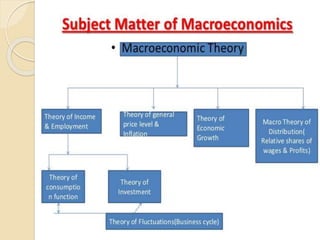
The document introduces macroeconomics, defined as the study of aggregates like national income and employment, with significant contributions by economist J.M. Keynes. It outlines the scope of macroeconomics, including theories on employment, national income, general price level, money, international trade, and economic growth, emphasizing its importance in policy formulation and economic problem-solving. The interdependence between microeconomics and macroeconomics is highlighted, showing how changes in one affect the other, reinforcing their complementary nature in addressing economic issues.