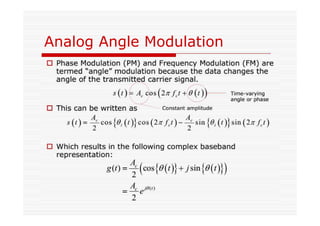
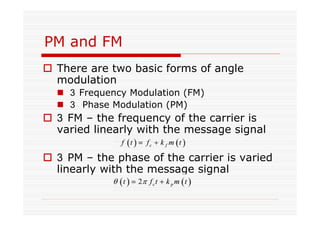
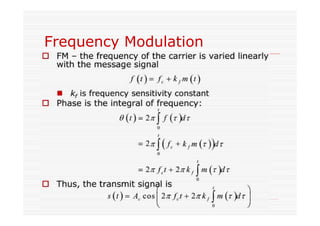
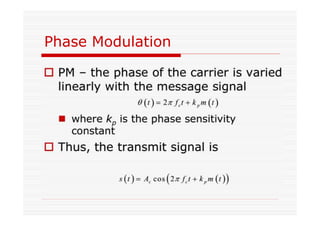
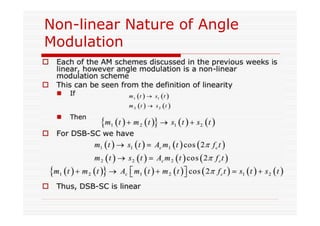
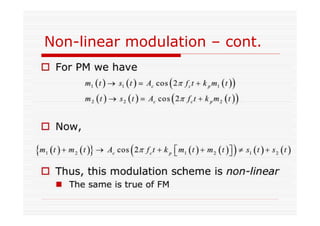
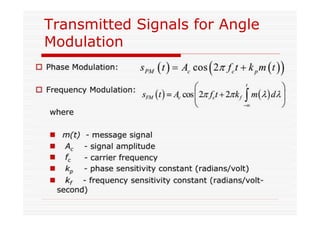
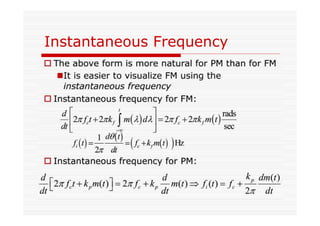
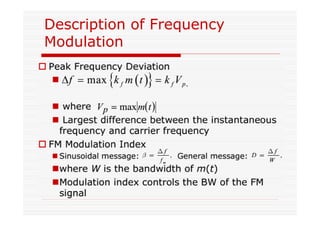
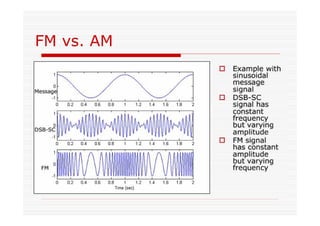
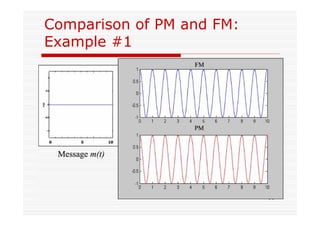
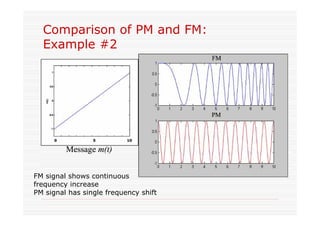
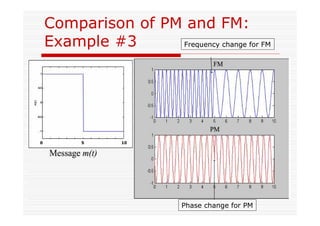
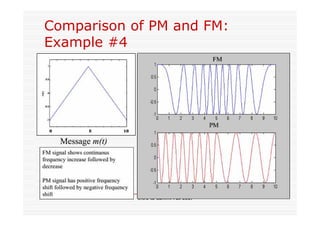
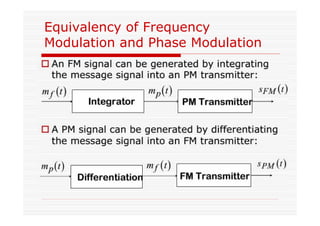
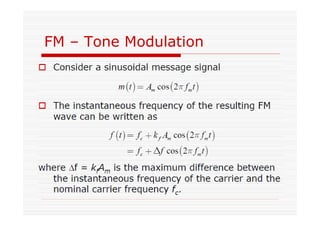
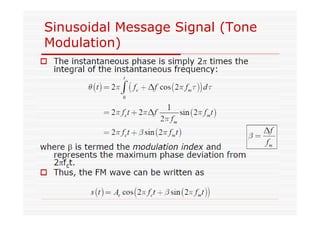
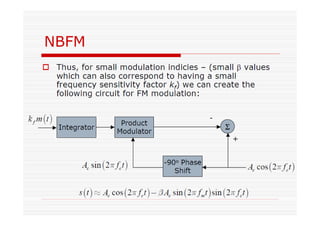
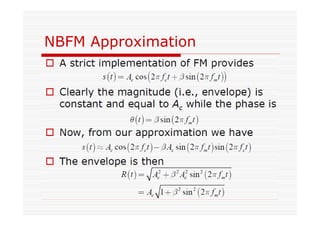
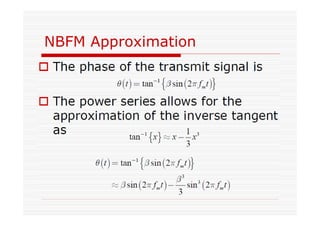
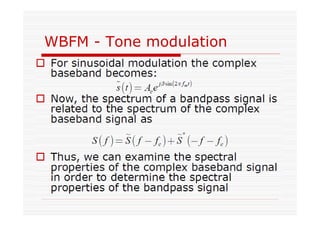
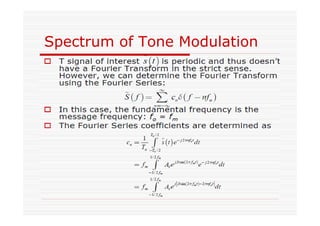
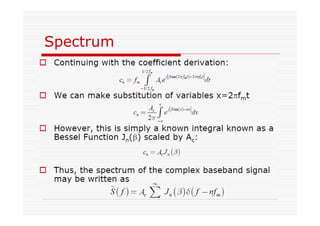
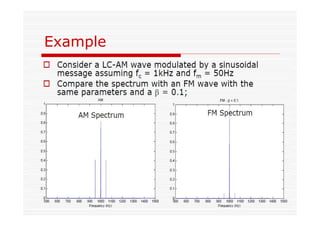
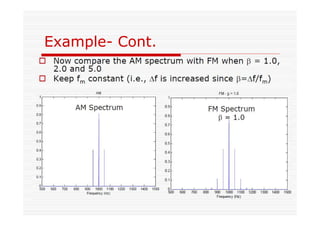
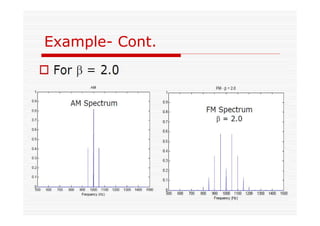
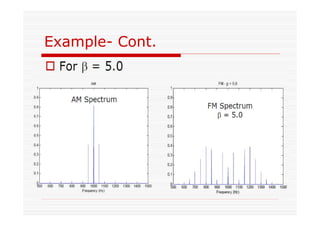
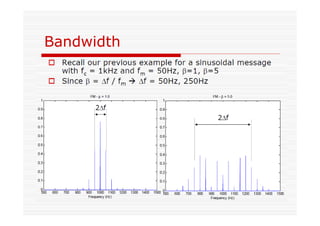
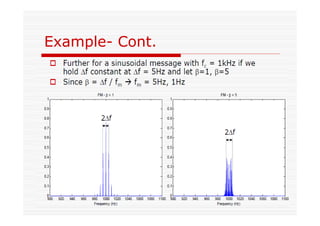
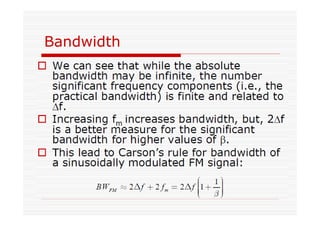
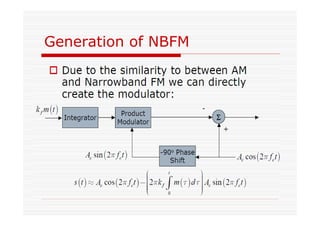
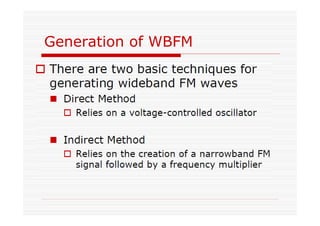
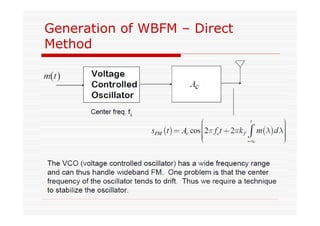
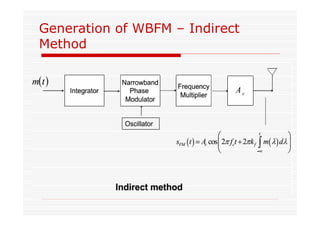
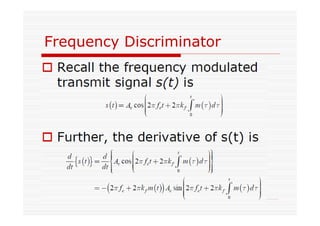
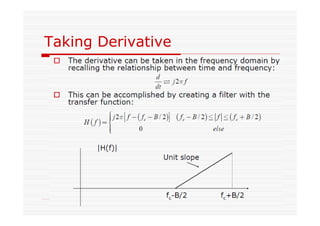
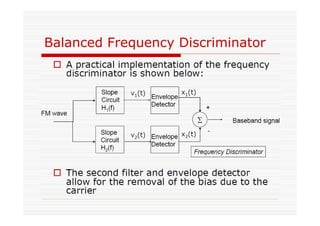
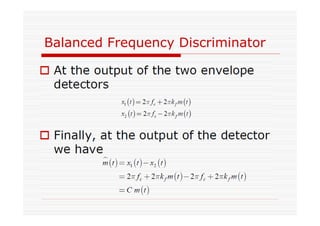
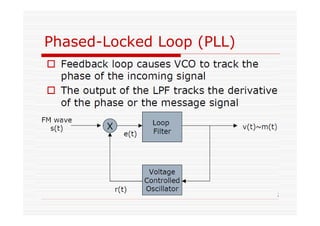
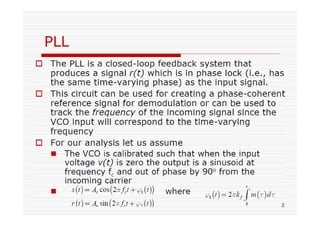
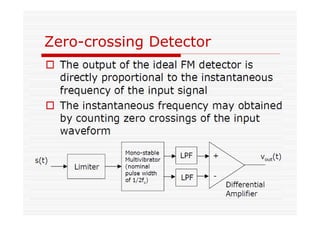
This document discusses an EEE 330 lecture on angle modulation and demodulation. It introduces phase modulation (PM) and frequency modulation (FM), the two main forms of analog angle modulation. PM varies the phase of the carrier linearly with the message signal, while FM varies the frequency of the carrier linearly. The document compares and contrasts PM and FM through examples and discusses narrowband FM, wideband FM, generation and demodulation of FM signals, and practical FM demodulators like the frequency discriminator and phased-locked loop.