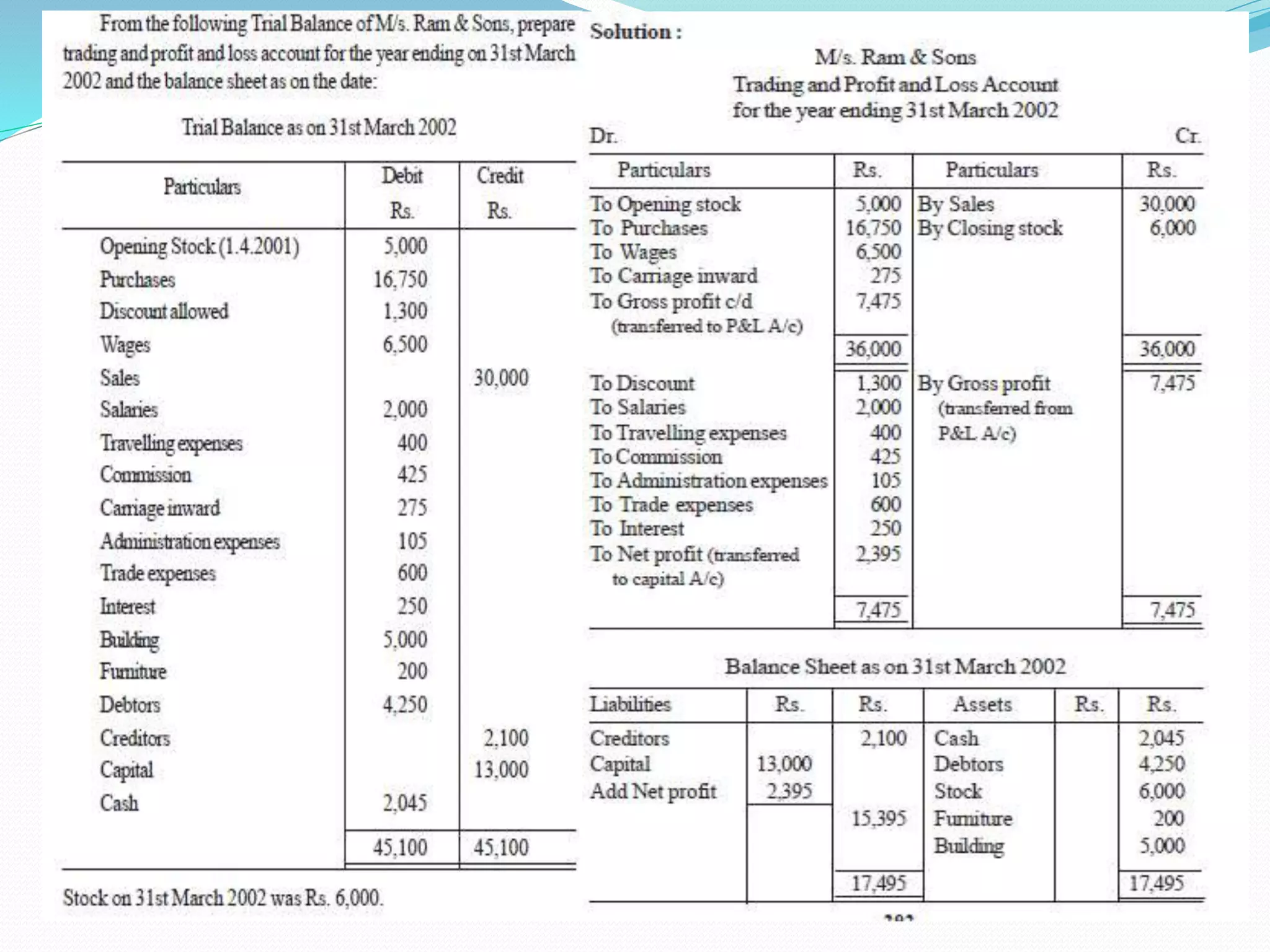
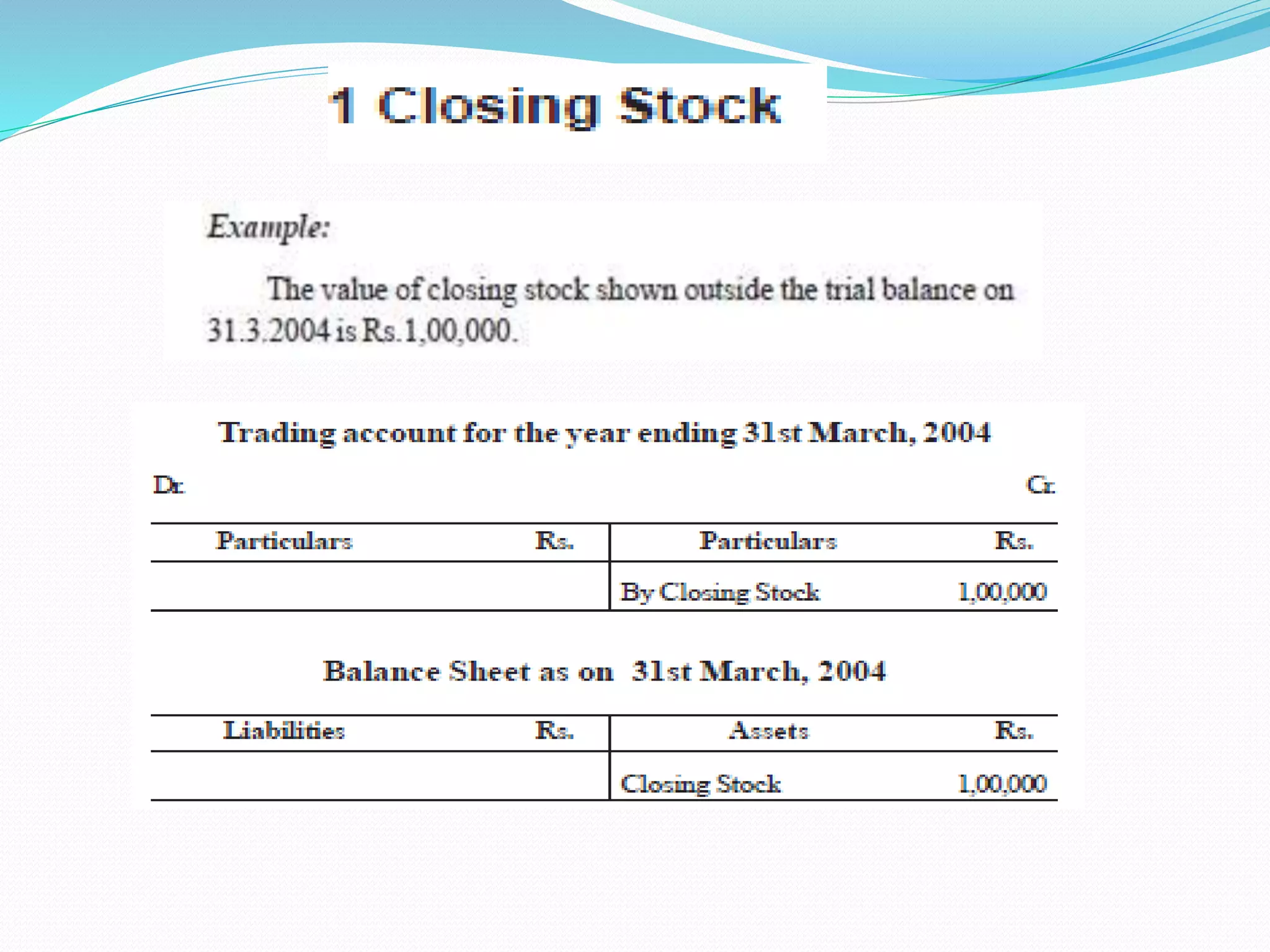
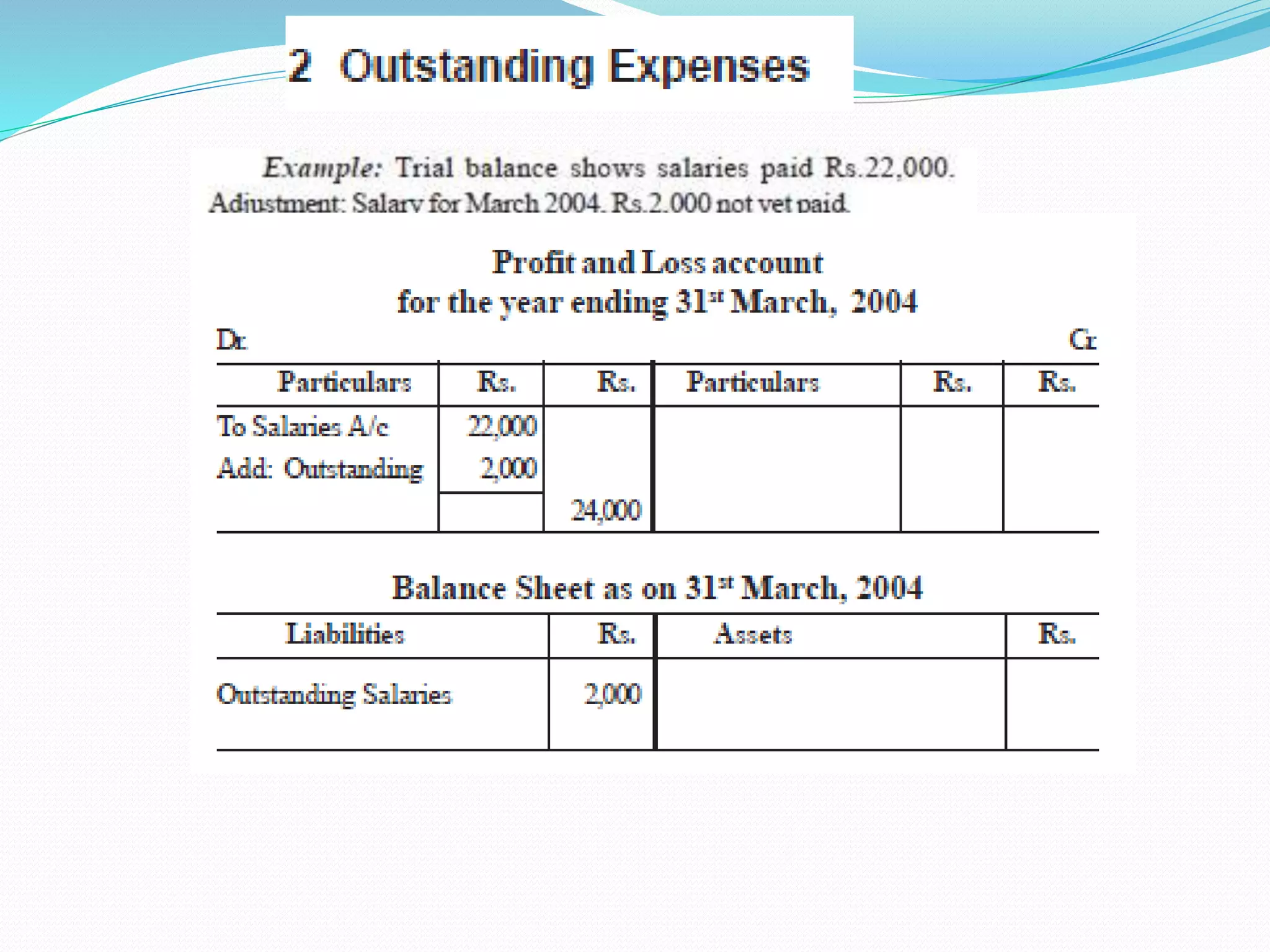
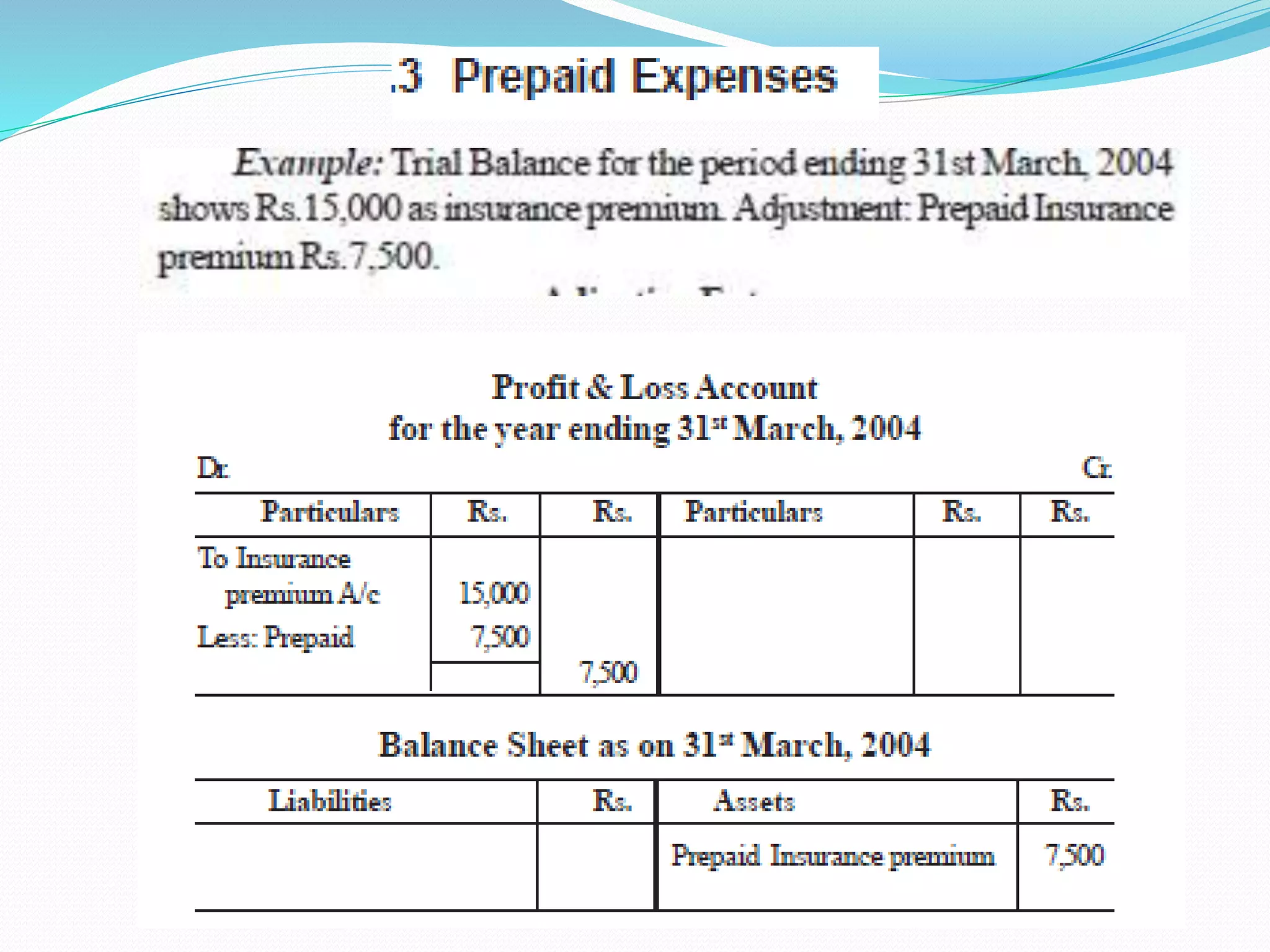
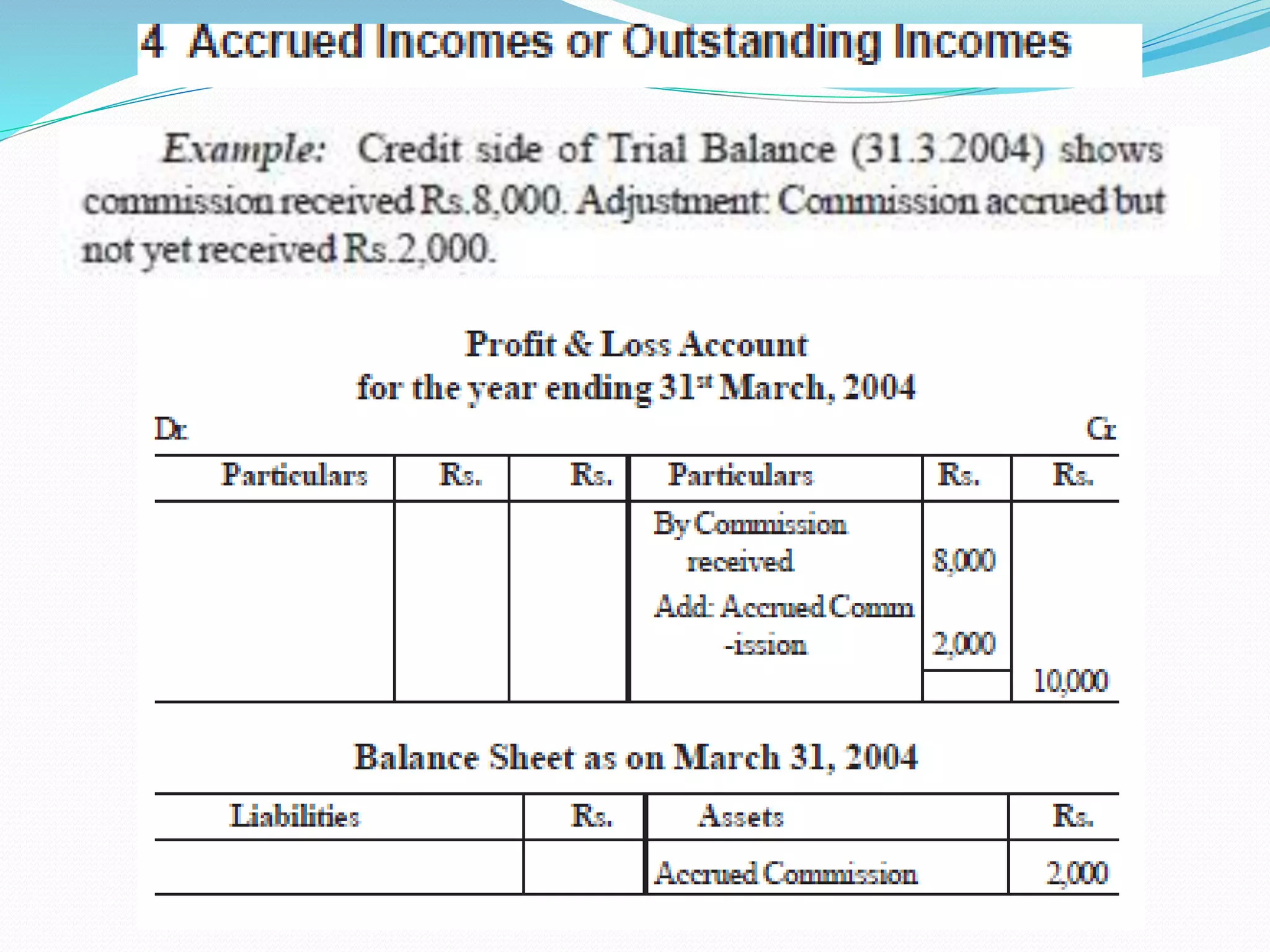
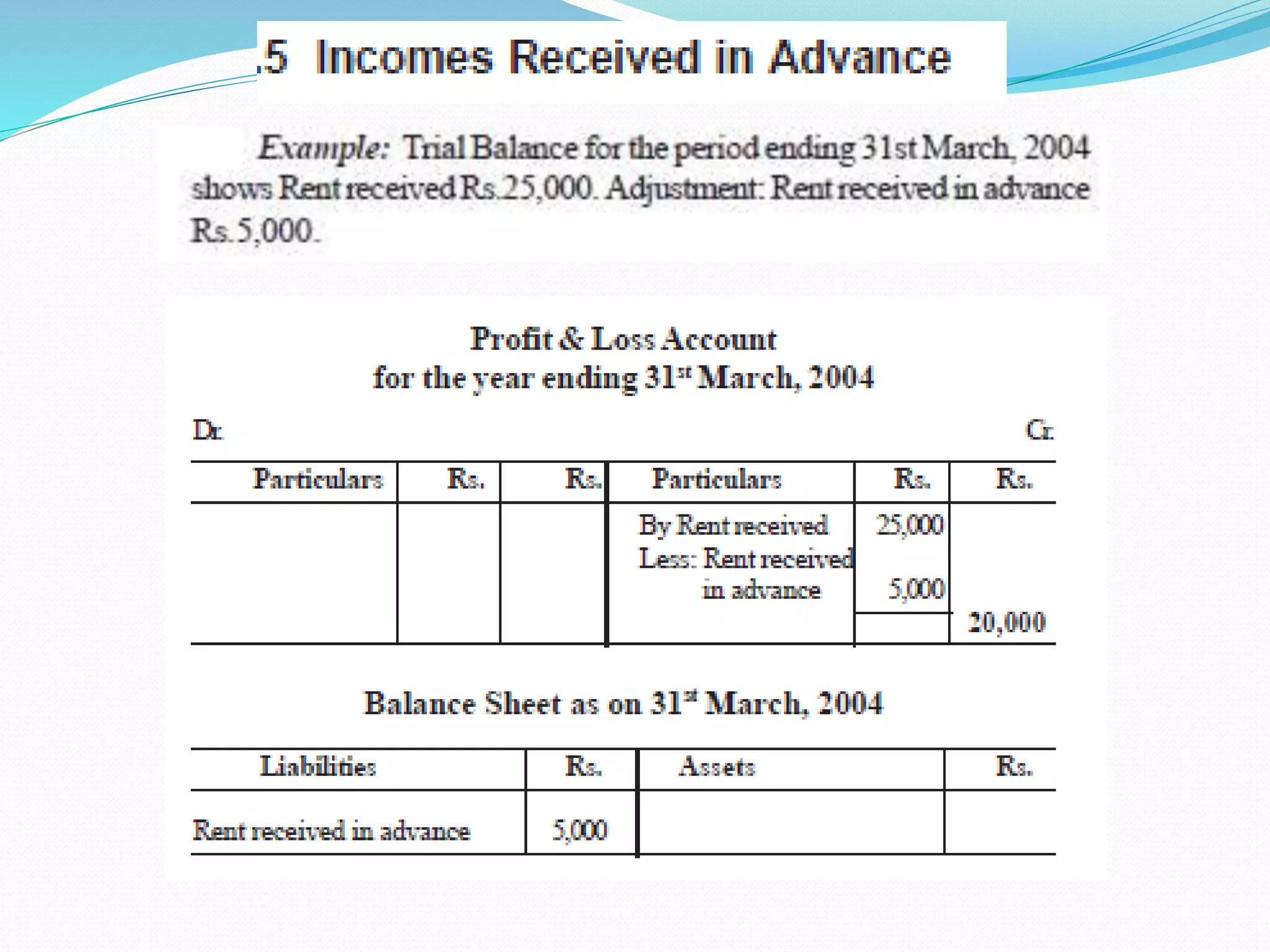
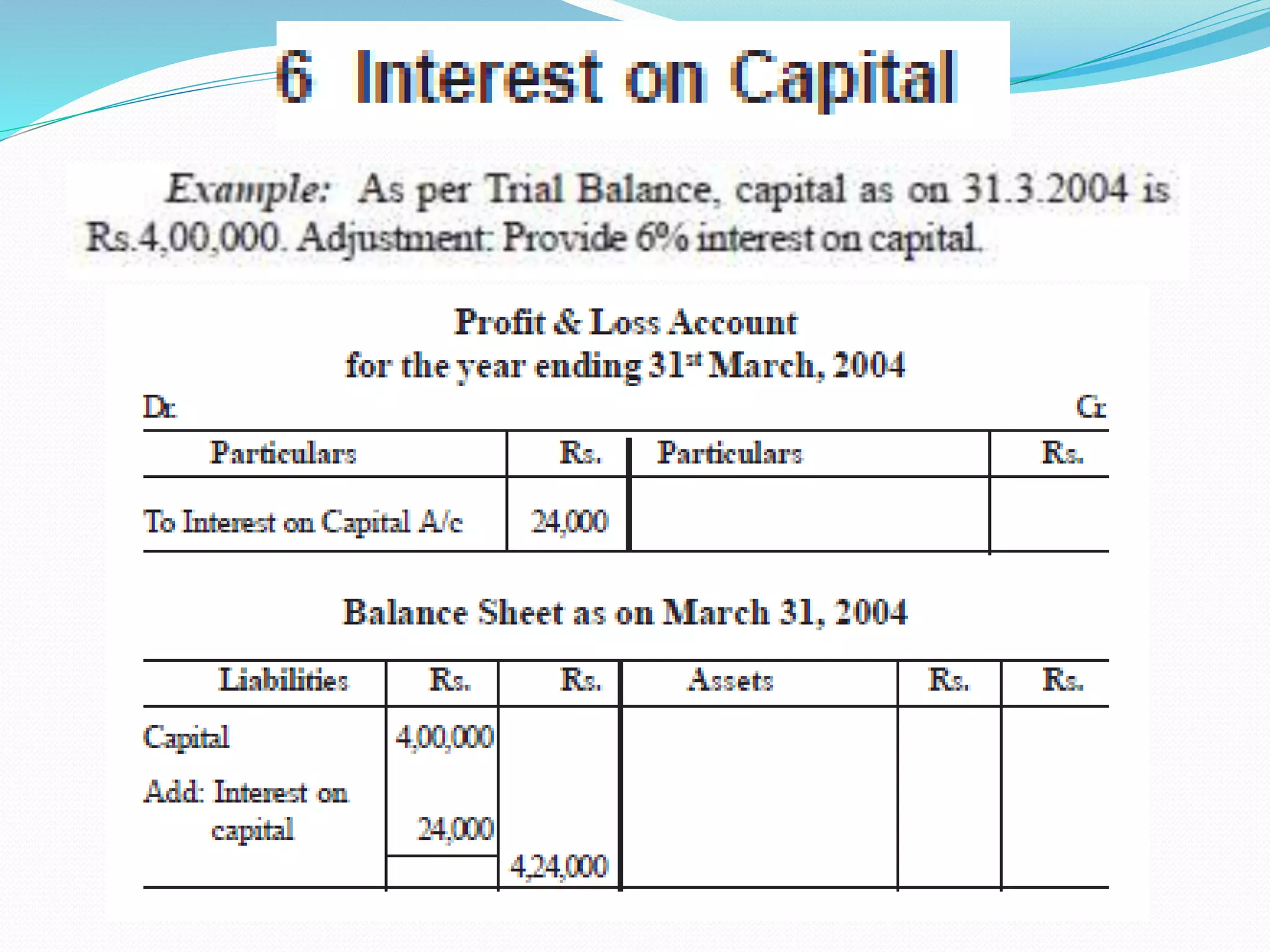
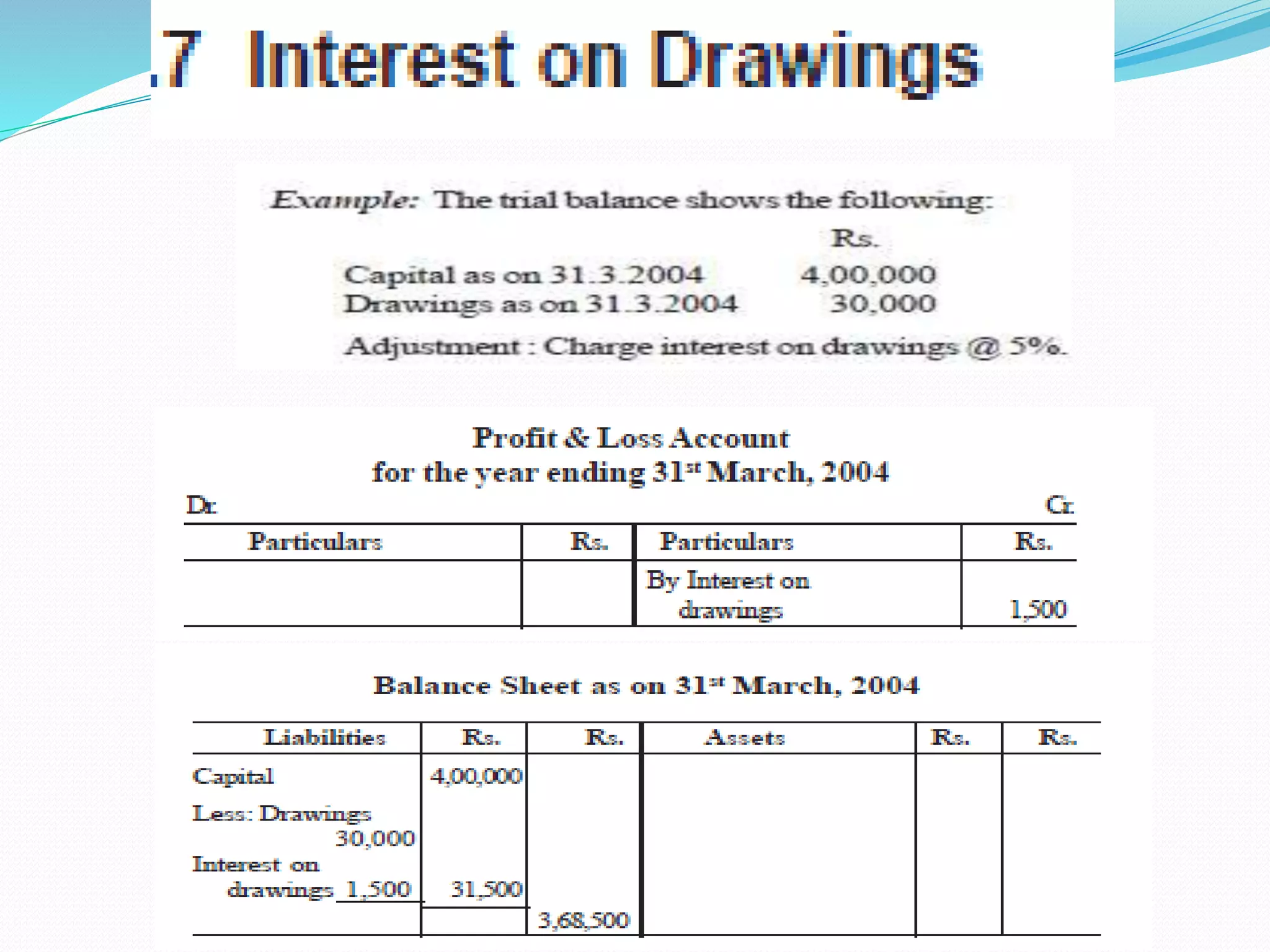
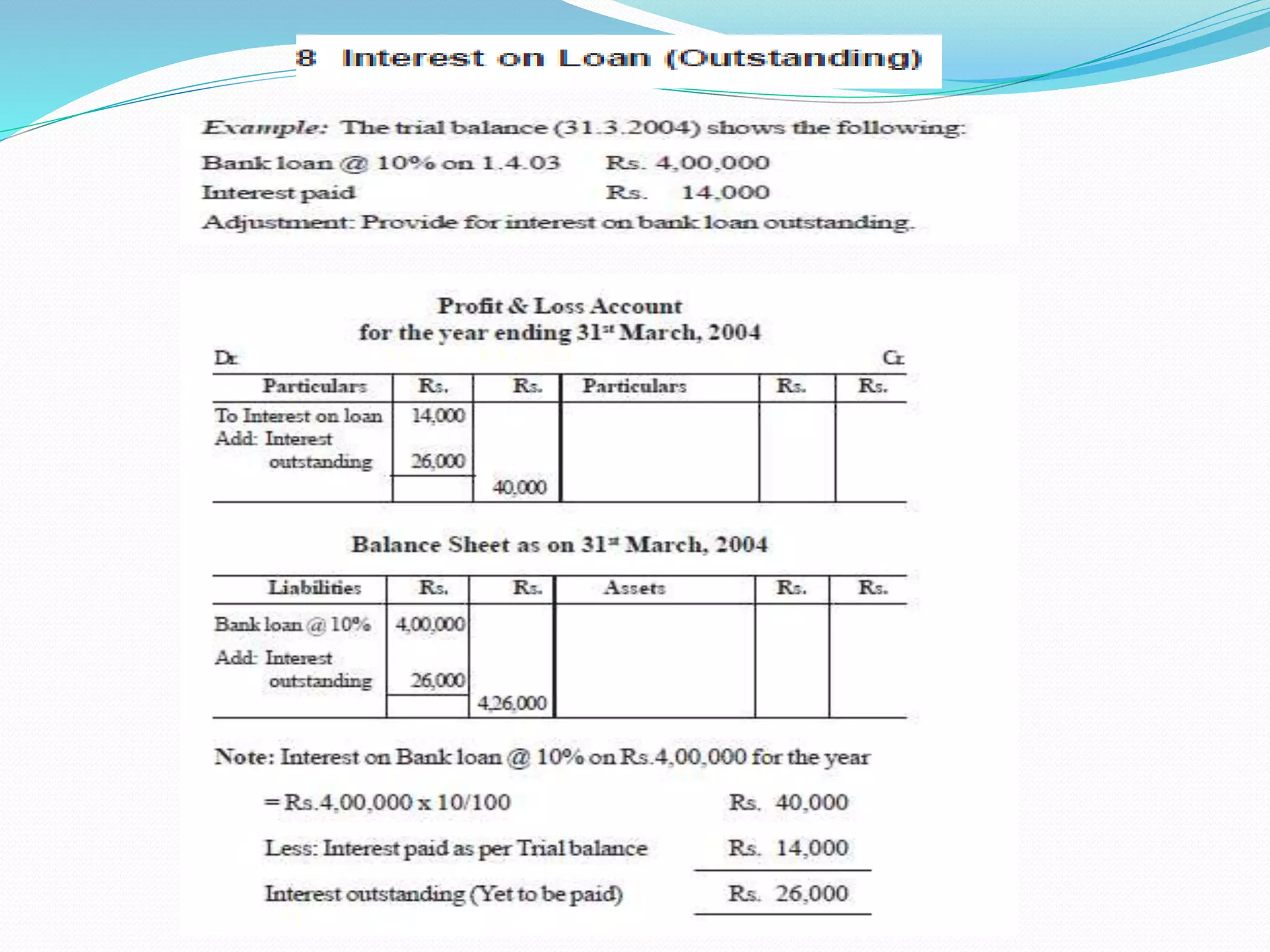
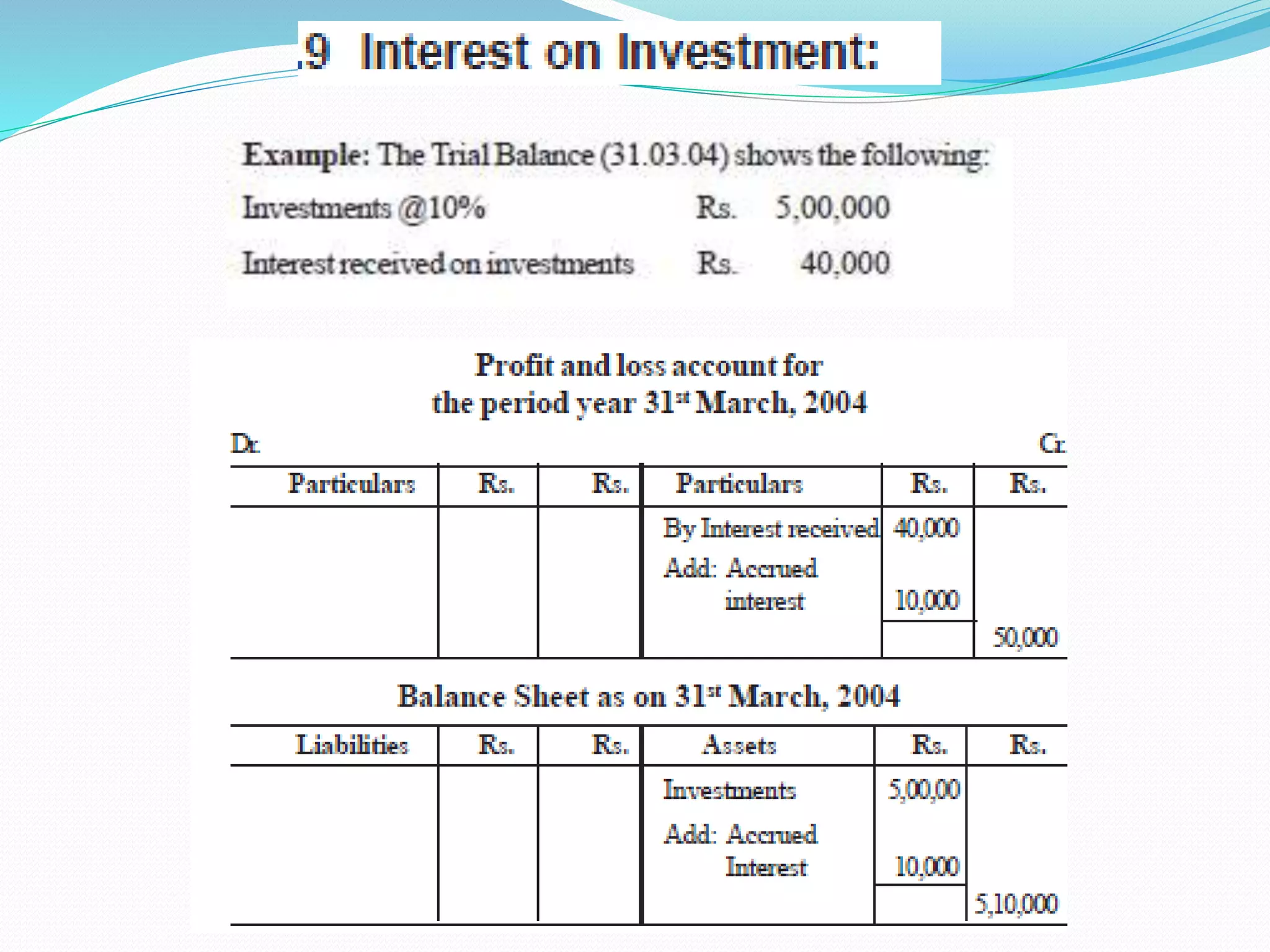
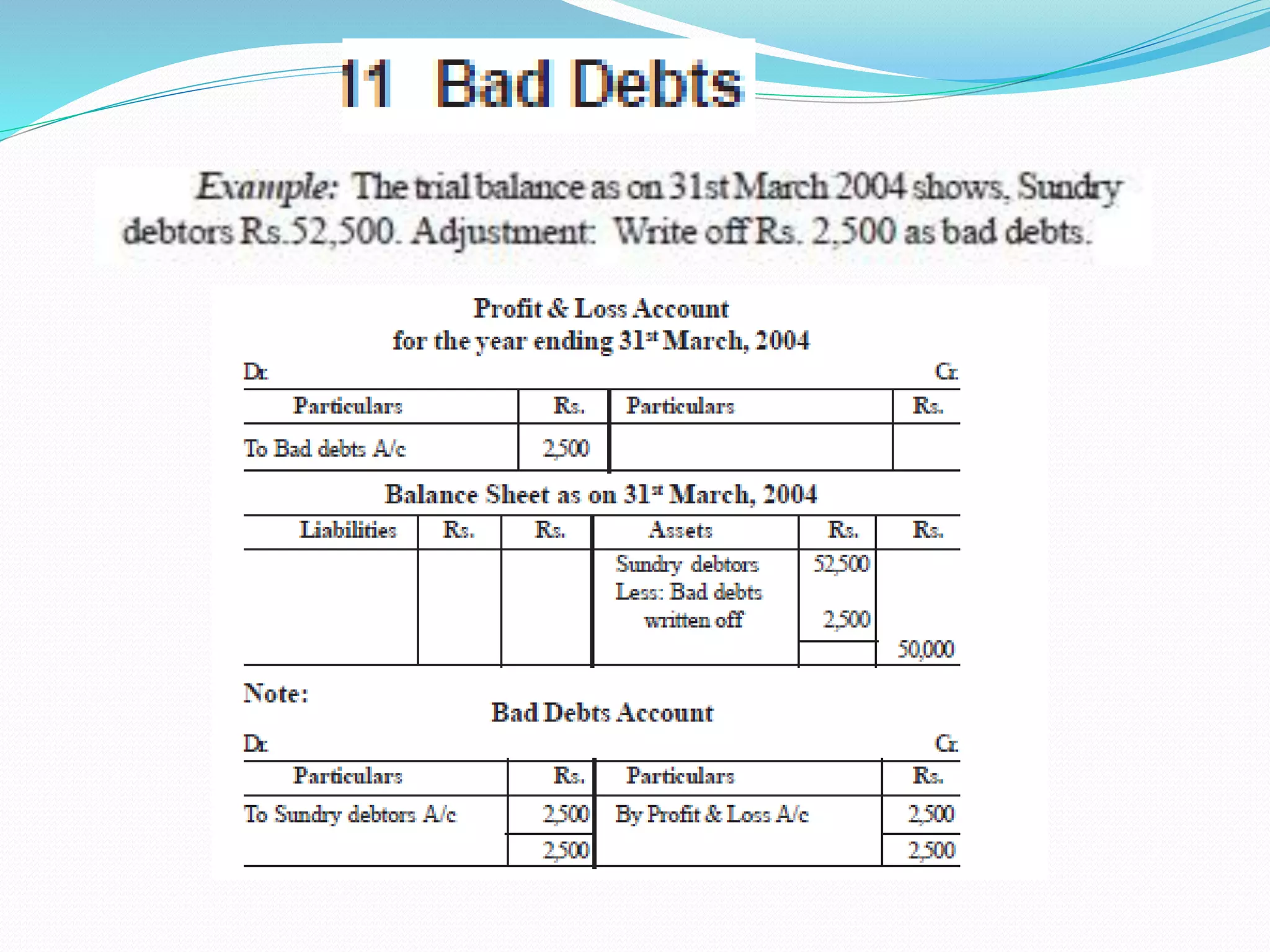
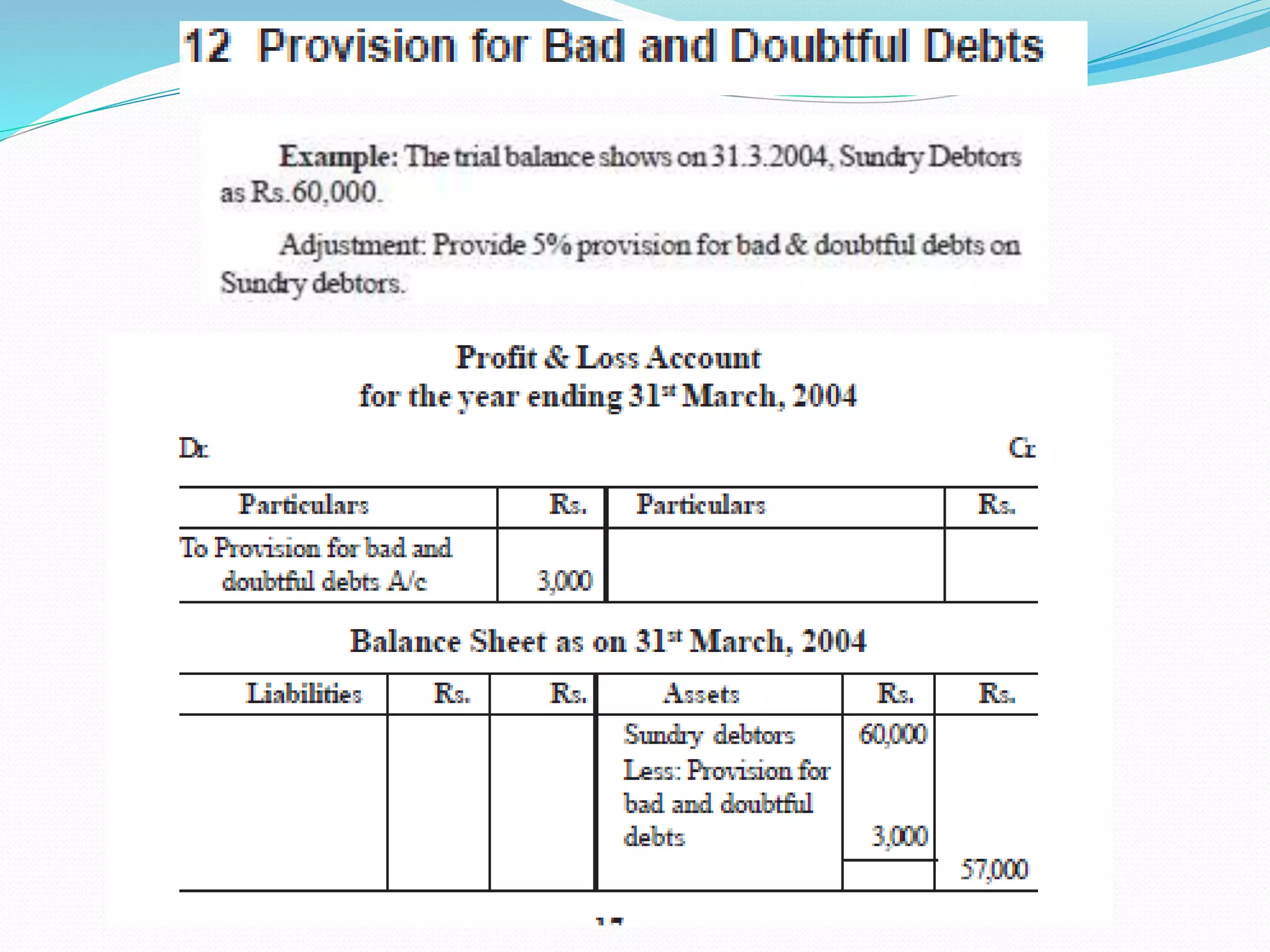
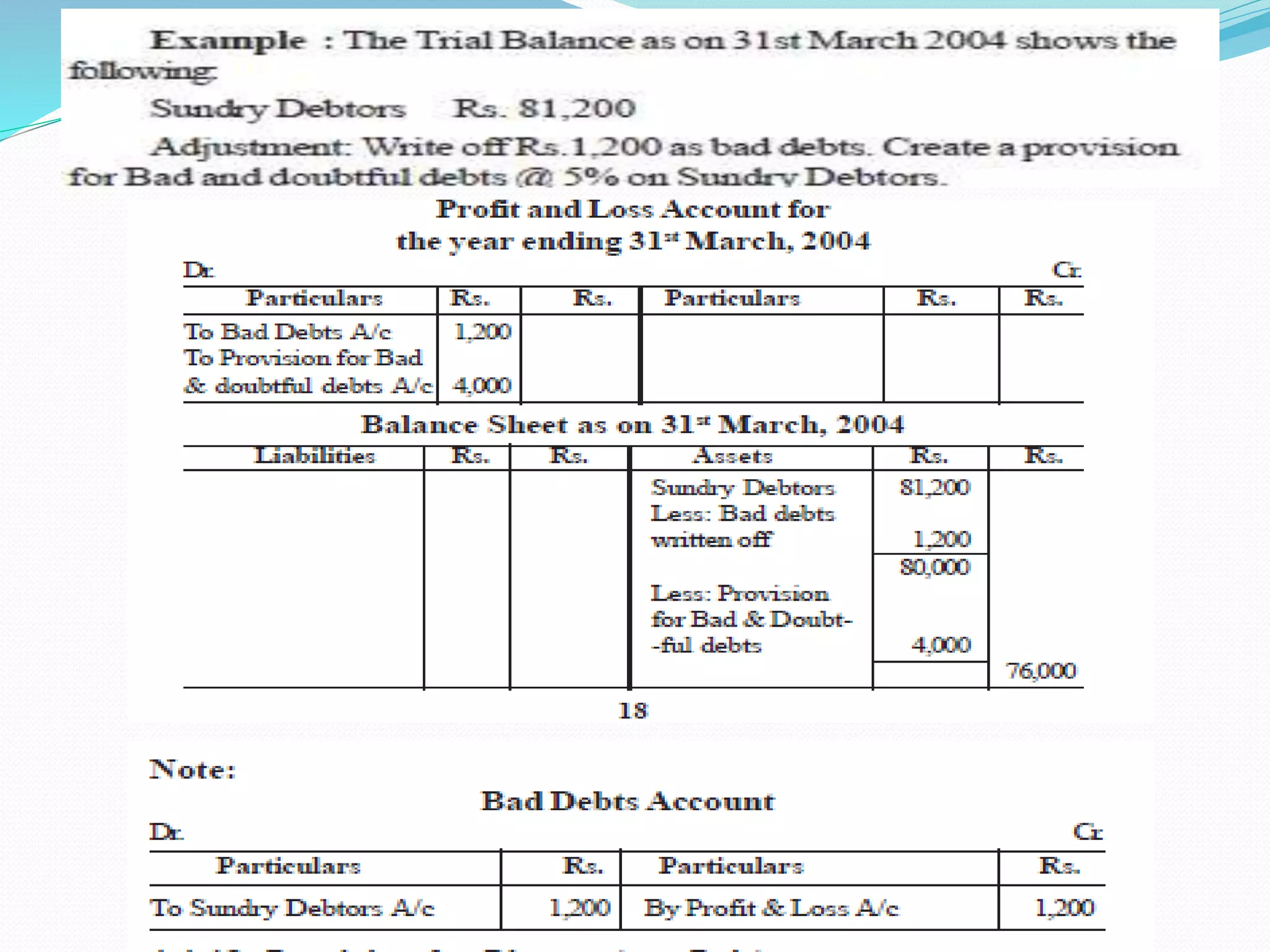
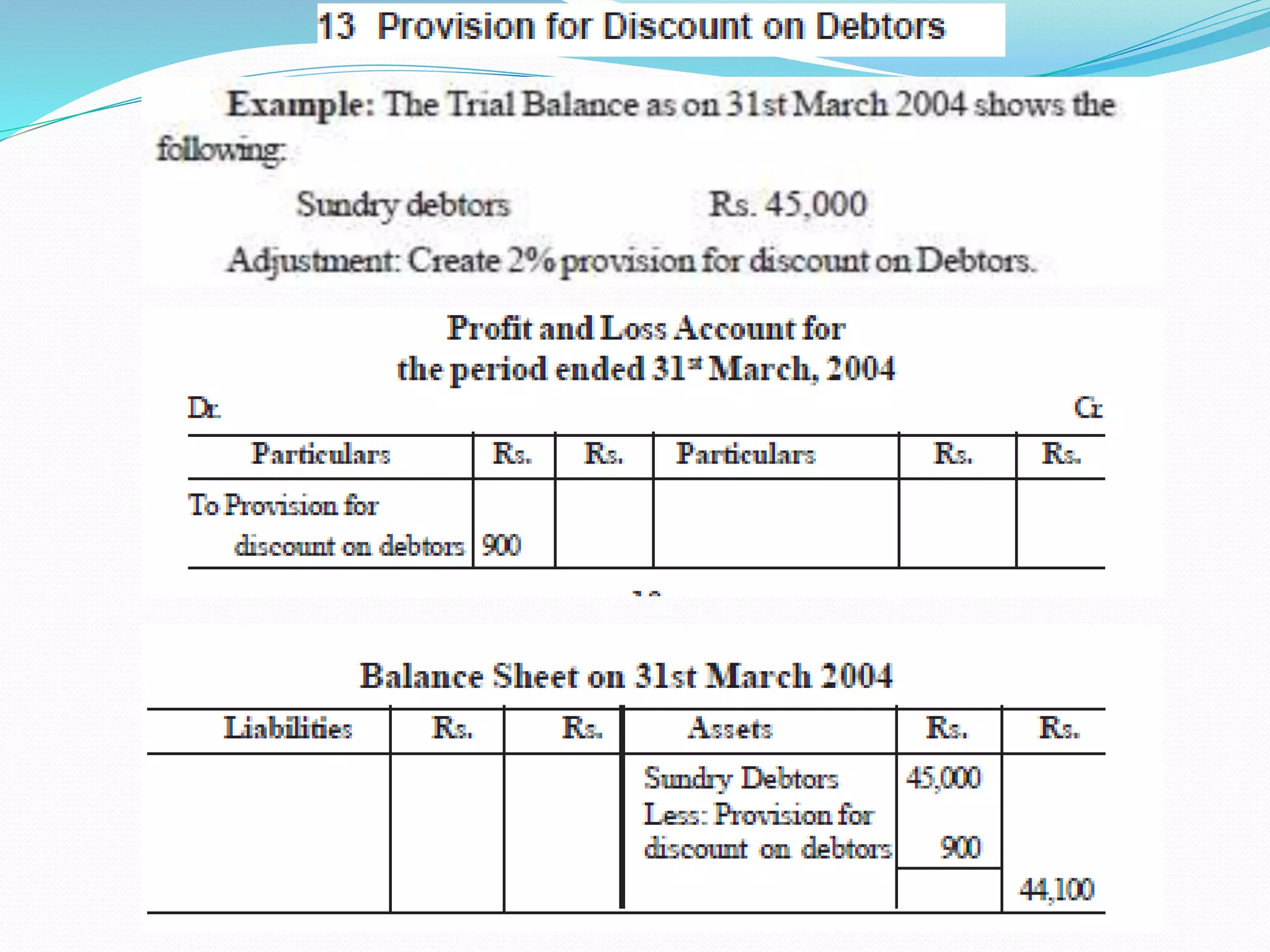
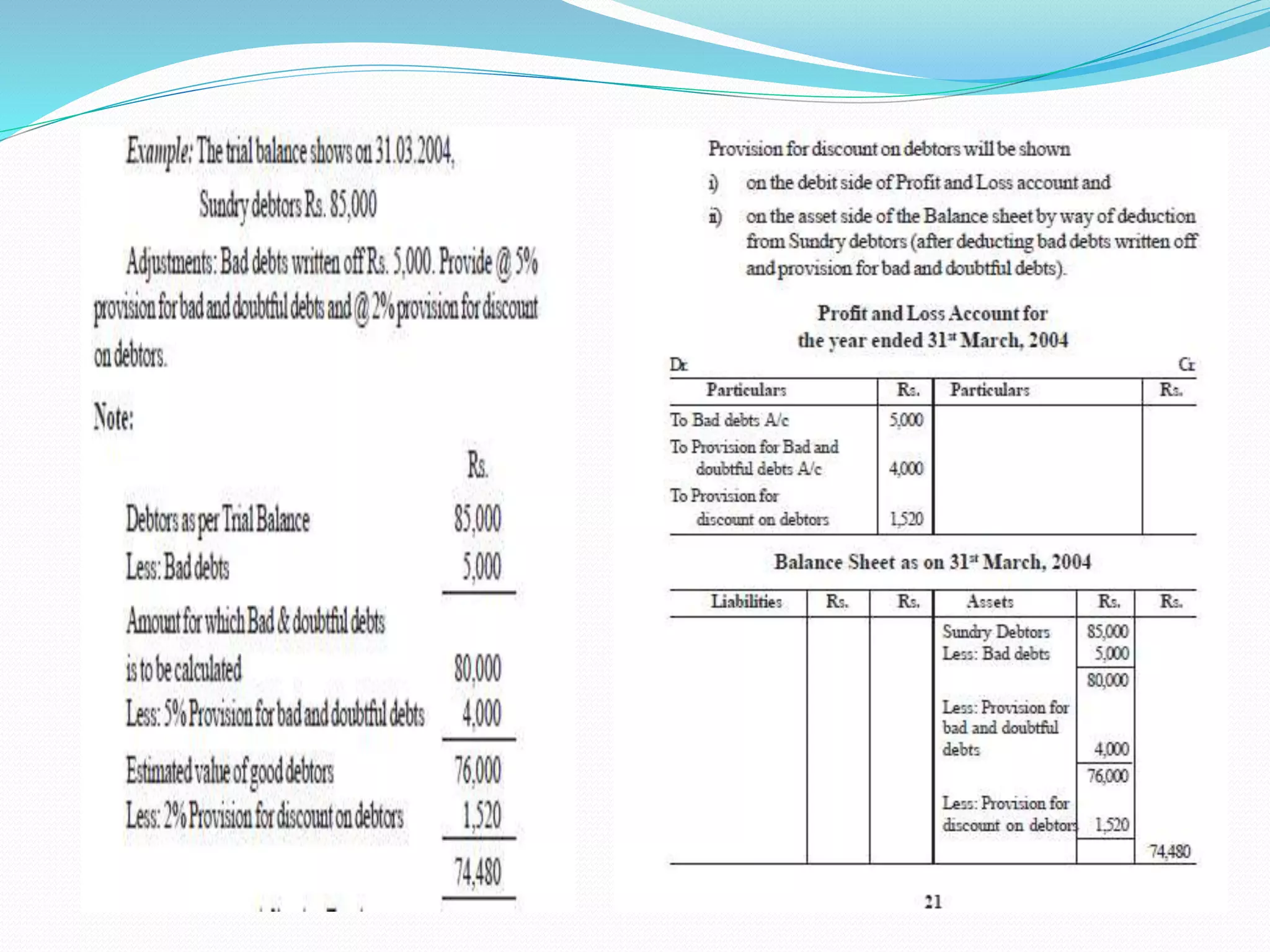
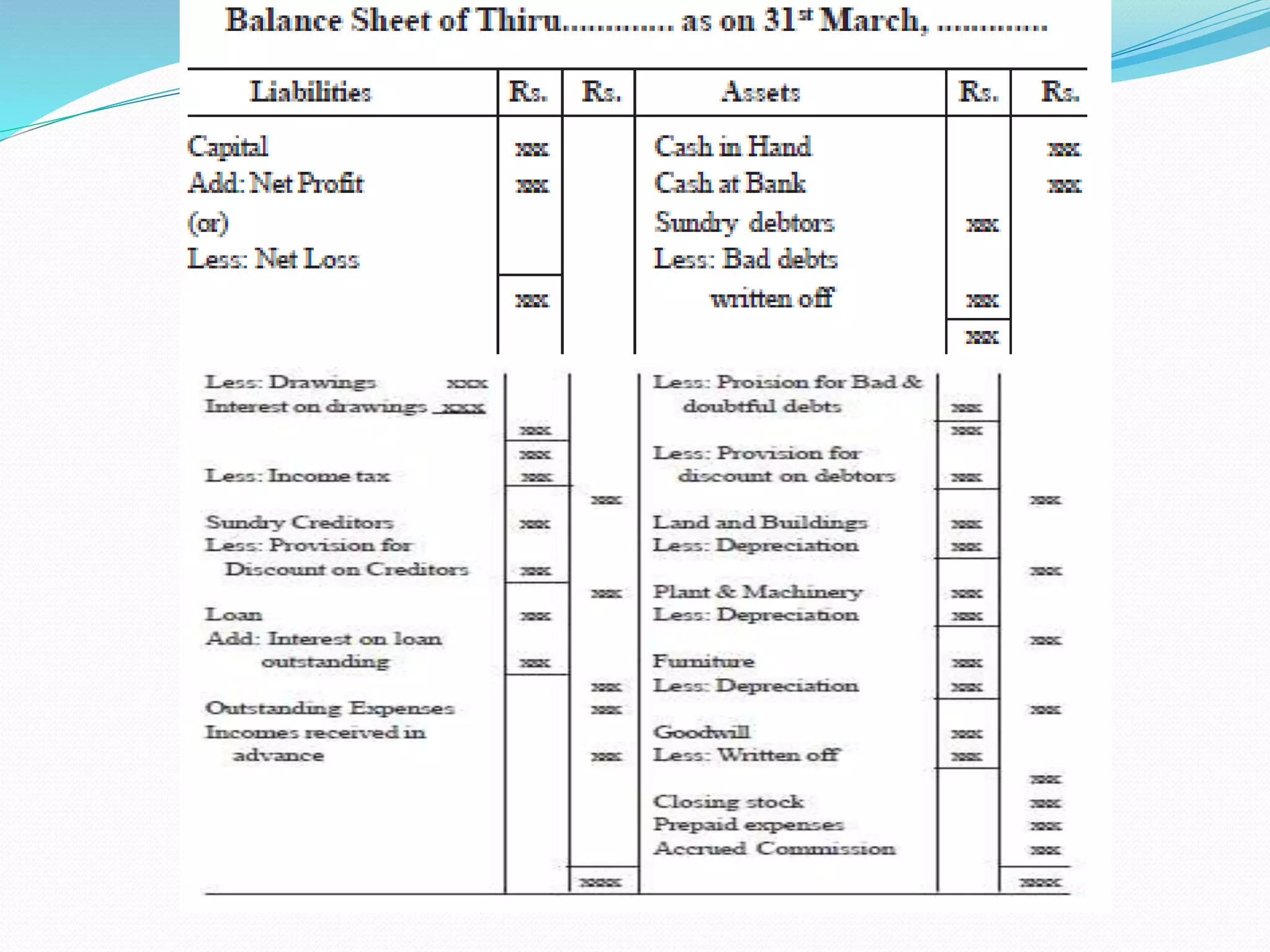
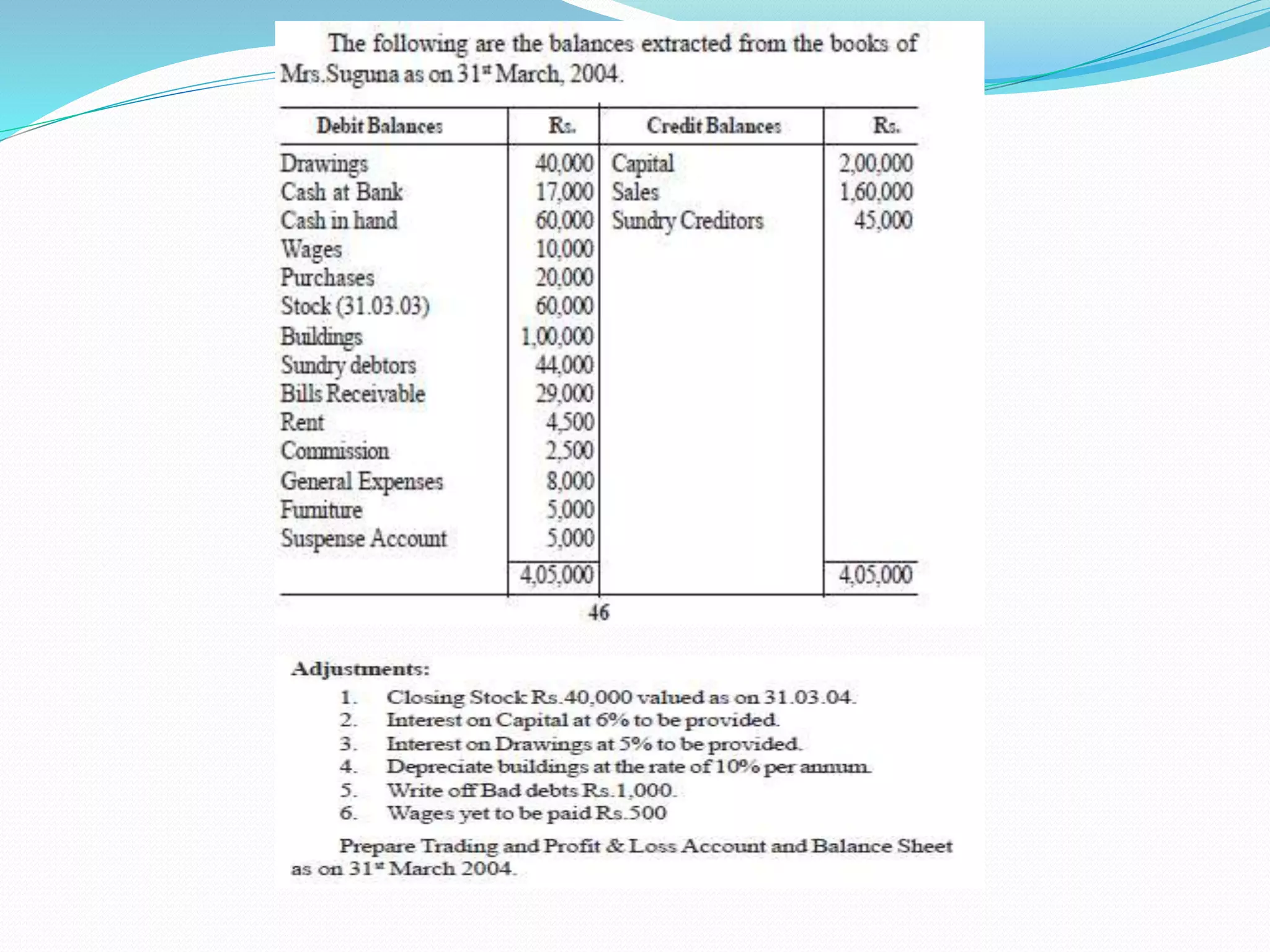
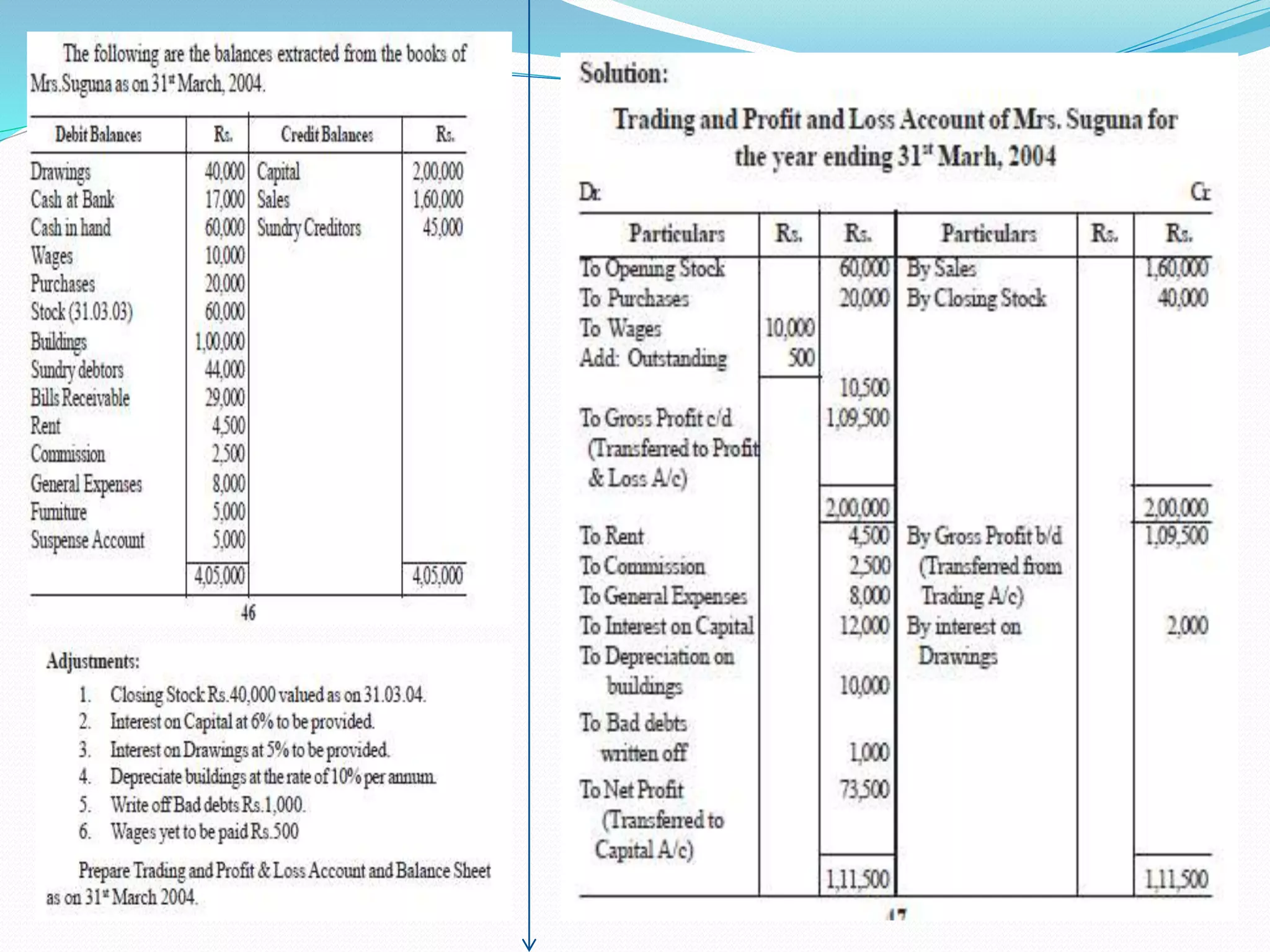
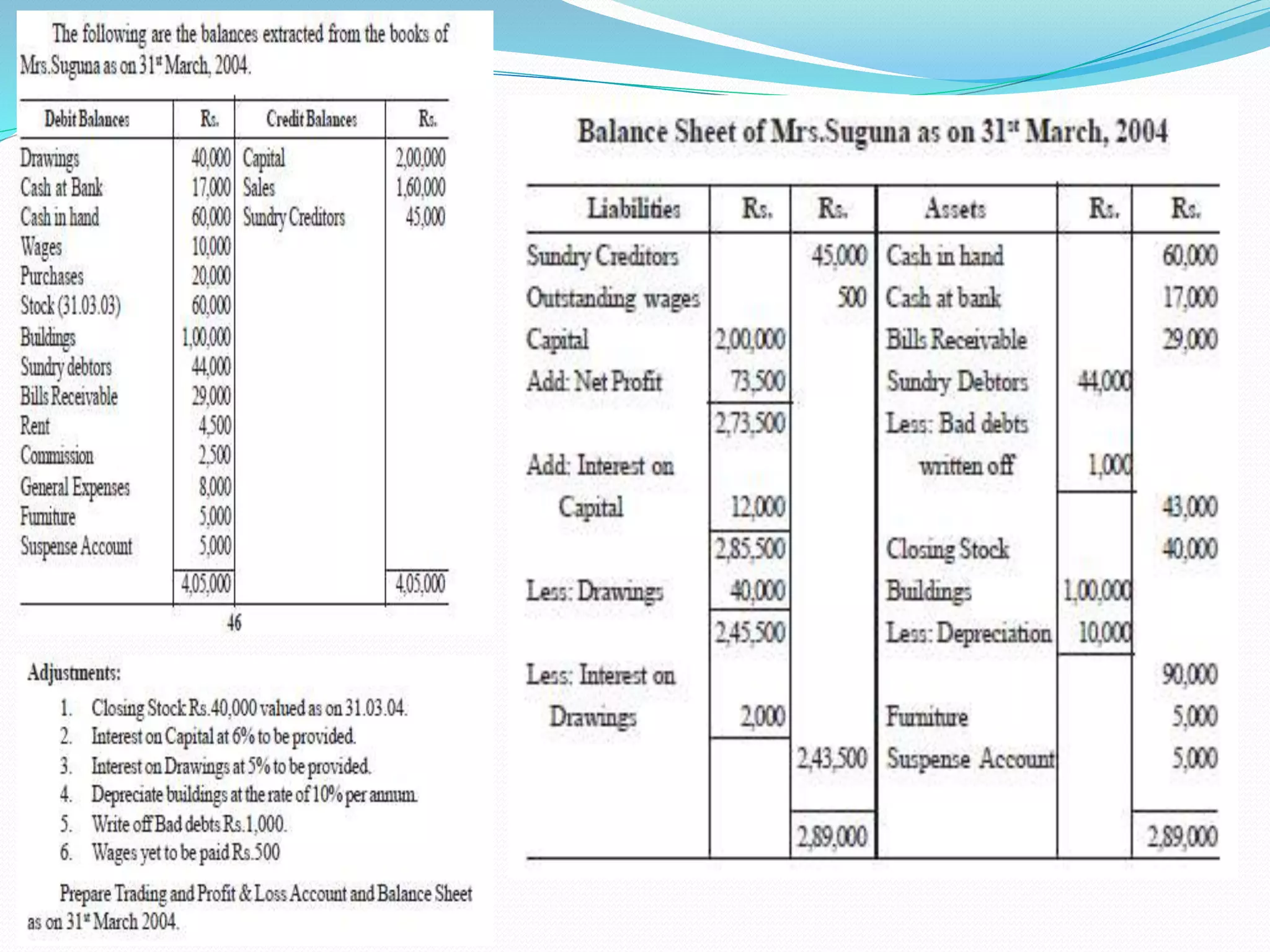
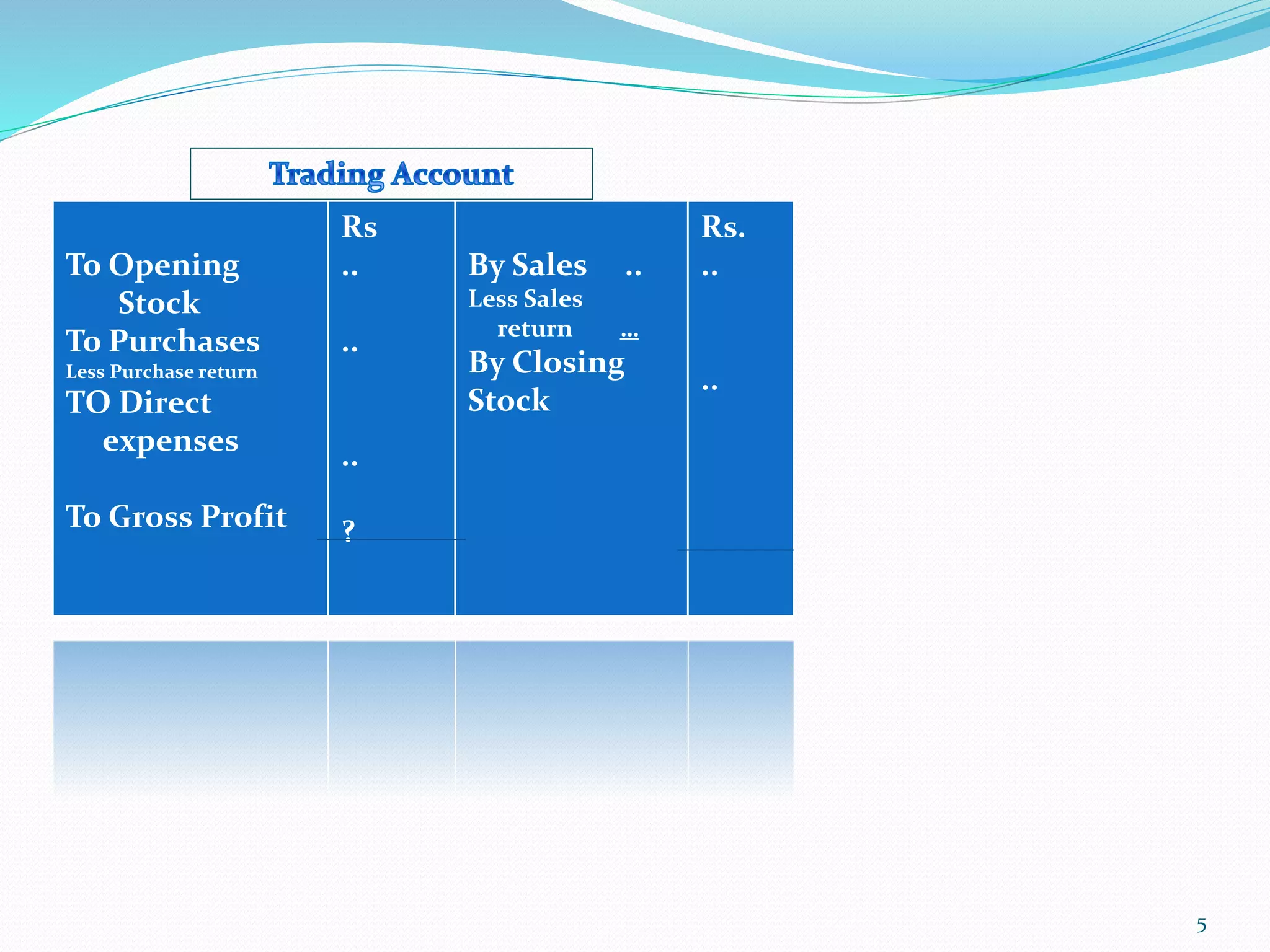
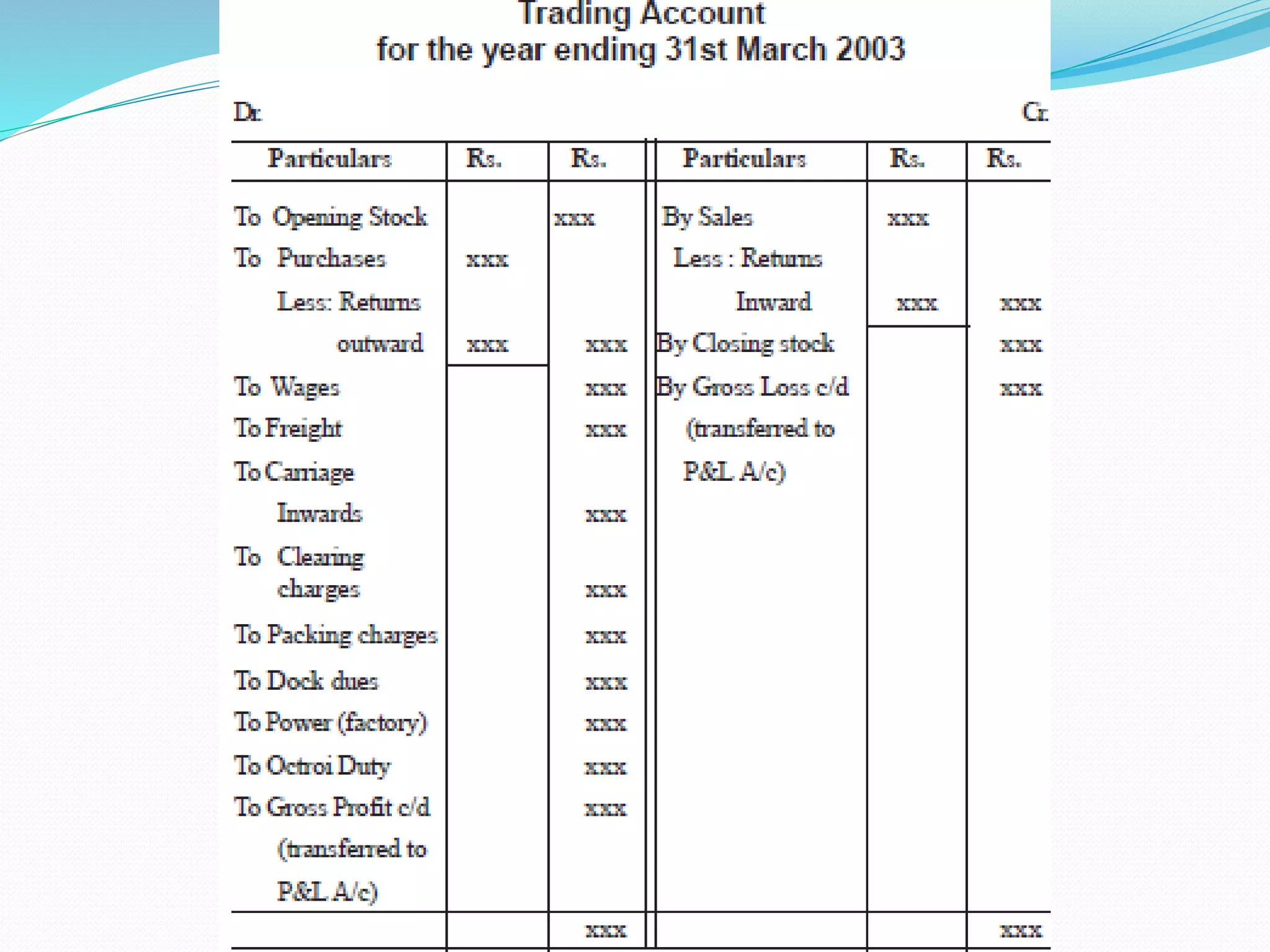
The lecture by Srinivas M outlines the accounting cycle, detailing the preparation of final accounts, including trading and profit and loss accounts, and balance sheets. It explains key concepts such as gross profit, cost of goods sold, and various direct and indirect expenses. Additionally, the document includes examples for preparing accounts that illustrate how to compute gross and net profit for different cases.




![Prepare a trading account of Mr.Devan for the year
ended 31st March 2015.
Opening stock 5,700
Purchases 1,58,000
Purchases returns 900
Sales 2,62,000
Sales returns 600
Closing stock was valued at Rs.8,600.
[Answer : Gross profit Rs. 1,07,200]
7](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/topic9finalaccounts-161227051430/75/Topic-9-final-accounts-7-2048.jpg)

![Prepare profit and loss account of Mrs. Nandini for
the year ended 31st Dec. 2001 from the following.
Gross profit 1,25,000 Discount paid 600
Salaries 15,000 Discount received 1,000
Rent 5,000 Interest paid 500
Carriage outwards 1,000 Interest received 700
Selling expenses 500 Commission earned 2,000
Income from investment 1,500
[Answer : Net profit Rs.1,07,600]
12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/topic9finalaccounts-161227051430/75/Topic-9-final-accounts-12-2048.jpg)
![The following balances are taken from the books of M/s.
RGV Ltd. Prepare profit and loss account for the year
ended 31st March 2012.
Gross profit 5,25,000 Salaries & wages 1,00,000
Rent 10,000 Depreciation 5,000
Interest on loan 5,000 Office expenses 1,500
Distribution charges 2,500 Salesman salary 8,000
Bad debts 2,200 Stationery and printing 500
Commission received 3,000 Discount received 2,000
Interest received 5,000 Advertising 9,000
Taxes and insurance 2,000
[Answer : Net profit Rs. 3,89,300]
13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/topic9finalaccounts-161227051430/75/Topic-9-final-accounts-13-2048.jpg)