The document discusses infection, including its definition, types, causes, sources, and modes of transmission. It defines infection as the invasion and multiplication of microorganisms such as bacteria, viruses, and parasites within the body. There are several types of infections including primary, secondary, hospital-acquired, and latent infections. Infections can be caused by a variety of microbes including viruses, bacteria, fungi and parasites. Sources of infection are either endogenous from inside the body or exogenous from outside sources. Modes of transmission include direct or indirect contact, inhalation, ingestion, insects, congenitally from mother to fetus, and iatrogenically during medical procedures.


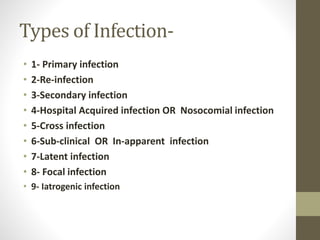
![• Primary infection- Initial infection of a microorganism in
host.
• Re-infection- Subsequent infection after primary infection
from the same microorganism.
• Secondary infection-New microorganism sets up an infection
in a pre-existing infectious disease.
• Hospital Acquired Infection- Infection developed in
hospitalized patient, not present at the time of their
admission.
[Also known as “Nosocomial Infection”]
TYPES-](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/topic-infectionsourcespreadbychhavi-200916051805/85/Topic-Infection-Types-Source-and-Spread-by-Chhavi-Saini-4-320.jpg)





