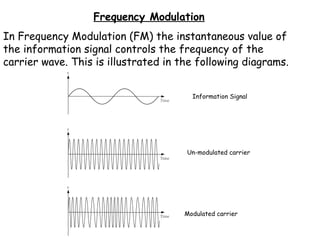
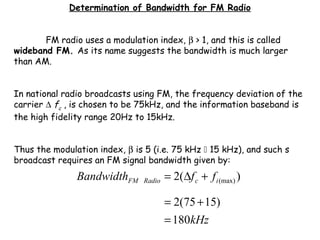
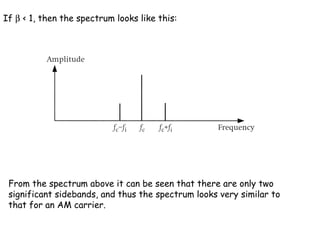
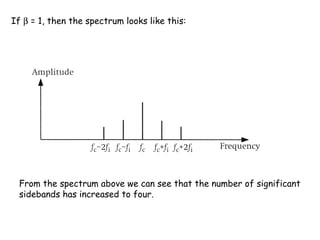
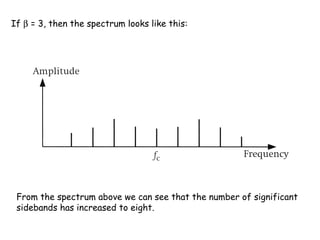
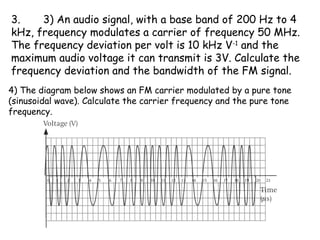
The document discusses frequency modulation (FM) and provides examples of how a carrier wave's frequency is modulated by an audio signal. Key points:
- In FM, the audio signal controls the instantaneous frequency of the carrier wave, increasing it when the audio is positive and decreasing it when negative.
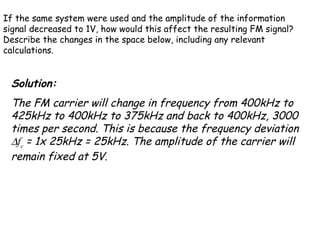
- The maximum change in the carrier's frequency from its base value is called the frequency deviation (Δfc).
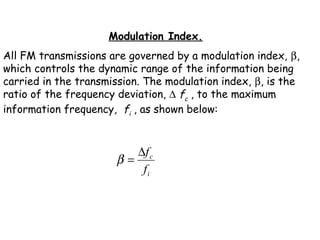
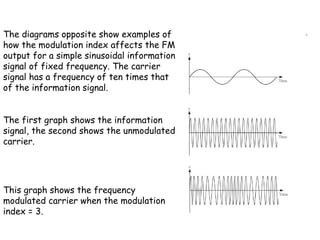
- The modulation index (β) is the ratio of frequency deviation to the maximum audio frequency and determines the dynamic range and spectrum of the FM signal.
- For β > 1, called wideband FM, the bandwidth is much larger than for amplitude modulation and more sidebands are significant.