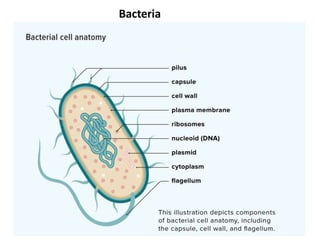
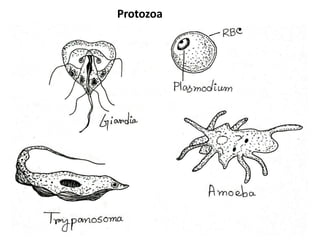
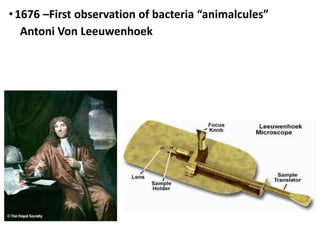
This document provides an overview of microbiology, including its definition as the study of microorganisms and its various branches such as medical, industrial, and food microbiology. Key historical milestones in microbiology are highlighted, including the development of vaccines and advancements in microscopy. The importance of microbiology for nursing practice is also emphasized, particularly in relation to infection control and immune response.