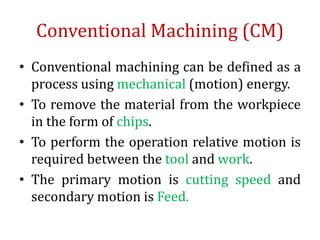
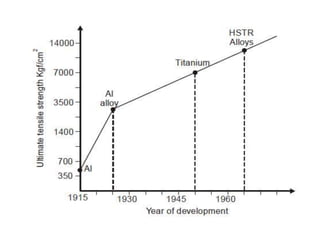
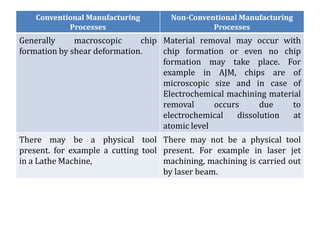
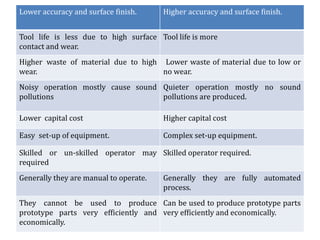
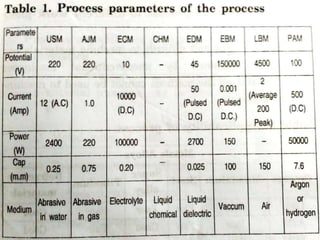
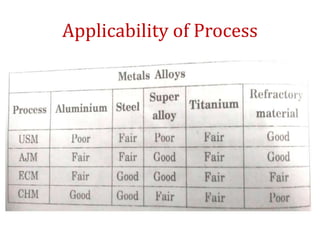
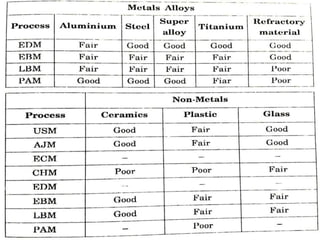
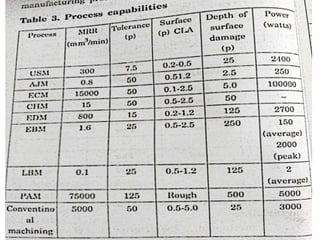
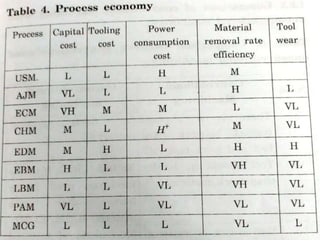
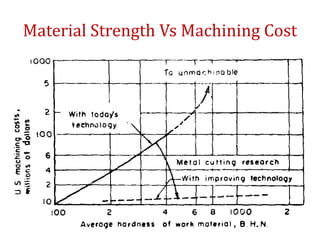
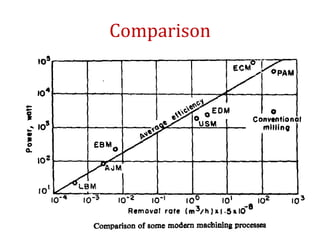
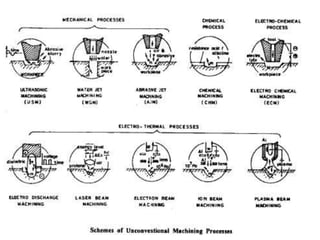
The document discusses conventional and unconventional machining processes, describing characteristics of each such as chip formation, tool-workpiece contact, accuracy, and energy domains involved. It classifies unconventional machining processes into categories based on the type of energy used like mechanical, thermal, electrical, or chemical. Examples are provided for each category and factors for selecting the appropriate machining process are outlined.