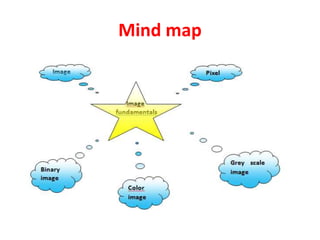
The document defines key concepts related to digital images, including:
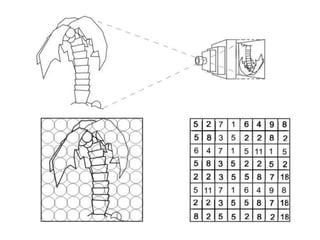
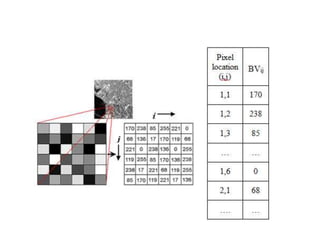
1. A digital image is a 2D array of pixels, where each pixel represents a color or intensity value.
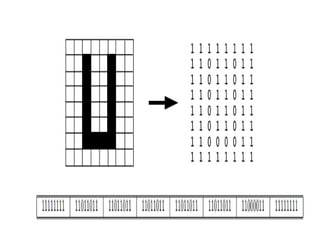
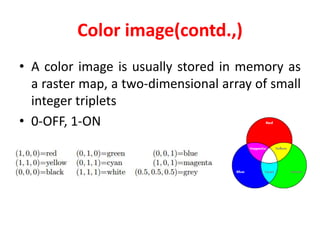
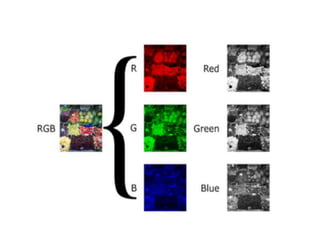
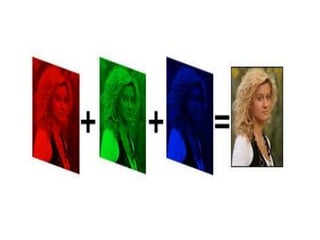
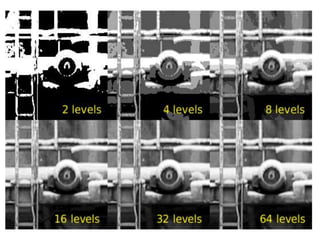
2. There are three main types of digital images: binary, grayscale, and color. Binary images have two possible values per pixel, grayscale images represent intensity on a scale of grays, and color images use multiple values per pixel to represent colors.
3. Image resolution depends on the number of pixels and their size - more and smaller pixels allow clearer representation of details.