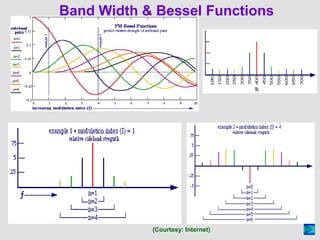
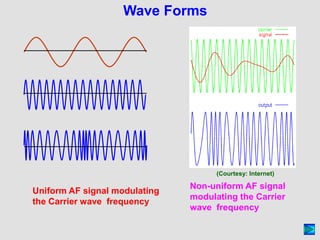
Frequency modulation (FM) is a process that changes the frequency of a carrier wave in accordance with an audio frequency (AF) signal. The instantaneous frequency of the modulated wave is equal to the carrier frequency plus a proportionality constant multiplied by the modulating signal. This creates a maximum deviation from the carrier frequency known as the peak deviation. The modulation index for FM is the ratio of the peak deviation to the modulating frequency. FM uses Bessel functions to generate an infinite number of sidebands around the carrier frequency, keeping the overall power constant. Benefits of FM include noise reduction and the ability for multiple transmitters to operate on the same frequency without interference, while drawbacks are its wider bandwidth requirement and smaller reception area compared
![Theory:
The instantaneous frequency ‘’of modulated wave is:
= c + kEm cos mt
(where k is proportionality constant which depends on the modulating system)
If cos mt = ± 1, then = c ± kEm
or = c ±
(where = kEm is maximum or peak deviation in carrier frequency)
Note that depends on the magnitude of Em and not upon c.
Instantaneous value of FM voltage is: e = Ec cos
is given by the following steps:
d = dt d = 2 dt d = 2 (c + kEm cos mt ) dt
On integration, we get
= ct + (/ m) sin mt
e = Ec cos [ct + (/ m) sin mt] = Ec cos (ct + mf sin mt)
where mf = / m is modulation index for FM
e m= Em cos mt & ec = Ec cos (ct + )](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2frequencymodulation-201006102823/85/concept-of-FM-Frequency-modulation-class-12th-full-ppt-3-320.jpg)