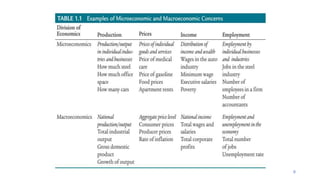
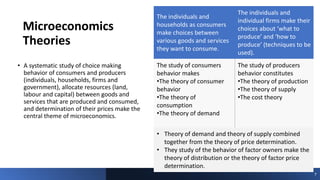
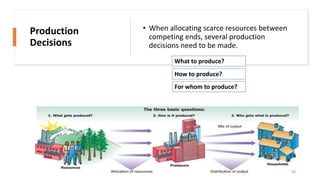
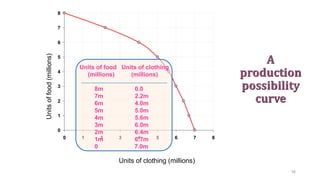
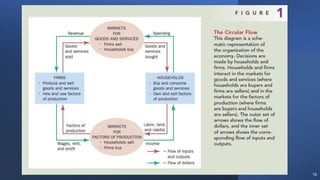
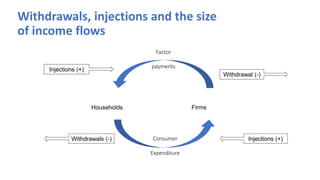
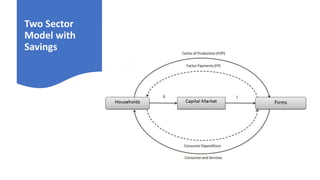
This document provides an introduction and overview of microeconomics. It defines microeconomics as the study of individual economic decision-making units like households and firms, and the determination of prices and outputs. The document outlines some key microeconomics concepts like scarcity, choice, opportunity cost, production possibility frontier, factors of production, and circular flow. It also discusses different economic systems and schools of economic thought.