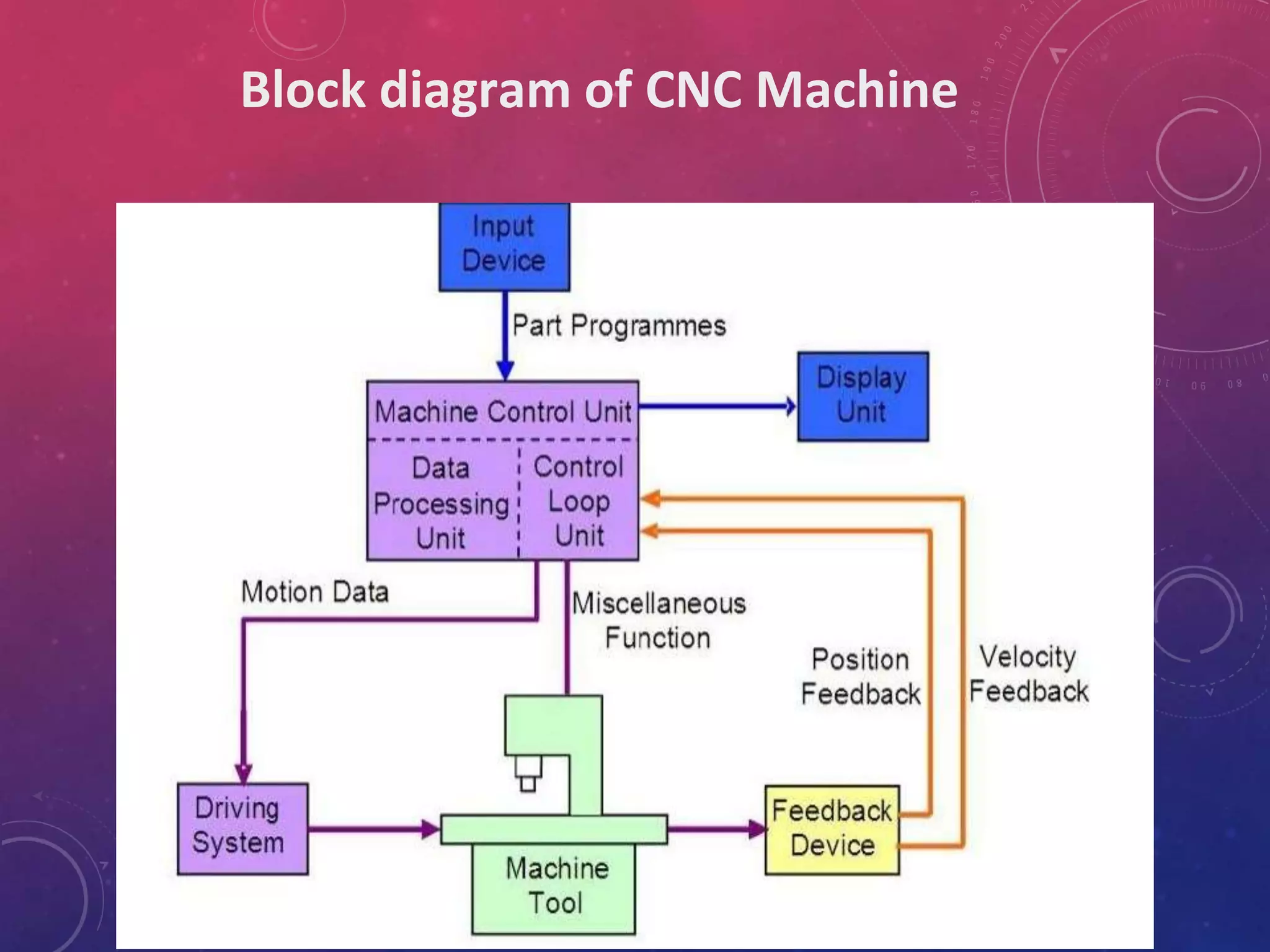
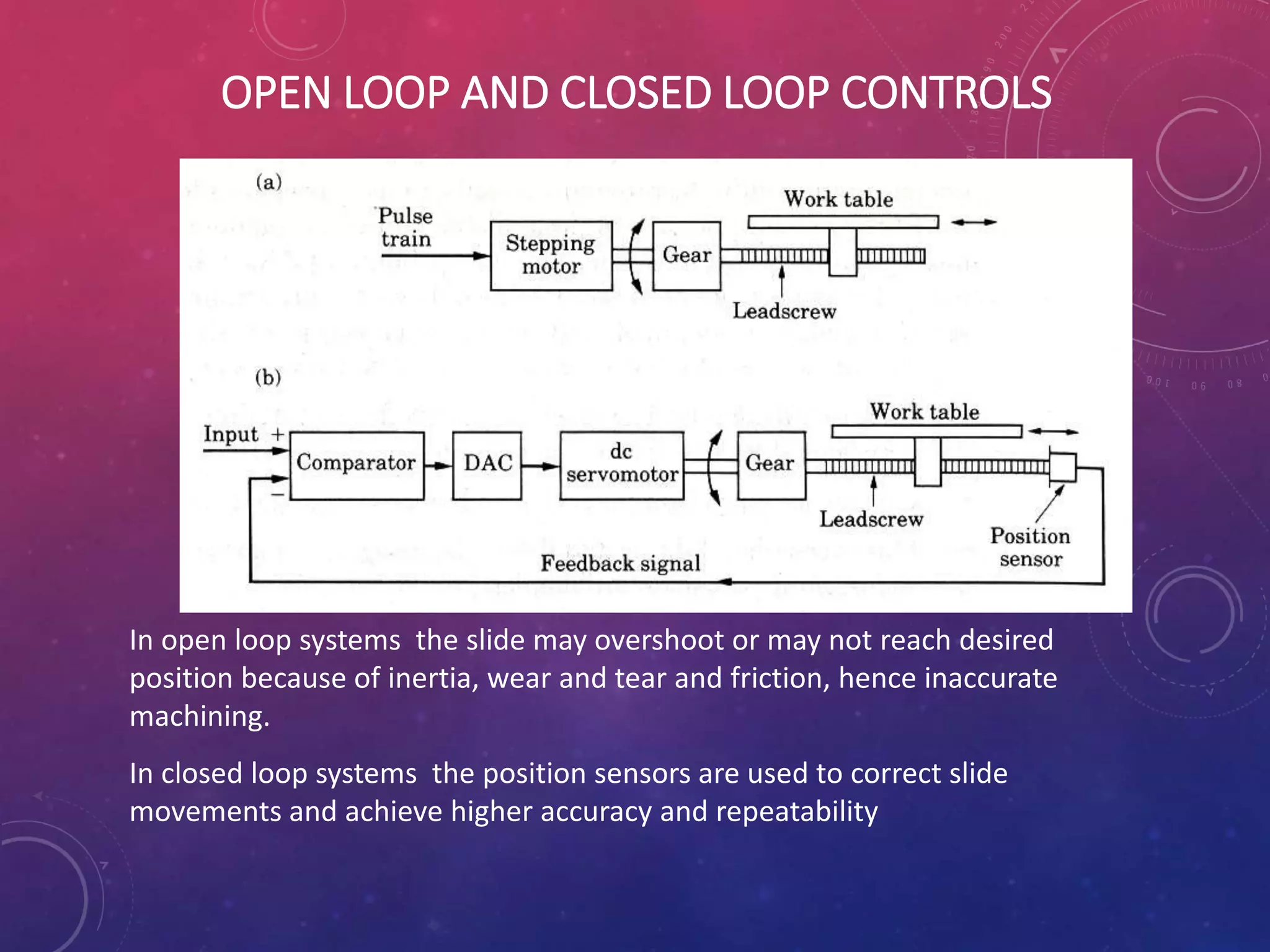
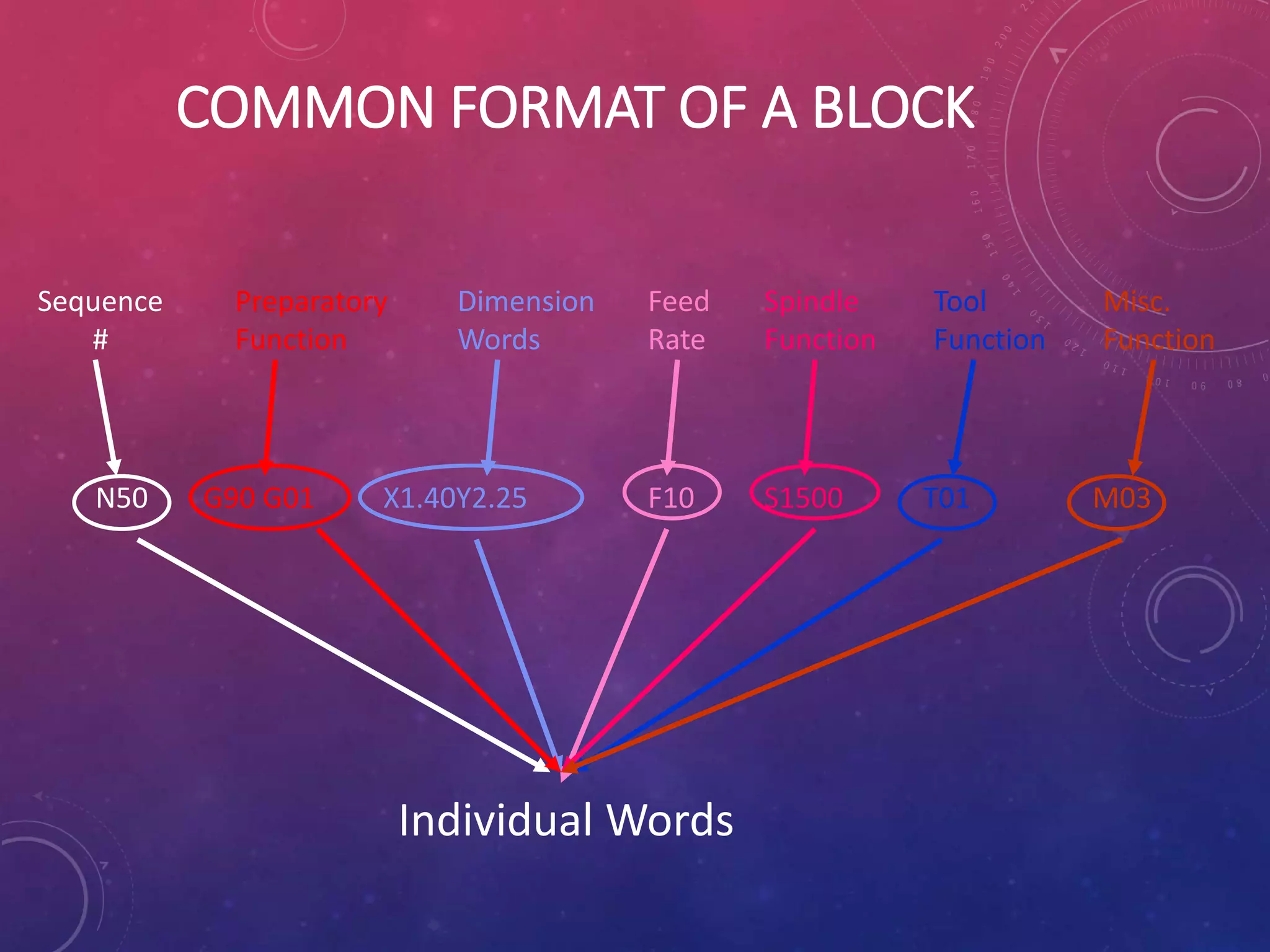
This document provides an overview of CNC (computer numerical control) machines. It discusses the history and evolution of CNC machines from the 1940s to present day. The key elements of a CNC machine are described as the input device, machine control unit, machine tool, driving system, feedback devices, and display unit. The document also covers the basic programming and operation of CNC machines using G and M codes to control axes movement, feed rates, spindle speeds, tool changes, and other functions. Advantages of CNC include easier programming and reducing human errors, while challenges include high setup costs and requiring computer and programming knowledge.