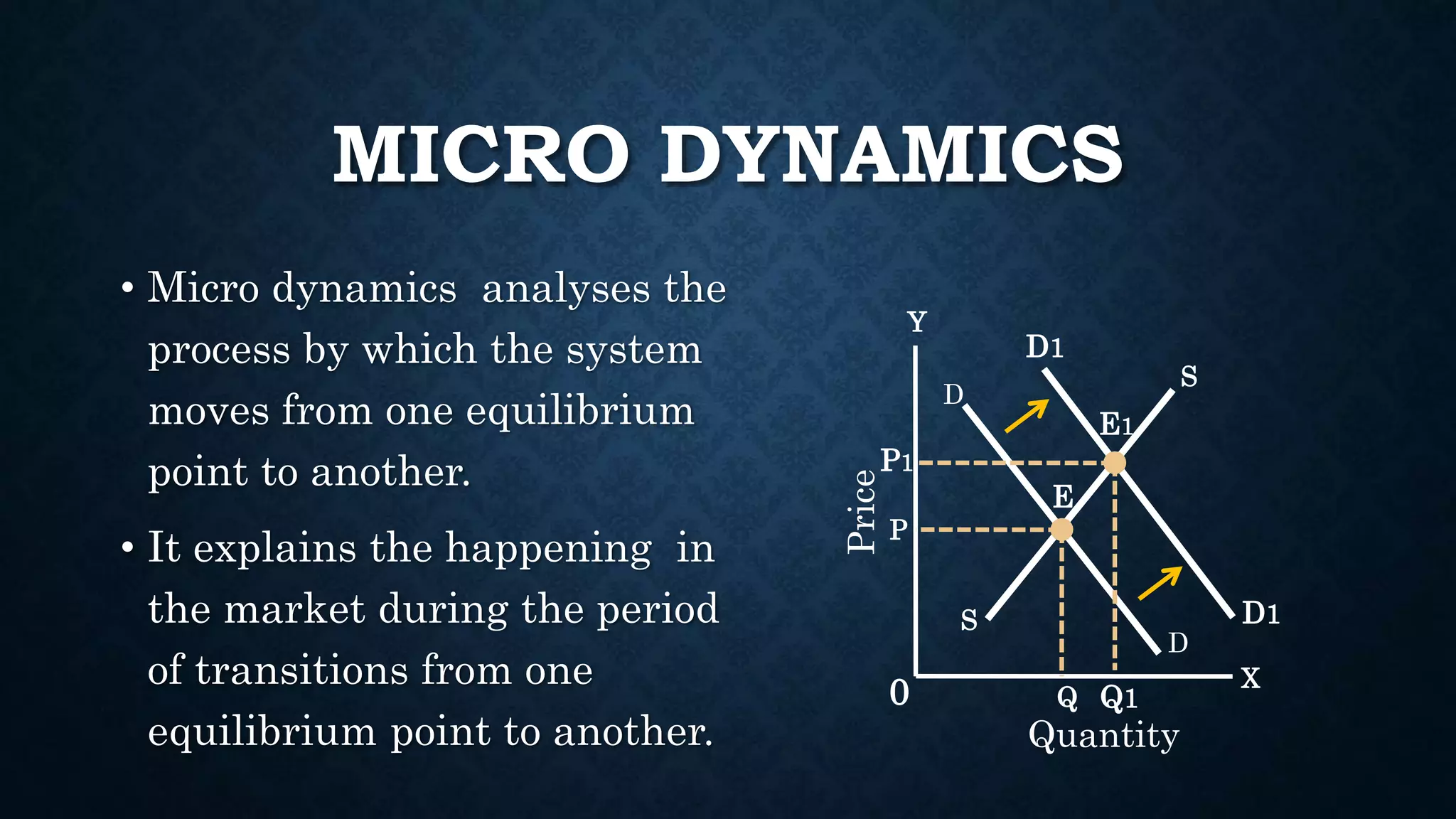
This document provides an introduction to microeconomics. It defines microeconomics as the study of individual economic decision-makers and markets. Microeconomics analyzes how households and firms make choices and how they interact in markets. It examines supply and demand at the individual level and studies pricing and output decisions by producers. The document also outlines different types of microeconomics including microstatic, comparative microstatic, and microdynamics and discusses some common uses of microeconomic analysis.