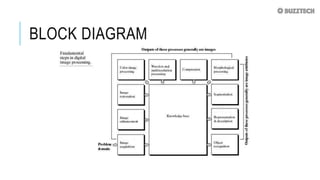
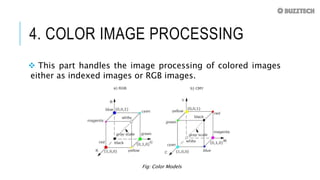
The document outlines the fundamental steps in digital image processing, which include image acquisition, enhancement, restoration, and color processing, among others. Each step serves a specific purpose, such as improving image quality, recovering degraded images, or compressing data for efficient storage and transmission. The document also discusses segmentation, representation, description, and recognition, emphasizing the importance of various techniques and processes in handling digital images.