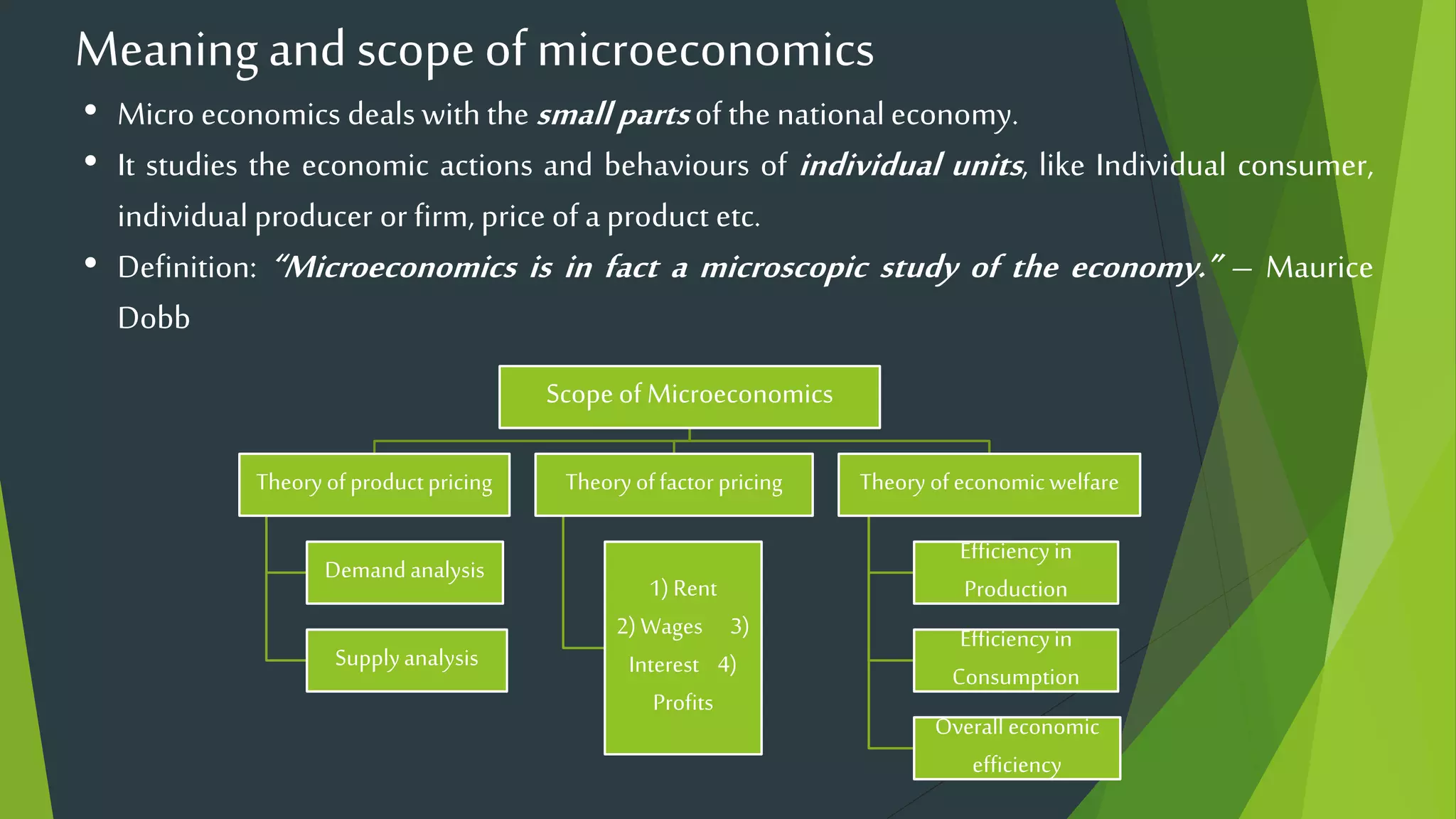
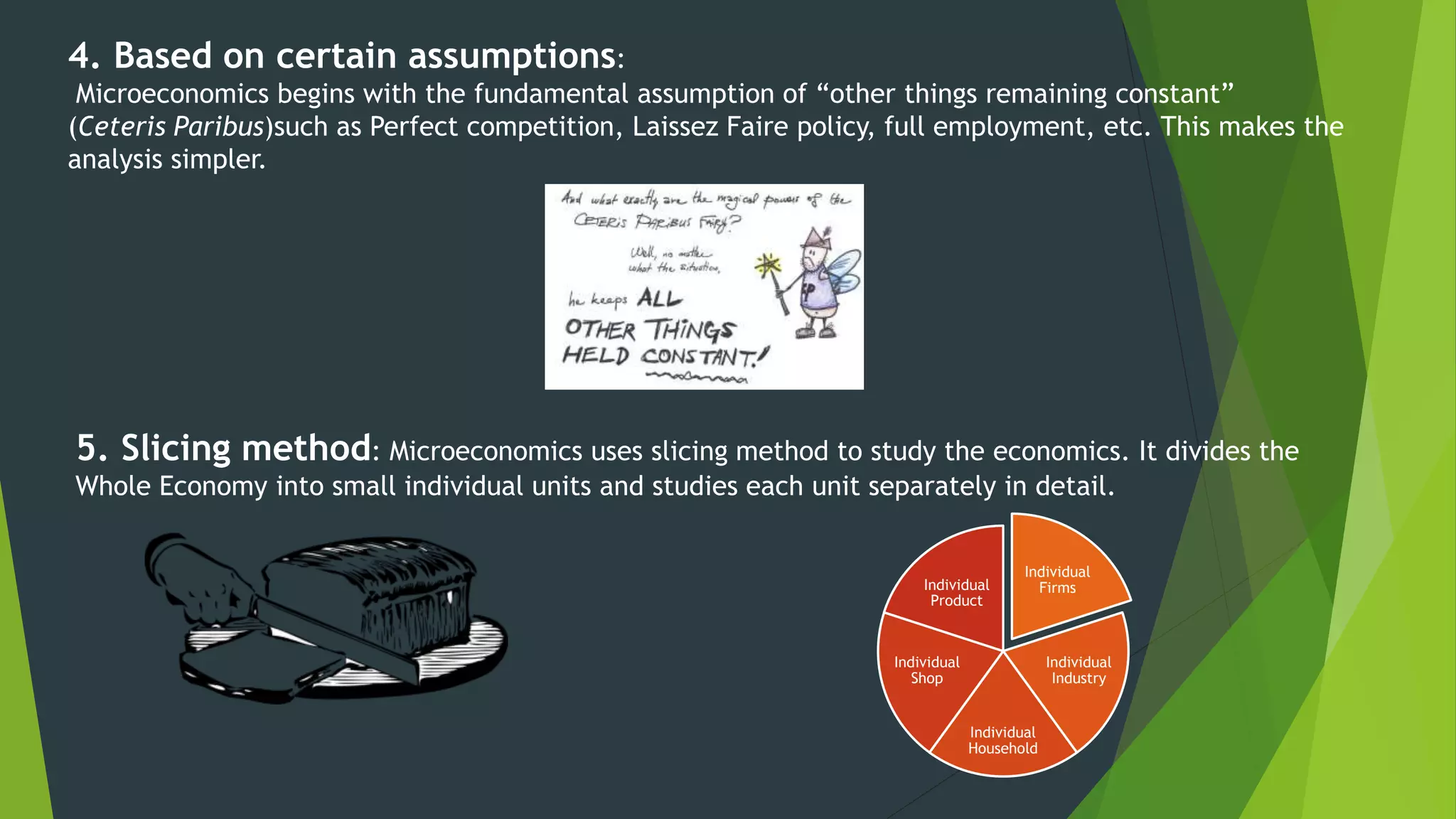
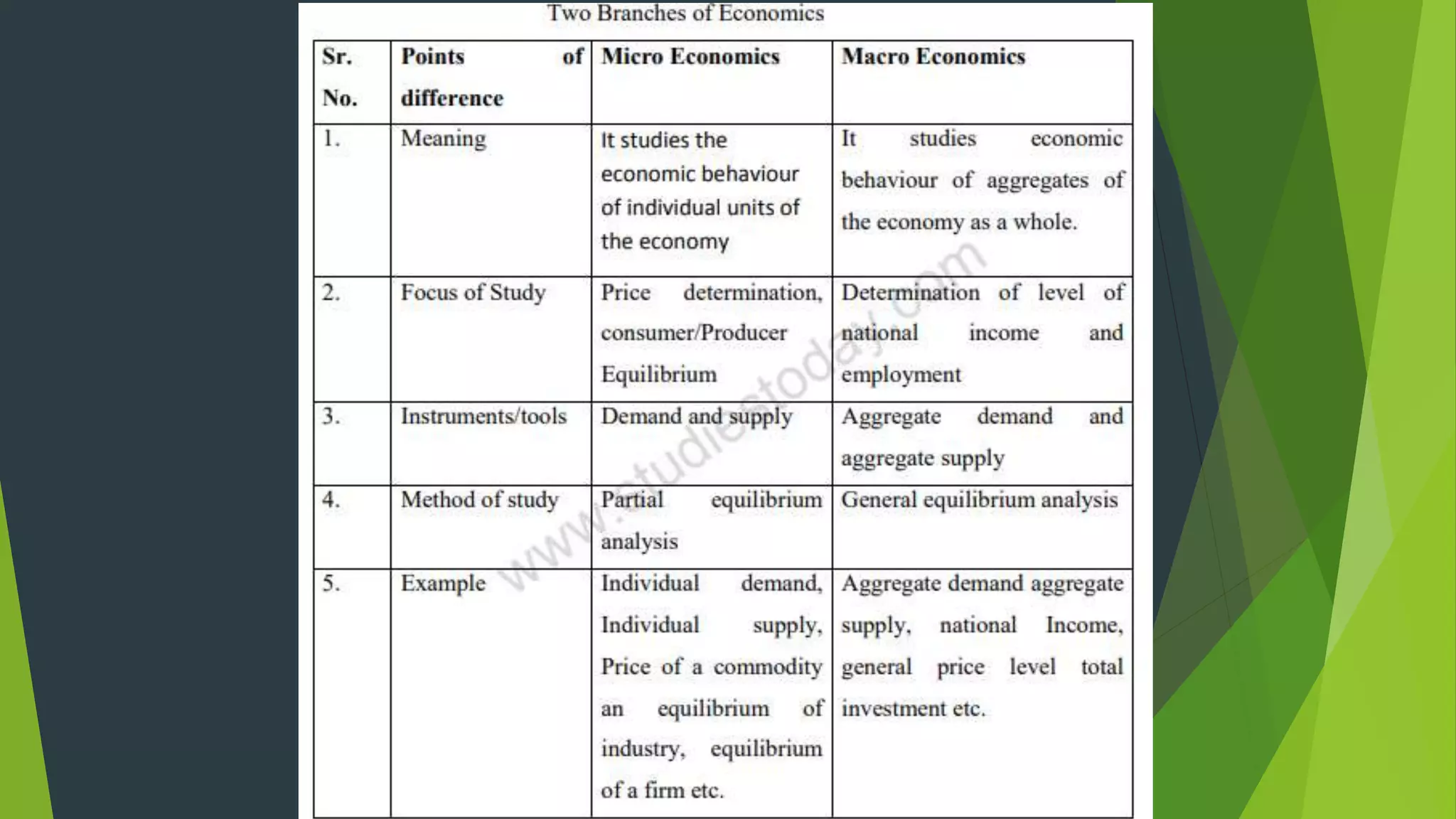
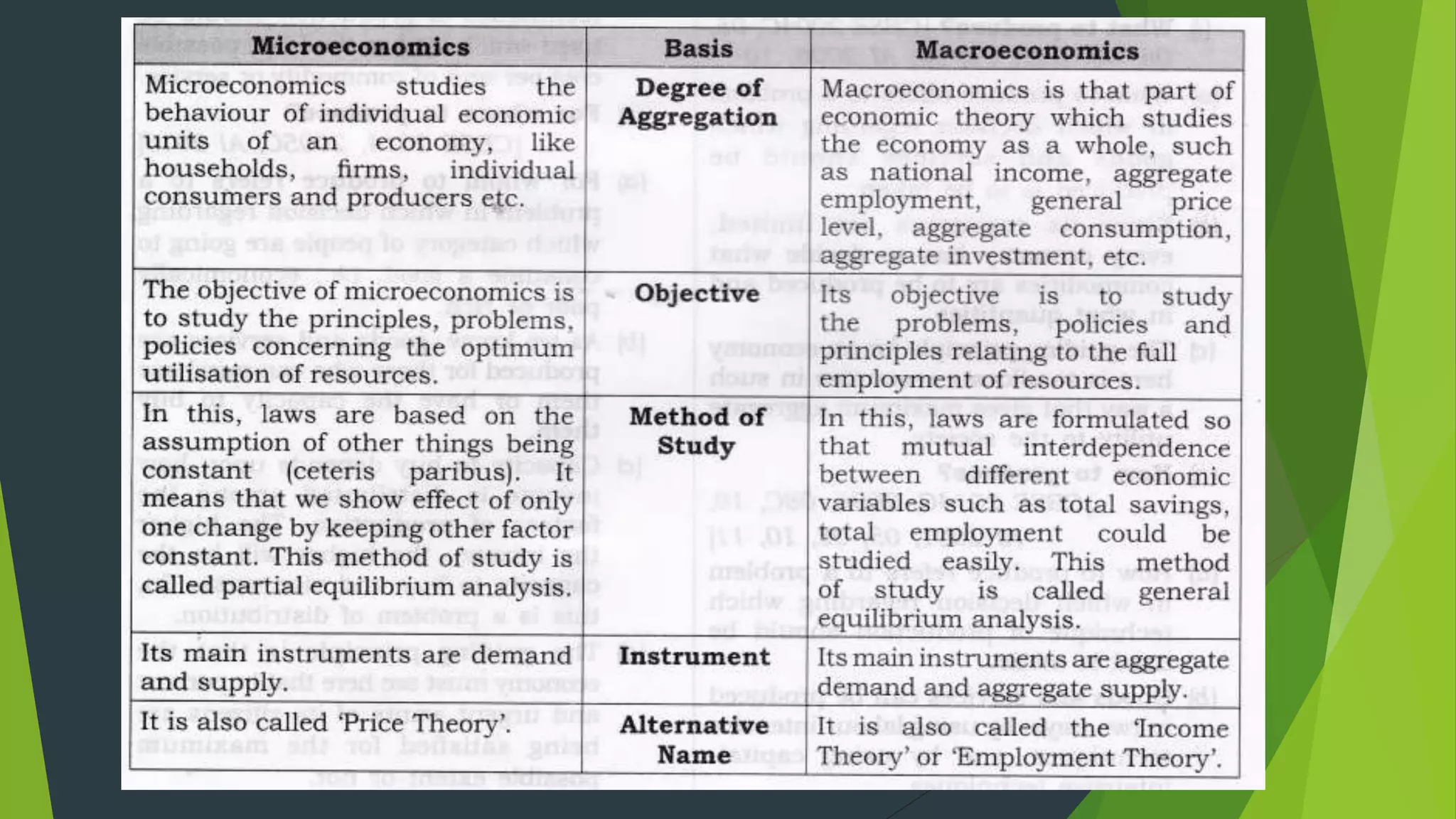
This document provides an overview of microeconomics and macroeconomics. It defines microeconomics as studying small parts of the economy like individual consumers, firms, and prices. Macroeconomics is defined as studying large aggregates and the economy as a whole, including concepts like national income, price levels, and business cycles. The document also outlines some key differences between microeconomics and macroeconomics such as their level of analysis, use of partial vs general equilibrium, and policy orientation. It provides examples of topics covered in each field and their importance.